A Journey Through the Land of Steppes and Mountains: Understanding the Physical Geography of Kazakhstan
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Land of Steppes and Mountains: Understanding the Physical Geography of Kazakhstan
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Land of Steppes and Mountains: Understanding the Physical Geography of Kazakhstan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Land of Steppes and Mountains: Understanding the Physical Geography of Kazakhstan

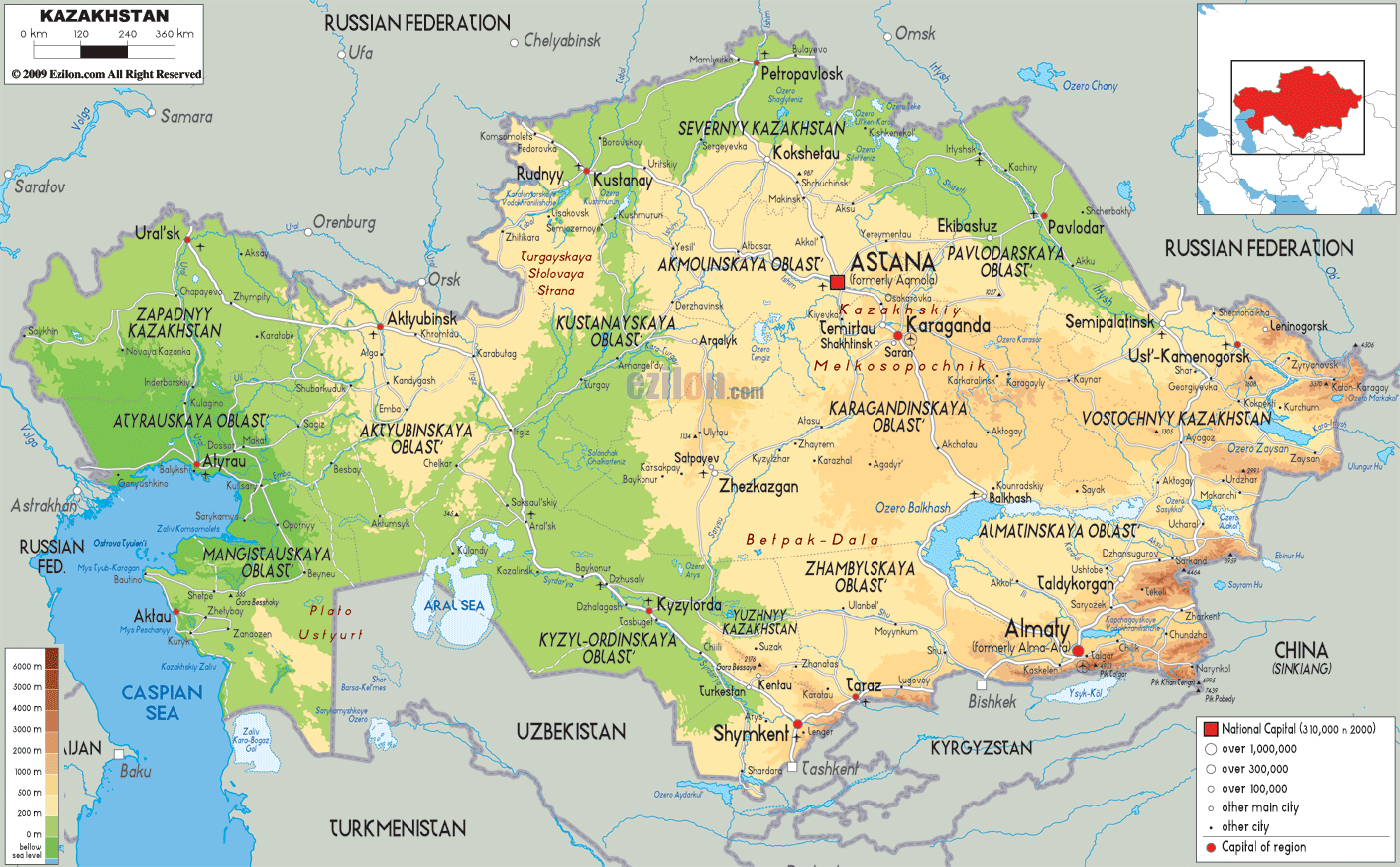
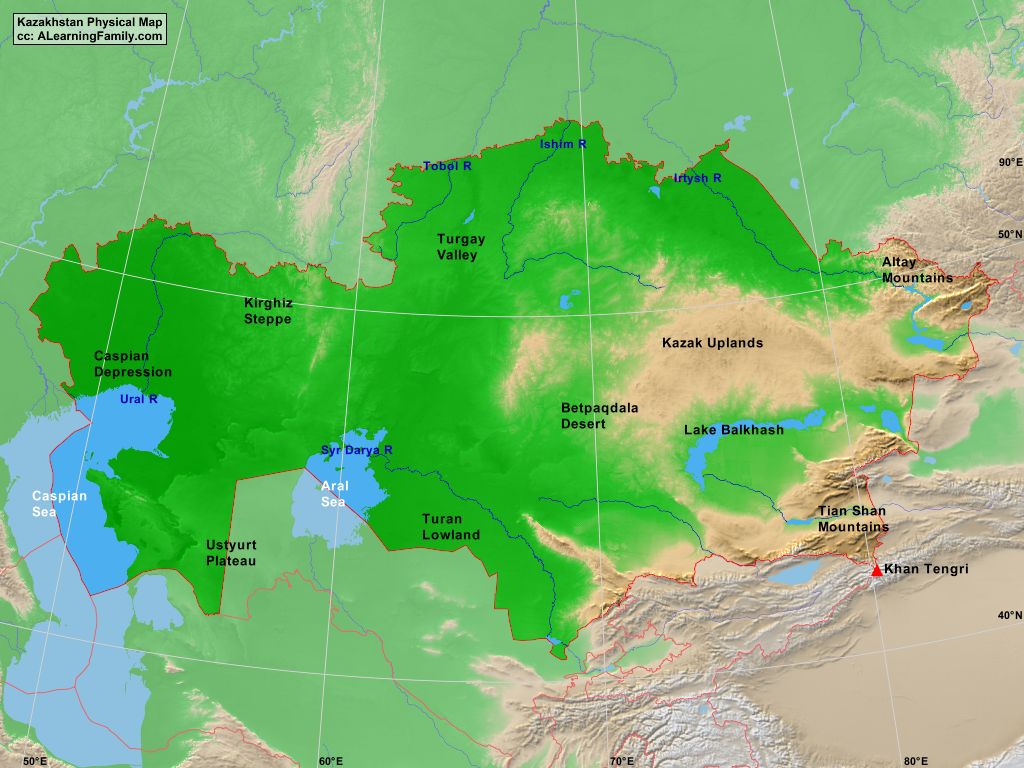
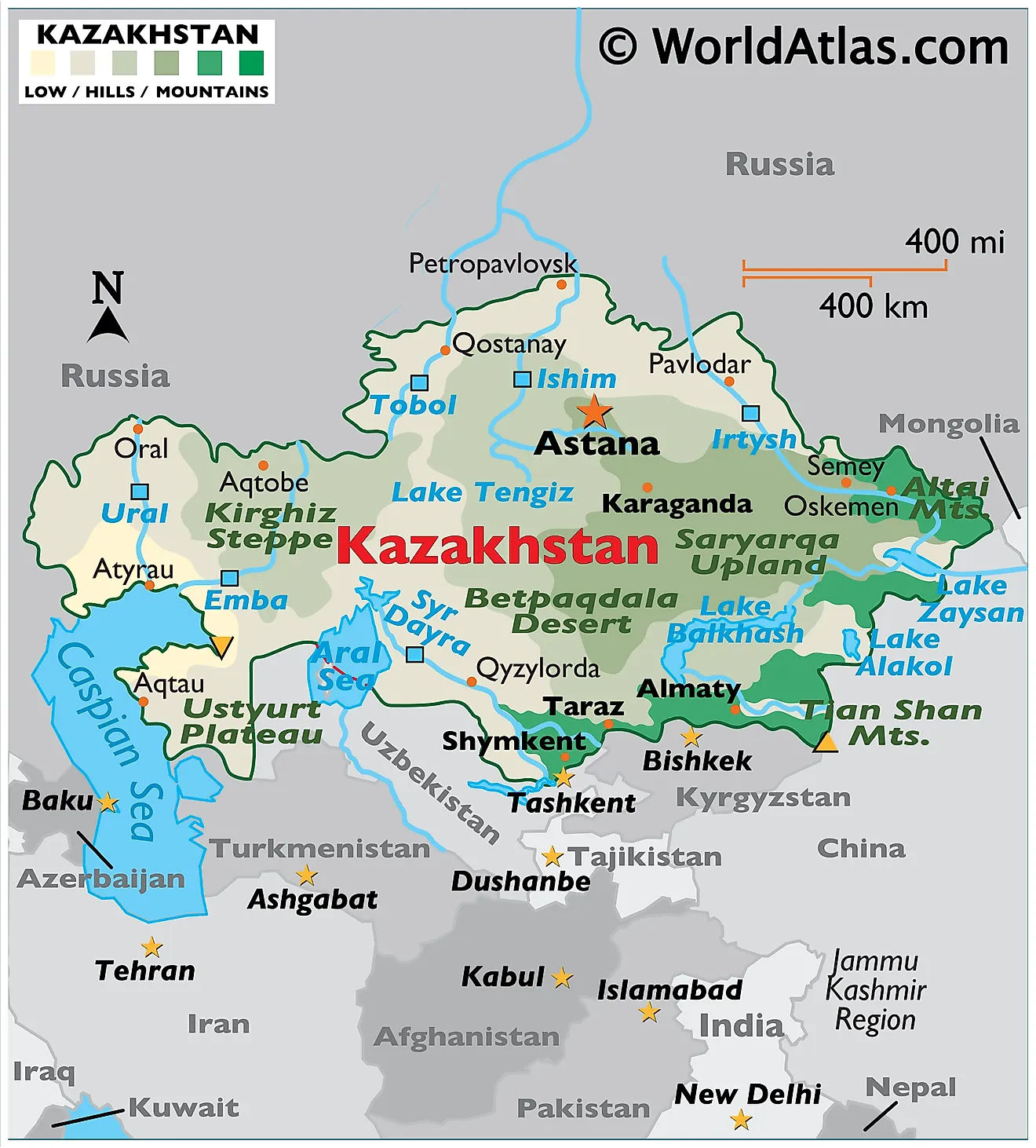
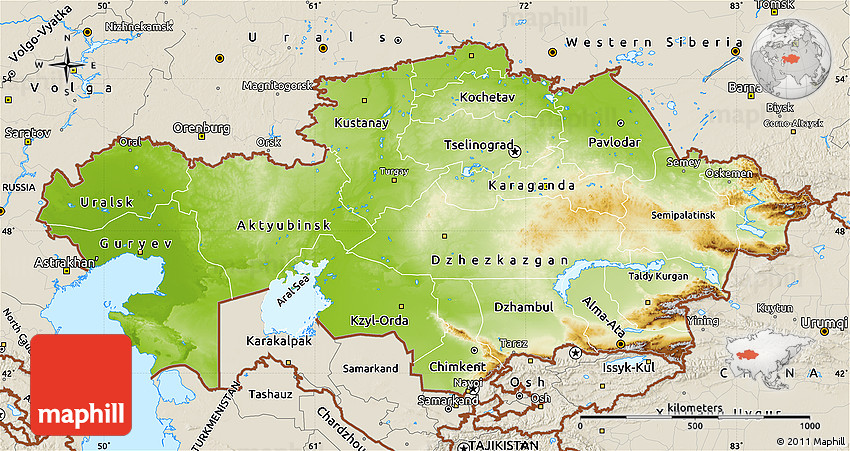
Kazakhstan, the ninth-largest country in the world, sprawls across a vast expanse of Central Asia, encompassing a diverse tapestry of landscapes. Its physical geography is a captivating blend of expansive steppes, towering mountains, arid deserts, and fertile river valleys, offering a rich tapestry of natural wonders. Understanding the physical map of Kazakhstan is crucial for appreciating its unique environment, its rich history, and its diverse cultural landscape.
A Vast and Varied Terrain:
The physical map of Kazakhstan reveals a country dominated by vast plains and plateaus, collectively known as the Kazakh Steppe. This expansive, semi-arid region stretches across the northern and western parts of the country, characterized by rolling grasslands and scattered salt marshes. The steppes are a vital ecosystem, supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna, including the endangered Saiga antelope.
To the south and east, the landscape transforms dramatically, giving way to towering mountain ranges. The Tian Shan, meaning "Celestial Mountains," forms a formidable natural boundary along the southeastern border, reaching heights of over 7,000 meters. The Altai Mountains, located in the eastern part of the country, also boast impressive peaks, contributing to the dramatic topographic diversity of Kazakhstan.
The Role of Water: Rivers and Lakes
Water plays a crucial role in shaping Kazakhstan’s physical landscape. The country is home to a network of major rivers, including the Syr Darya, the Amu Darya, and the Irtysh River. These rivers serve as vital lifelines, providing water for irrigation, drinking, and transportation. They also contribute to the formation of fertile valleys, supporting agriculture and human settlements.
Kazakhstan also boasts a number of large lakes, most notably Lake Balkhash, the world’s largest endorheic lake. This unique lake is divided into two distinct parts: a western, salty basin and an eastern, freshwater basin. Other important lakes include Lake Zaysan and Lake Alakol, both located in the eastern part of the country.
Aridity and Deserts:
The southern and western parts of Kazakhstan are characterized by arid conditions, leading to the presence of extensive deserts. The Kyzylkum Desert, meaning "Red Sands," is one of the largest deserts in Central Asia, known for its sand dunes and sparse vegetation. The Karakum Desert, located in the southwestern part of the country, is another notable desert, characterized by its unique ecosystem and diverse fauna.
Geological Diversity:
Kazakhstan’s geological history is as fascinating as its current landscape. The country sits on the Eurasian Plate and has been shaped by tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, and erosion over millions of years. This geological history is reflected in the diverse rock formations, mineral deposits, and fossil sites found across the country.
The Importance of Understanding the Physical Map
Understanding the physical map of Kazakhstan is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Environmental Management: The physical map provides insights into the country’s natural resources, including water, minerals, and land. This information is vital for sustainable resource management and environmental conservation.
- Infrastructure Development: The physical map informs the planning of transportation networks, energy infrastructure, and other essential infrastructure projects. Understanding the topography, climate, and soil conditions is essential for optimizing infrastructure development.
- Agriculture and Food Security: The physical map highlights the distribution of fertile land, water resources, and suitable climates for agriculture. This information is essential for developing sustainable agricultural practices and ensuring food security.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The physical map helps researchers and policymakers understand the potential impacts of climate change on Kazakhstan’s environment. This knowledge is crucial for developing adaptation strategies and mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Tourism and Recreation: The physical map showcases the country’s stunning natural landscapes, from the majestic mountains to the vast steppes. This information is valuable for promoting tourism and recreation opportunities.
FAQs
Q: What are the highest mountains in Kazakhstan?
A: The highest mountains in Kazakhstan are located in the Tian Shan range, with Peak Khan Tengri reaching a height of 7,010 meters.
Q: What are the major rivers in Kazakhstan?
A: The major rivers in Kazakhstan include the Syr Darya, the Amu Darya, and the Irtysh River.
Q: What are the main types of vegetation found in Kazakhstan?
A: The main types of vegetation found in Kazakhstan include steppes, deserts, and forests.
Q: What are the major mineral deposits in Kazakhstan?
A: Kazakhstan is rich in mineral resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, iron ore, copper, and zinc.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Kazakhstan’s environment?
A: Kazakhstan faces a number of environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, air pollution, and climate change.
Tips for Using the Physical Map of Kazakhstan
- Identify key geographical features: Focus on identifying the major mountain ranges, rivers, lakes, and deserts.
- Understand the elevation: Pay attention to the different elevation levels, as they indicate the variations in climate and vegetation.
- Study the distribution of natural resources: Analyze the map to understand the location of oil, gas, mineral deposits, and other natural resources.
- Consider the impact of climate change: Use the map to assess the potential impacts of climate change on different regions of Kazakhstan.
Conclusion
The physical map of Kazakhstan provides a window into the country’s diverse and captivating landscapes. From the sprawling steppes to the towering mountains, Kazakhstan’s physical geography is a testament to the power of nature. Understanding this physical landscape is essential for appreciating the country’s unique environment, its rich history, and its diverse cultural landscape. By studying the physical map, we can gain a deeper understanding of Kazakhstan’s natural resources, its environmental challenges, and its potential for sustainable development.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Land of Steppes and Mountains: Understanding the Physical Geography of Kazakhstan. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!