A Geographic Overview of Kazakhstan and its Neighbors: A Crossroads of Cultures and Resources
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of Kazakhstan and its Neighbors: A Crossroads of Cultures and Resources
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of Kazakhstan and its Neighbors: A Crossroads of Cultures and Resources. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of Kazakhstan and its Neighbors: A Crossroads of Cultures and Resources

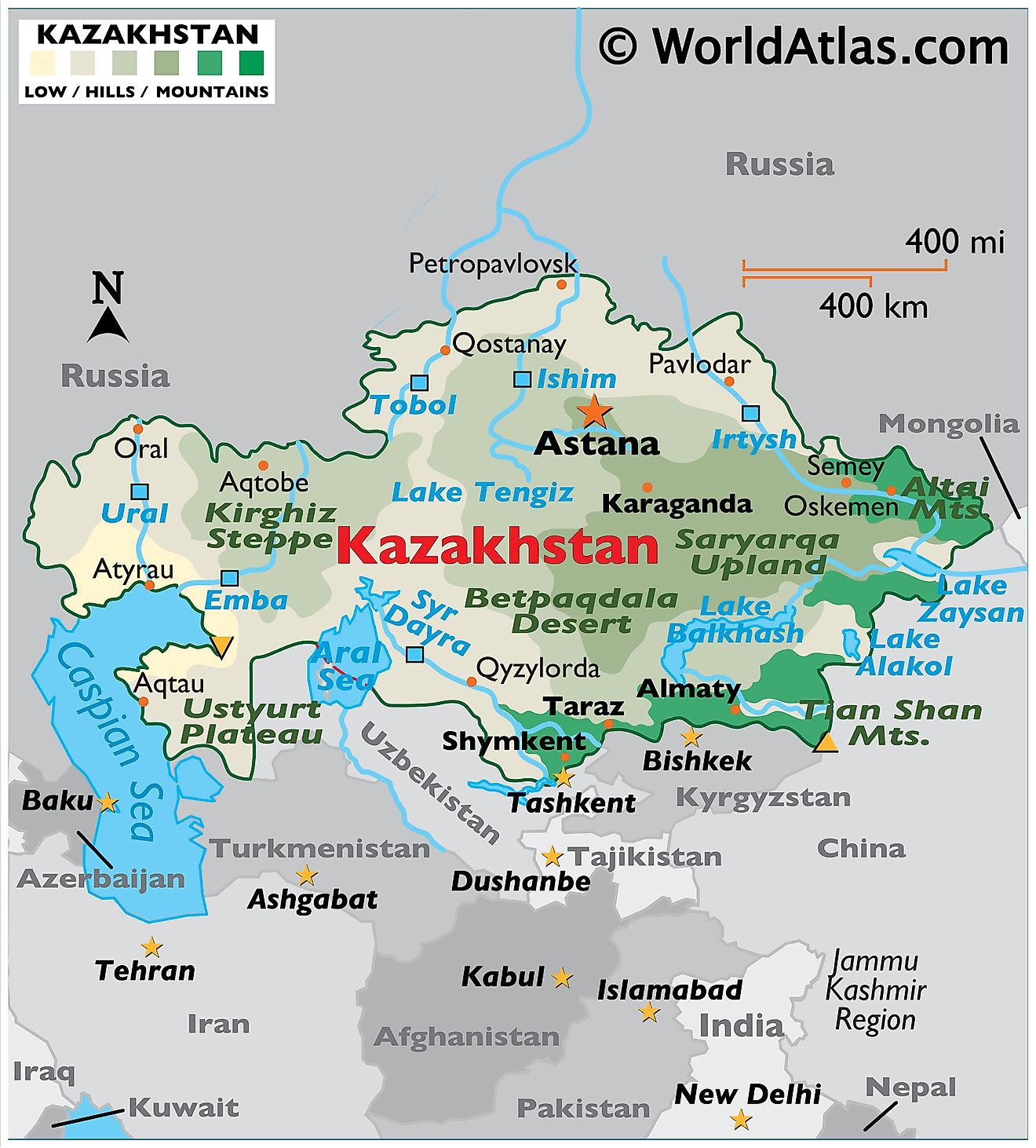
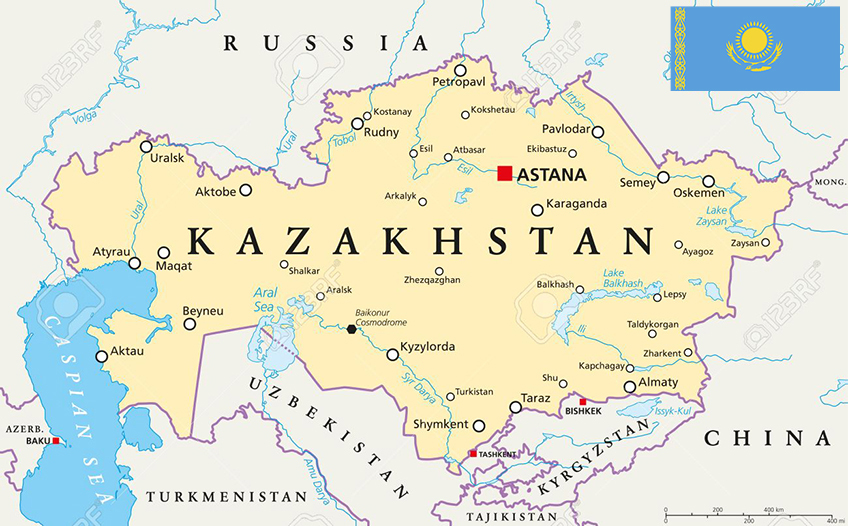
Kazakhstan, the largest landlocked country in the world, occupies a pivotal position in Central Asia, bordering five nations: Russia to the north, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southwest. This strategic location has shaped Kazakhstan’s history, culture, and economy, making it a vital node in the Eurasian landmass.
A Land of Diverse Landscapes:
Kazakhstan’s vast territory, encompassing over 2.7 million square kilometers, showcases a remarkable diversity of landscapes. The north is dominated by the vast, flat steppe, a seemingly endless expanse of grassland that stretches towards the Russian border. To the south, the landscape transitions into the rugged Tian Shan mountains, a formidable range that forms a natural barrier between Kazakhstan and its southern neighbors. The western regions are characterized by the arid, desolate landscape of the Karakum Desert, while the eastern portion features the rolling hills and fertile valleys of the Altai Mountains.
A Tapestry of Ethnicities and Cultures:
This geographic diversity is mirrored in the cultural landscape of Kazakhstan. The country is home to a mosaic of ethnicities, with Kazakhs comprising the majority, followed by Russians, Uzbeks, Ukrainians, and other groups. This cultural blend is evident in the country’s rich traditions, languages, and artistic expressions. The traditional nomadic culture of the Kazakhs, with its emphasis on horseback riding, falconry, and music, remains a vital part of the national identity, while the influence of Russia and other neighboring cultures is also evident in the country’s modern society.
A Gateway to Resources and Trade:
Kazakhstan holds significant economic potential, boasting vast reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, and other minerals. This wealth has fueled economic growth in recent decades, transforming the country into a major player in the global energy market. The country’s strategic location, connecting East Asia with Europe, also makes it a vital hub for trade and transportation. The development of infrastructure, including pipelines, railroads, and highways, has further enhanced Kazakhstan’s role as a conduit for goods and services between major markets.
Understanding Kazakhstan’s Neighbors:
Russia: Kazakhstan’s northern neighbor, Russia, is a major economic and political power in the region. The two countries share a long history, with Kazakhstan having been part of the Soviet Union until 1991. Russia remains a key trading partner and a significant source of investment for Kazakhstan, and the two countries cooperate closely on security and regional issues.
China: To the east, China’s growing economic and political influence is increasingly felt in Central Asia. The two countries share a common border and have forged close economic ties, with China being a major investor in Kazakhstan’s energy sector. The development of the "One Belt, One Road" initiative has further strengthened the economic relationship between the two nations.
Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan: Kazakhstan’s southern neighbors, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, are both landlocked countries with economies heavily reliant on agriculture and mining. The three countries cooperate on regional issues, including water management and energy cooperation. However, historical tensions and competition for resources have also shaped the relationship between these countries.
Turkmenistan: Kazakhstan’s southwestern neighbor, Turkmenistan, is a predominantly desert country with vast reserves of natural gas. The two countries share a common border and have a history of cooperation in energy and transportation. However, the two countries have also experienced periods of political tension and economic rivalry.
The Importance of Regional Cooperation:
The geopolitical landscape of Central Asia is characterized by complex dynamics, with a mix of cooperation and competition among its various actors. Understanding the relationships between Kazakhstan and its neighbors is crucial for understanding the region’s economic, political, and security dynamics. Regional cooperation is essential for addressing common challenges such as environmental degradation, water scarcity, and security threats.
FAQs about Kazakhstan and its Neighbors:
Q: What is the main language spoken in Kazakhstan?
A: The official language of Kazakhstan is Kazakh, a Turkic language. Russian is also widely spoken, especially in urban areas and among older generations.
Q: What are the major industries in Kazakhstan?
A: Kazakhstan’s economy is dominated by the energy sector, with oil and natural gas being major exports. Other key industries include mining, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Kazakhstan?
A: The majority of Kazakhstan’s population is Muslim, primarily Sunni Islam. Other religions practiced in the country include Christianity, Judaism, and Buddhism.
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing Kazakhstan?
A: Kazakhstan faces a range of environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and air pollution. The country is also vulnerable to climate change, with increasing temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns.
Q: What are the key security challenges facing Kazakhstan?
A: Kazakhstan faces various security challenges, including terrorism, organized crime, and political instability in neighboring countries. The country is also a member of the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), a regional military alliance.
Tips for Travelers:
- Visa Requirements: Foreign nationals need a visa to enter Kazakhstan, except for citizens of some countries who may be eligible for visa-free entry or visa-on-arrival.
- Currency: The official currency of Kazakhstan is the tenge (KZT).
- Language: While Russian is widely spoken, learning some basic Kazakh phrases can enhance your travel experience.
- Culture: Respect the local customs and traditions, including dressing modestly when visiting religious sites.
- Safety: Overall, Kazakhstan is a safe country for travelers. However, it is always advisable to exercise caution and be aware of your surroundings.
Conclusion:
Kazakhstan, situated at the crossroads of Central Asia, is a country of immense geographic, cultural, and economic significance. Its strategic location, vast natural resources, and diverse population have shaped its history and continue to influence its future. Understanding the relationships between Kazakhstan and its neighbors is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the region, its potential for economic growth, and its role in the global geopolitical landscape. As Central Asia continues to evolve, Kazakhstan’s position as a bridge between East and West will likely become even more important in the years to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of Kazakhstan and its Neighbors: A Crossroads of Cultures and Resources. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!