Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Key Symbols
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Key Symbols
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Key Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Key Symbols
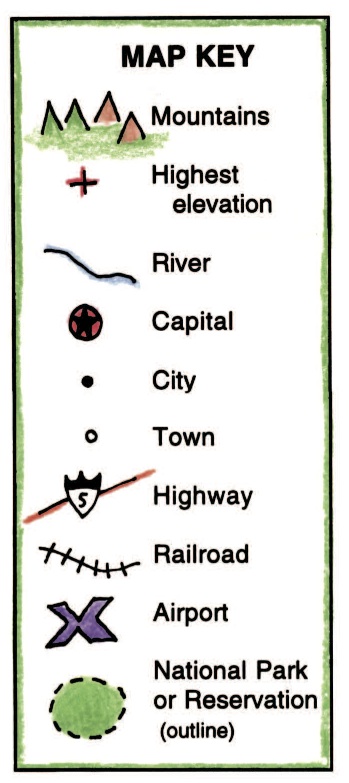
Maps, ubiquitous tools for navigating the world, rely on a standardized system of symbols to convey information efficiently and accurately. These symbols, collectively known as a map key or legend, act as a visual dictionary, translating abstract lines and shapes into tangible features of the real world. Understanding the language of map key symbols is crucial for extracting valuable insights from maps, whether for planning a road trip, exploring a new city, or analyzing geographical data.
The Foundation of Map Communication:
Map key symbols serve as the foundation of map communication, bridging the gap between abstract representations and real-world features. They provide a consistent and standardized framework for understanding the meaning of various elements depicted on the map. This consistency ensures that users, regardless of their background or location, can interpret the map with clarity and confidence.
Types of Map Key Symbols:
Map key symbols can be broadly categorized into:
-
Point Symbols: These symbols represent specific locations or features that occupy a single point on the map. Examples include:
- Cities, towns, and villages: Often represented by circles, squares, or stars, with their size indicating population density.
- Points of interest: Icons like churches, hospitals, or restaurants are used to denote specific landmarks.
- Airports: Typically represented by triangles or stylized airplanes.
- Railway stations: Often depicted with a small square with a cross inside.
-
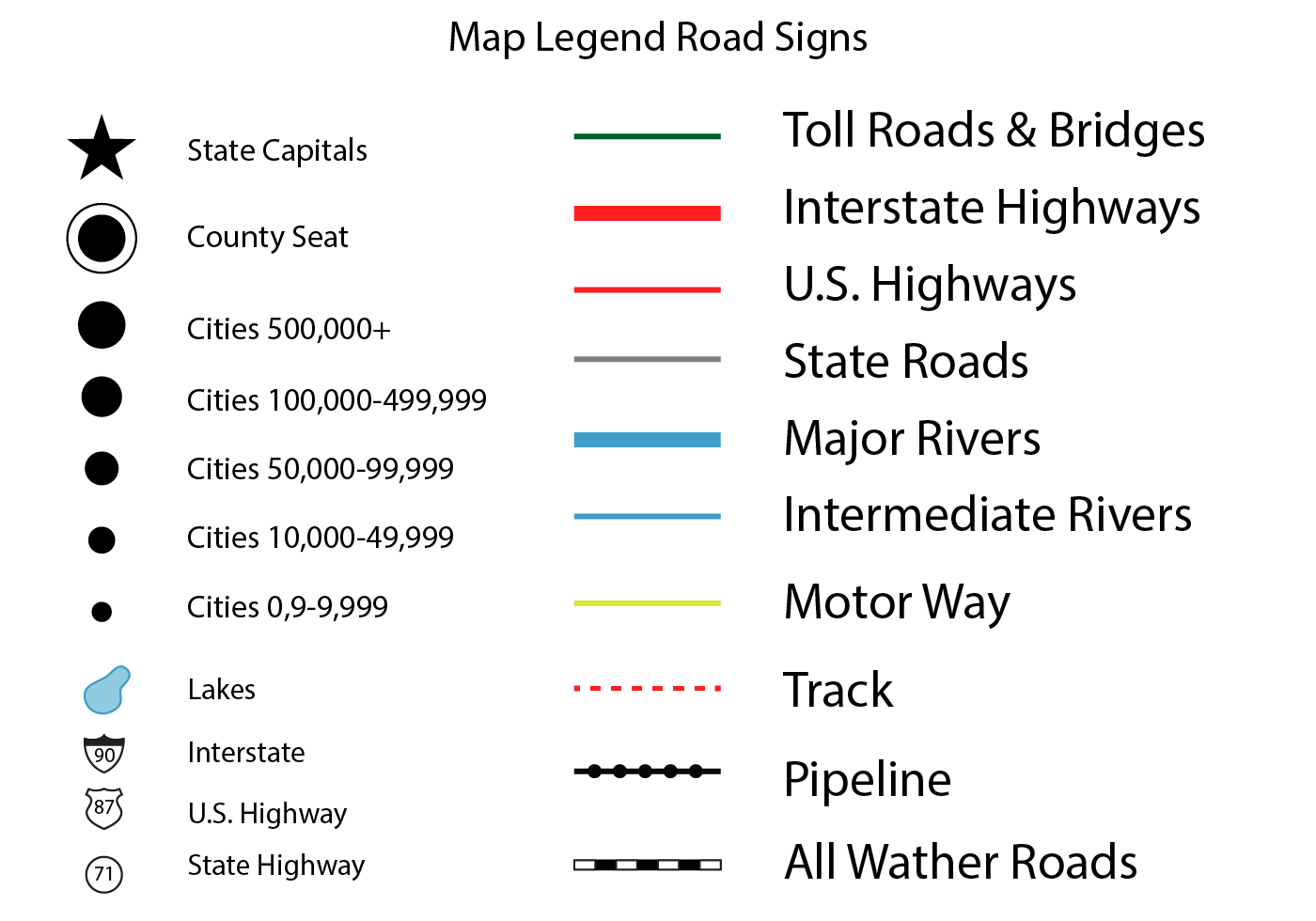
Line Symbols: These symbols represent linear features that extend across the map, such as:
- Roads: Represented by lines of varying thickness and color to indicate different road types (e.g., highways, secondary roads).
- Rivers and streams: Usually depicted by blue lines, with thicker lines representing larger waterways.
- Railways: Depicted by black or red lines, often with a dashed pattern.
- Boundaries: Lines that delineate political or geographical boundaries, often represented by solid lines or dashed lines with different colors.
-
Area Symbols: These symbols represent areas or regions on the map, often filled with color or patterns to differentiate them. Examples include:
- Land cover: Different colors are used to represent forests, grasslands, deserts, and other land cover types.
- Elevation: Contour lines are used to represent elevation changes, with different colors or patterns indicating different elevation ranges.
- Political boundaries: Different colors or patterns are used to distinguish different countries, states, or counties.
Beyond Visual Representation:
Map key symbols go beyond simple visual representation. They often incorporate additional information, such as:
- Size: The size of a symbol can indicate the relative importance or magnitude of a feature. For example, larger cities are often represented by larger circles on a map.
- Color: Color is a powerful tool for distinguishing different features and conveying specific information. For instance, blue is often used to represent water bodies, while green represents vegetation.
- Pattern: Patterns, such as stripes or dots, can be used to differentiate similar features or highlight specific characteristics. For example, different types of roads might be represented by different line patterns.
Decoding the Map Key:
The map key, often located in a corner or along the edge of the map, serves as a vital guide for understanding the symbols used. It provides a clear and concise explanation of each symbol, its corresponding feature, and any relevant details.
Benefits of Understanding Map Key Symbols:
- Enhanced Map Interpretation: A thorough understanding of map key symbols empowers users to interpret maps accurately and efficiently, extracting valuable information about the depicted environment.
- Informed Decision-Making: Knowledge of map key symbols enables users to make informed decisions based on the information presented, whether planning a route, selecting a location, or analyzing geographical data.
- Improved Spatial Awareness: By deciphering the language of maps, users develop a better understanding of spatial relationships between different features and gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the world.
FAQs by Map Key Symbols:
Q: What are the most common map key symbols?
A: Some of the most common map key symbols include:
- Point symbols: Cities, towns, airports, points of interest.
- Line symbols: Roads, rivers, railways, boundaries.
- Area symbols: Land cover, elevation, political boundaries.
Q: How do I identify different types of roads on a map?
A: Roads are often represented by lines of varying thickness and color. Thicker lines typically indicate highways or major roads, while thinner lines represent secondary roads. Different line patterns can also be used to differentiate road types (e.g., dashed lines for unpaved roads).
Q: What do contour lines on a map represent?
A: Contour lines represent points of equal elevation. They are typically depicted as brown or black lines, with closer spacing indicating steeper terrain.
Q: How can I tell the difference between a river and a stream on a map?
A: Rivers are typically represented by thicker blue lines, while streams are depicted by thinner blue lines.
Q: What are the different colors used to represent land cover on a map?
A: Common land cover colors include:
- Green: Forests and grasslands
- Brown: Deserts and barren land
- Blue: Water bodies
- Gray: Urban areas
Tips by Map Key Symbols:
- Examine the Map Key: Always carefully review the map key before attempting to interpret the map.
- Pay Attention to Color and Pattern: Color and pattern are important indicators of different features and their characteristics.
- Consider Scale: The scale of the map will influence the size and detail of symbols.
- Seek Additional Information: If you encounter an unfamiliar symbol, consult additional resources or online databases for clarification.
Conclusion by Map Key Symbols:
Map key symbols are a fundamental component of map communication, providing a standardized language for understanding and interpreting the information presented. By mastering the language of map key symbols, users can unlock a wealth of information, enhancing their spatial awareness, informing their decision-making, and fostering a deeper appreciation for the world around them.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Key Symbols. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!