A Geographical Perspective on South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape: A Map-Based Exploration
Related Articles: A Geographical Perspective on South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape: A Map-Based Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Perspective on South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape: A Map-Based Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Perspective on South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape: A Map-Based Exploration
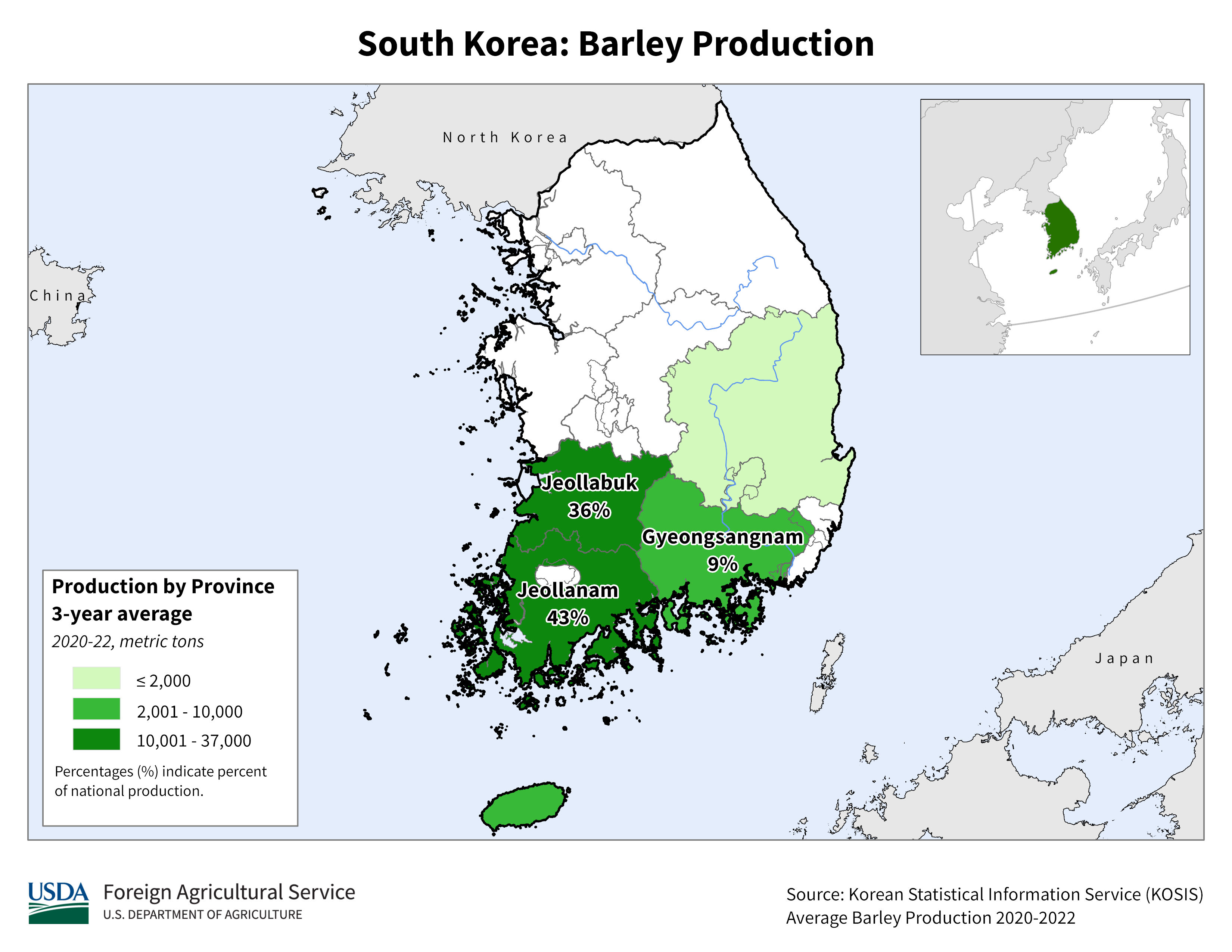
South Korea, a nation known for its technological advancements and bustling urban centers, possesses a surprisingly diverse and vibrant agricultural landscape. Understanding this landscape requires delving beyond the modern skyscrapers and into the intricate network of farms that sustain the nation’s food security and cultural heritage. This article explores South Korea’s agricultural geography through the lens of a map, highlighting the key features, challenges, and opportunities that shape its farming practices.
The Physical Landscape and its Influence on Agriculture
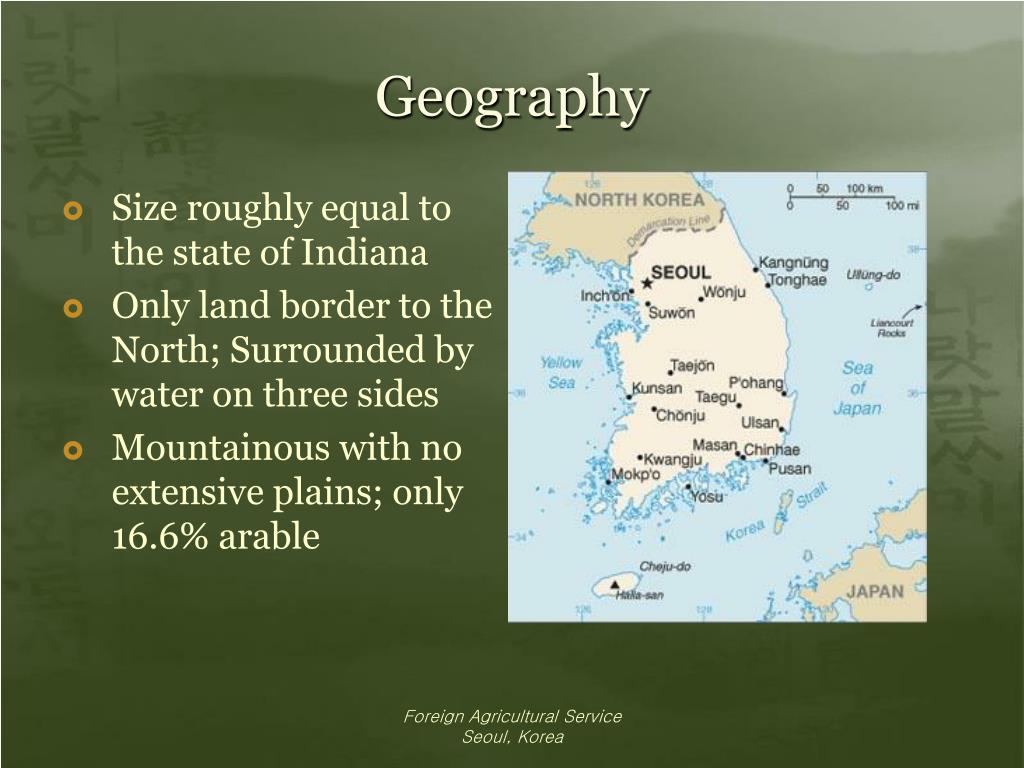
South Korea’s topography, characterized by mountainous terrain, limited arable land, and a temperate climate, significantly influences its agricultural production. The Taebaek Mountains, running along the eastern coast, dominate the landscape, leaving only narrow coastal plains and valley floors suitable for cultivation. This geographical constraint has led to the development of a unique agricultural system, adapted to the specific challenges of limited space and diverse microclimates.
The Map Unveils a Mosaic of Farming Practices
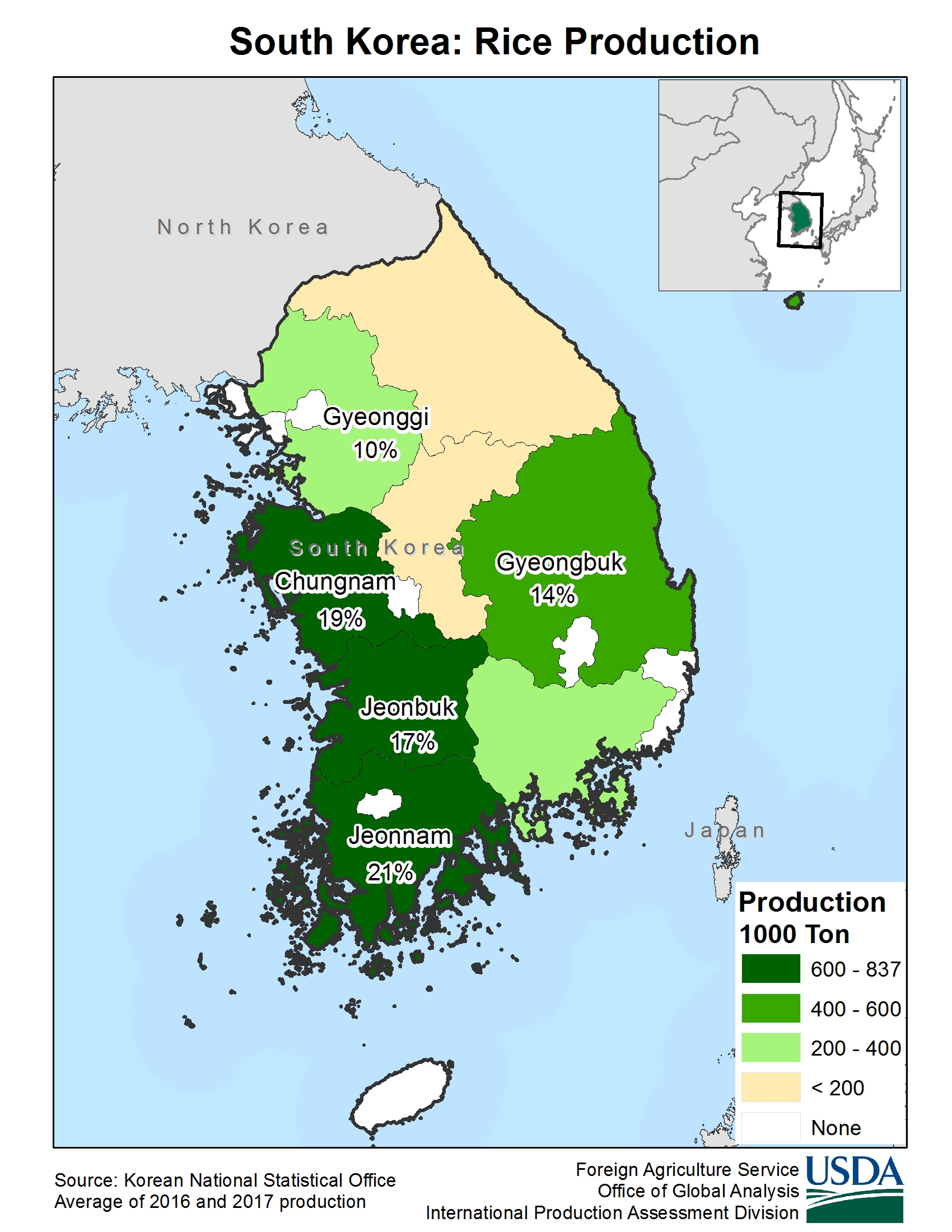
A map of South Korea’s agricultural landscape reveals a mosaic of farming practices, each reflecting the unique characteristics of its region. The coastal plains, primarily in the west and south, are dominated by rice cultivation, benefiting from ample rainfall and fertile alluvial soil. These areas also support the production of other staple crops like barley and wheat.
In contrast, the mountainous regions, characterized by steep slopes and limited access, are primarily dedicated to fruit orchards and vegetable farms. The cool, mountainous air and abundant sunshine create ideal conditions for cultivating fruits like apples, pears, and grapes, while the fertile slopes are well-suited for growing vegetables like kimchi cabbage and radishes.
A Closer Look at Key Agricultural Regions
1. The Gyeonggi Province: The Breadbasket of South Korea
The Gyeonggi Province, surrounding Seoul, is the country’s most important agricultural region. This area boasts fertile plains, a temperate climate, and efficient irrigation systems, making it ideal for producing a wide range of crops, including rice, vegetables, and fruits. The Gyeonggi Province is also home to numerous greenhouses, allowing for year-round production of various crops.
2. The Jeolla Provinces: The Home of Rice and Kimchi
The Jeolla Provinces, located in the southwest, are known as the "rice bowl" of South Korea. The fertile plains of the Honam region, along with ample rainfall, create ideal conditions for rice cultivation. These provinces are also major producers of kimchi cabbage, a staple ingredient in Korean cuisine.
3. The Gangwon Province: The Land of Apples and Pears
The Gangwon Province, situated in the eastern region, is characterized by its mountainous terrain and cool climate. These conditions are perfect for growing apples, pears, and other temperate fruits. The province is also known for its production of ginseng, a valuable medicinal herb.
4. The Jeju Island: A Unique Agricultural Paradise
Jeju Island, located off the southern coast, offers a unique agricultural environment. The volcanic soil, mild climate, and abundant sunshine support the cultivation of a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and even tropical crops like citrus fruits. Jeju Island is also known for its production of seaweed and black pork.
Challenges and Opportunities in South Korea’s Agricultural Sector
Despite its diverse landscape and resilient farmers, South Korea’s agricultural sector faces significant challenges. The increasing urbanization and aging population have led to a decline in the number of farmers and a shift towards larger, more mechanized farms. This trend has also resulted in a decrease in the area dedicated to agricultural production.
Furthermore, South Korea’s reliance on imported agricultural products, particularly grains, poses a threat to its food security. This reliance stems from the limited arable land and the high cost of domestic production. However, the government is actively pursuing policies to promote domestic production and reduce reliance on imports.
Despite these challenges, South Korea’s agricultural sector offers numerous opportunities. The growing demand for high-quality, safe food, particularly from the domestic market, presents a significant opportunity for farmers to focus on niche markets and value-added products.
Innovation and Sustainability in South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape
In response to these challenges, South Korea is embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices to enhance agricultural productivity and ensure food security. The adoption of precision agriculture, smart farming techniques, and vertical farming systems is transforming traditional farming practices. These innovations allow for efficient resource utilization, reduced environmental impact, and increased crop yields.
A Map-Based Insight into South Korea’s Agricultural Future
The map of South Korea’s agricultural landscape serves as a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s food security and its potential for sustainable development. By highlighting the unique characteristics of each region, the map reveals the intricate interplay between geography, farming practices, and the challenges and opportunities facing the agricultural sector.
FAQs about South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape
1. What are the major agricultural products of South Korea?
South Korea’s major agricultural products include rice, vegetables, fruits, livestock, and seafood.
2. What are the main challenges facing South Korea’s agricultural sector?
The main challenges include limited arable land, aging population, urbanization, and reliance on imported agricultural products.
3. How is South Korea addressing these challenges?
South Korea is addressing these challenges through innovative technologies, sustainable farming practices, and government policies aimed at promoting domestic production and food security.
4. What is the future of agriculture in South Korea?
The future of agriculture in South Korea is likely to be characterized by increased adoption of technology, sustainable practices, and a focus on niche markets and value-added products.
Tips for Exploring South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape
1. Visit a local farmers market: Immerse yourself in the local agricultural culture by visiting a traditional farmers market. You can sample fresh produce, interact with farmers, and learn about the unique products of the region.
2. Take a farm tour: Many farms in South Korea offer tours to visitors, providing insights into their farming practices and the challenges they face.
3. Explore agricultural museums: South Korea has several agricultural museums that showcase the history of farming in the country, from traditional methods to modern technologies.
Conclusion
South Korea’s agricultural landscape is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of its farmers. Despite the challenges of limited land and a changing demographic, the nation’s agricultural sector is embracing innovation and sustainability to ensure food security and promote a vibrant agricultural future. The map of South Korea’s agricultural landscape serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complex interplay of geography, farming practices, and the nation’s food system. By recognizing the unique characteristics of each region and the challenges and opportunities facing the sector, South Korea can continue to develop a sustainable and thriving agricultural landscape for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Perspective on South Korea’s Agricultural Landscape: A Map-Based Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!