Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance
- 3.1 The Importance of Map Keys: A Language of Symbols
- 3.2 Elements of a Map Key: Decoding the Visual Language
- 3.3 Examples of Map Keys in Action: Demystifying the Visual Landscape
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Map Key Functionality
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Map Keys
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Map Key Design
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Cartography
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance

Maps are powerful tools that guide us through physical and conceptual landscapes. They provide a visual representation of the world, allowing us to navigate, explore, and understand spatial relationships. However, maps are more than just pictures; they rely on a crucial element: the map key, also known as a legend. This unassuming component holds the key to unlocking the map’s true meaning, transforming a seemingly abstract image into a comprehensible guide.
The Importance of Map Keys: A Language of Symbols
A map key acts as a translator, bridging the gap between the map’s visual language and our understanding of the real world. It translates the abstract symbols and colors used on the map into concrete meanings, making the information accessible and understandable. Imagine a map without a key – a jumble of lines, shapes, and colors, devoid of any clear meaning. The key provides the necessary context, allowing us to interpret the map’s symbols and derive valuable information.
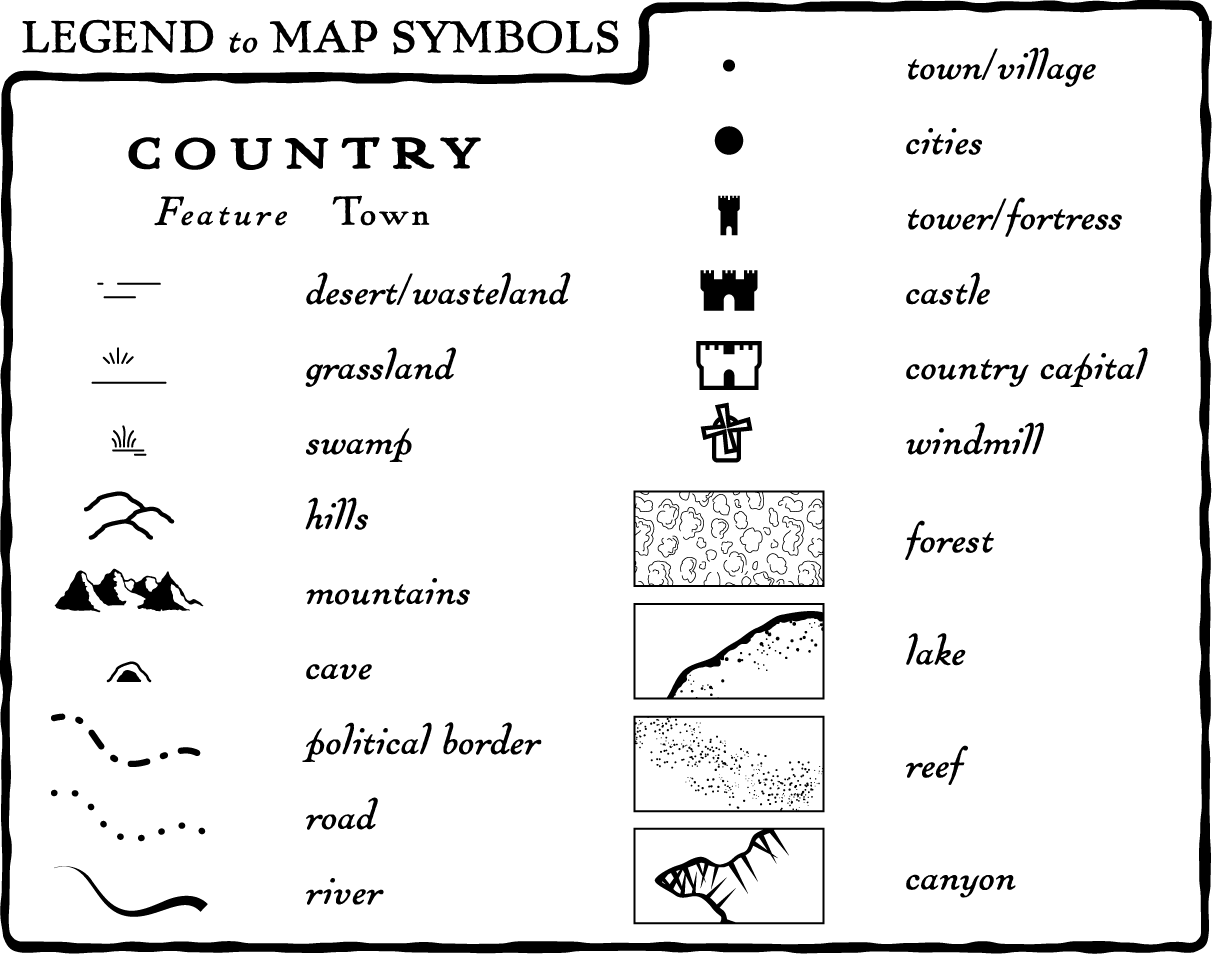
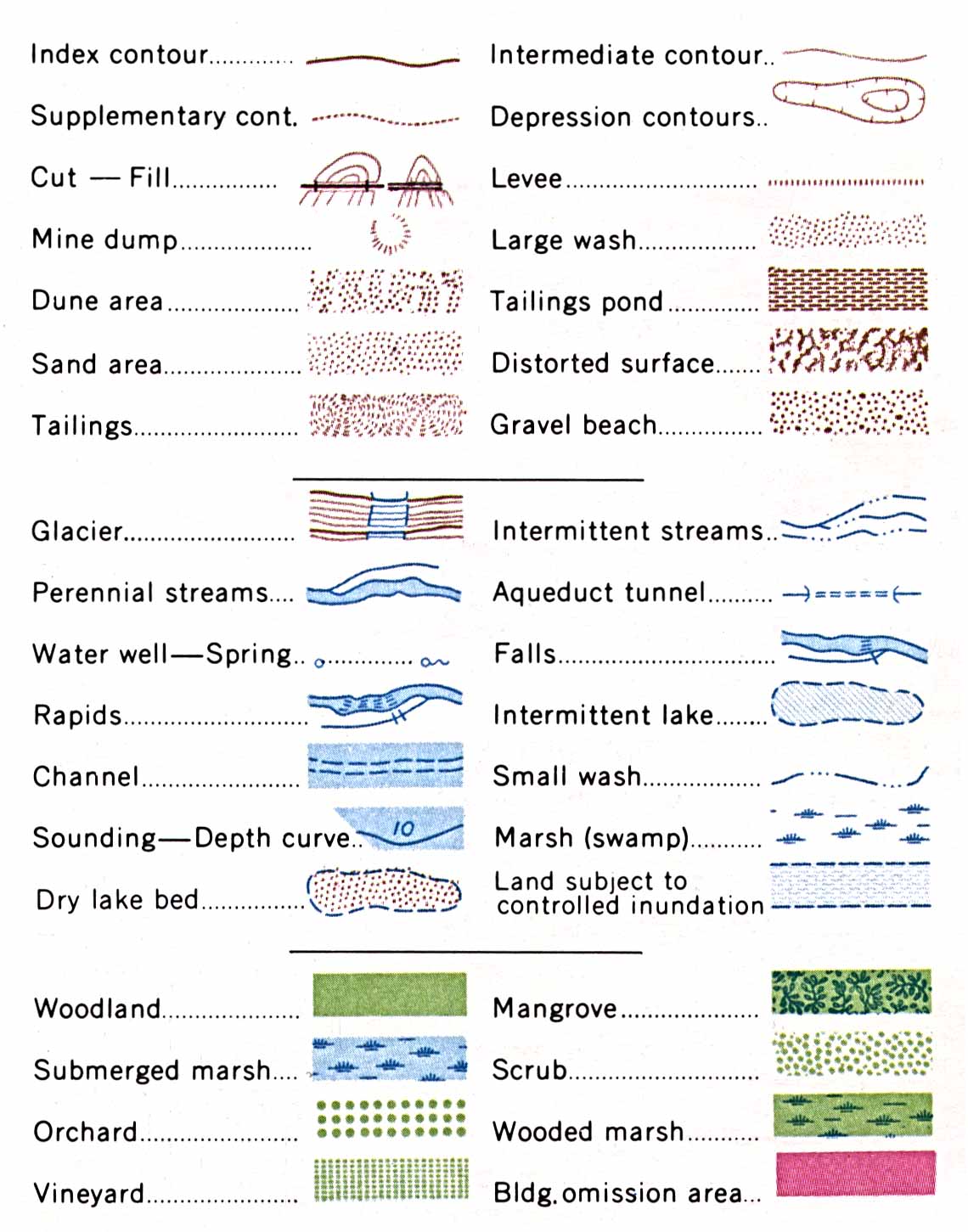
Elements of a Map Key: Decoding the Visual Language
A map key typically includes a variety of elements, each serving a specific purpose:
- Symbols: These are the visual representations used on the map to depict specific features. Examples include lines for roads, dots for cities, and shaded areas for different land types.
- Labels: These provide textual descriptions of the symbols, clarifying their meaning. For instance, a symbol for a highway might be labeled "Interstate Highway."
- Colors: Colors are often used to differentiate features and enhance clarity. For example, blue might represent water bodies, green might represent forests, and red might represent urban areas.
- Scale: The map key often includes a scale bar, which helps determine the real-world distance represented by a given distance on the map.
- North Arrow: This indicates the direction of north, allowing users to orient themselves on the map.
Examples of Map Keys in Action: Demystifying the Visual Landscape
Let’s examine some real-world examples of map keys and their applications:
- Road Maps: Road maps rely heavily on map keys to differentiate between different types of roads (e.g., highways, state roads, local roads), indicating their direction, and highlighting important landmarks.
- Topographical Maps: These maps use contour lines to depict elevation changes, with different colors representing different altitude ranges. The map key translates these colors into specific elevation values, allowing users to understand the terrain’s topography.
- Weather Maps: Weather maps use symbols and colors to represent various weather phenomena, such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and cloud cover. The map key explains the meaning of these symbols, enabling users to interpret weather patterns and make informed decisions.
- Historical Maps: These maps often use symbols and colors to represent historical events, settlements, or boundaries. The map key provides context, explaining the meaning of these symbols and helping users understand historical narratives.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Map Key Functionality
Map keys can be further enhanced to improve clarity and accessibility:
- Hierarchical Organization: Complex maps with numerous symbols can benefit from a hierarchical organization of the key, grouping related symbols together for easier identification.
- Visual Hierarchy: Using different sizes, colors, and font weights within the key can emphasize important features and guide the user’s attention.
- Interactive Keys: Digital maps often incorporate interactive keys, allowing users to hover over symbols or select them to reveal more detailed information.
- Accessibility Features: Map keys can be designed to be accessible to individuals with visual impairments, using alternative formats like audio descriptions or braille.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Map Keys
Q: What is the difference between a map key and a map legend?
A: The terms "map key" and "map legend" are often used interchangeably, with both referring to the same component. However, "legend" might be more appropriate when the key includes extensive descriptions or narrative explanations of the symbols.
Q: Why are map keys important for navigation?
A: Map keys are essential for navigation because they provide the necessary information to interpret the map’s symbols and understand the environment. Without a key, navigating based on the map would be impossible.
Q: How can I create my own map key?
A: Creating a map key involves identifying the features you want to represent, choosing appropriate symbols, and labeling them clearly. Consider your target audience and the level of detail required when designing your key.
Q: Are there any standard map key conventions?
A: While there are no strict conventions, certain symbols and colors have become widely accepted for representing specific features, such as blue for water, green for vegetation, and red for urban areas.
Q: How do map keys evolve with technology?
A: Digital maps have revolutionized map keys, enabling interactive and dynamic features. Users can now access detailed information by clicking on symbols, explore different layers of information, and even personalize their map keys.
Tips for Effective Map Key Design
- Keep it concise: Avoid overwhelming users with excessive information.
- Use clear and consistent language: Ensure the labels are easy to understand and consistent with the symbols.
- Prioritize visual clarity: Choose symbols and colors that are easily distinguishable and visually appealing.
- Consider your target audience: Tailor the key’s complexity and language to the audience’s knowledge and experience.
- Test your key: Ensure the key is effective by testing it with potential users and gathering feedback.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Cartography
The map key, though often overlooked, plays a crucial role in our understanding and interpretation of maps. It serves as the bridge between the abstract visual language of maps and our real-world understanding, making maps accessible and informative tools. By recognizing the importance of map keys and designing them effectively, we can ensure that maps continue to serve as powerful guides for navigation, exploration, and knowledge.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Keys and Their Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!