Delving into the Depths: Understanding Elevation Maps
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Elevation Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: Understanding Elevation Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Elevation Maps

The world is not a flat surface. It undulates, rises, and falls, creating a complex tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus. To effectively represent this intricate topography, cartographers utilize a specialized type of map known as an elevation map. These maps are essential tools for understanding the physical landscape, informing critical decisions in fields ranging from urban planning and infrastructure development to environmental management and disaster preparedness.
The Art of Visualizing Elevation:
Elevation maps employ various techniques to visually represent the third dimension – height – on a two-dimensional surface. The most common methods include:
-
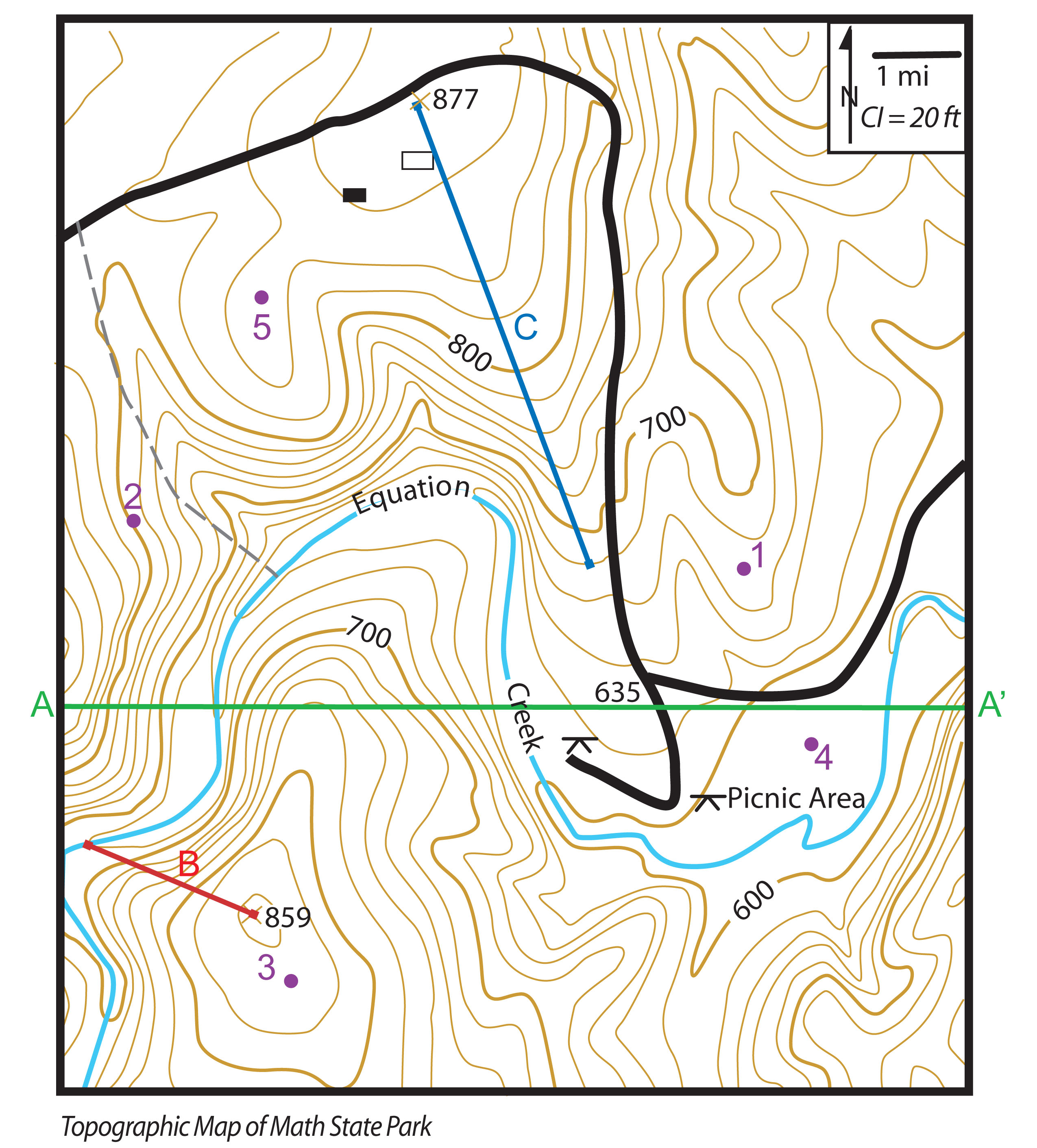
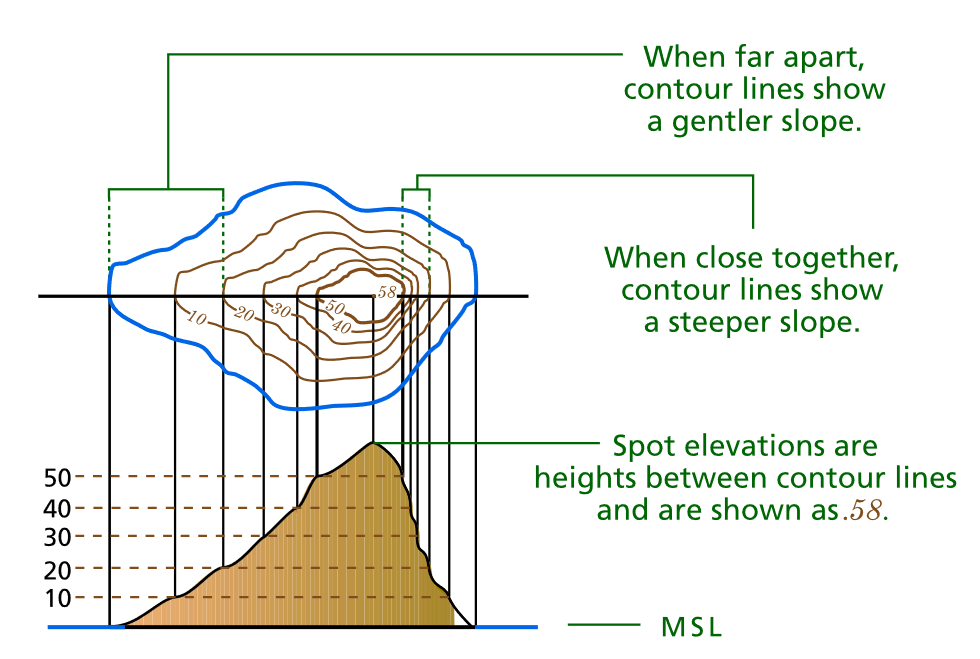
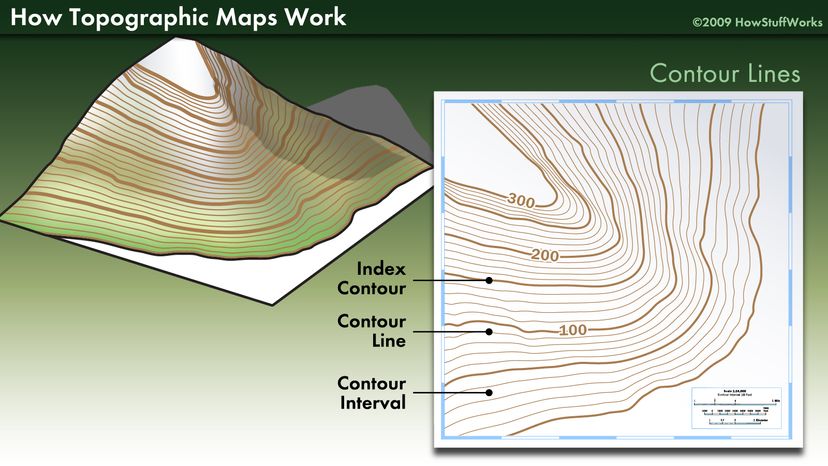
Contour Lines: This classic technique uses lines connecting points of equal elevation, forming a network of contours that depict the shape of the terrain. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope. This method offers a precise representation of elevation changes and is widely used in topographic maps.
-
Hypsometric Tinting: This approach utilizes different colors to represent different elevation ranges. Higher elevations are typically depicted with lighter or warmer colors, while lower elevations are shown in darker or cooler hues. This technique provides a visually appealing and intuitive representation of elevation variations, allowing for quick identification of high and low areas.
-
Shaded Relief: This technique simulates the appearance of the terrain as it would be illuminated by sunlight. It uses shading to create the illusion of three-dimensionality, highlighting ridges, valleys, and other topographic features. Shaded relief maps are visually striking and effectively communicate the overall shape of the landscape.
-
3D Models: Advancements in technology have enabled the creation of three-dimensional digital models of the terrain. These models provide a highly realistic and interactive representation of elevation, allowing users to explore the landscape from various perspectives.
Beyond Visual Representation:
Elevation maps are not merely visual aids. They serve as crucial data sources for a wide range of applications:
-
Planning and Development: Urban planners rely on elevation maps to identify suitable locations for infrastructure projects, considering factors like slope, drainage, and potential hazards. These maps help in optimizing the placement of roads, buildings, and other structures, minimizing environmental impact and ensuring safety.
-
Environmental Management: Understanding elevation is critical for managing natural resources and mitigating environmental risks. Elevation maps aid in identifying areas prone to flooding, landslides, or erosion, allowing for targeted conservation efforts and disaster preparedness strategies.
-
Navigation and Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts use elevation maps to plan routes, assess difficulty levels, and understand potential hazards. These maps provide essential information about terrain features, elevation changes, and access points, enhancing safety and enjoyment during outdoor activities.
-
Scientific Research: Scientists across various disciplines, including geology, geography, and climatology, rely on elevation maps for data analysis and modeling. These maps help in understanding the formation of landscapes, predicting climate change impacts, and studying the distribution of flora and fauna.
The Importance of Accuracy:
The accuracy of elevation data is crucial for the effectiveness of these maps. Modern technologies like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and aerial photography provide highly precise elevation measurements, enabling the creation of detailed and reliable elevation maps.
FAQs:
Q: How do I find an elevation map for a specific location?
A: Numerous online platforms and government agencies offer access to elevation maps. Popular options include Google Earth, USGS (United States Geological Survey), and various mapping software applications.
Q: What are the different units used for elevation measurement?
A: Elevation is typically measured in meters (m) or feet (ft). The choice of units depends on the region and the specific map source.
Q: Can I create my own elevation map?
A: While creating professional-grade elevation maps requires specialized software and data, you can create basic elevation representations using online tools or mapping software.
Tips:
- Understand the map’s scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map to determine the level of detail provided.
- Identify contour lines: Learn to interpret contour lines to understand elevation changes and slope gradients.
- Use color gradients: Familiarize yourself with the color scheme used to represent different elevation ranges.
- Explore different map types: Experiment with different types of elevation maps, such as topographic maps, shaded relief maps, and 3D models, to find the one that best suits your needs.
Conclusion:
Elevation maps are indispensable tools for understanding and interacting with the Earth’s surface. They provide a visual representation of the terrain, aiding in decision-making across various fields. By understanding the different techniques used to depict elevation and the vast applications of these maps, individuals can gain valuable insights into the physical world and make informed decisions for a better future.
![[DIAGRAM] Elevation From Sea Level Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](http://maps.risingsea.net/wetland_loss/tides_wetlands_elevation.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: Understanding Elevation Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!