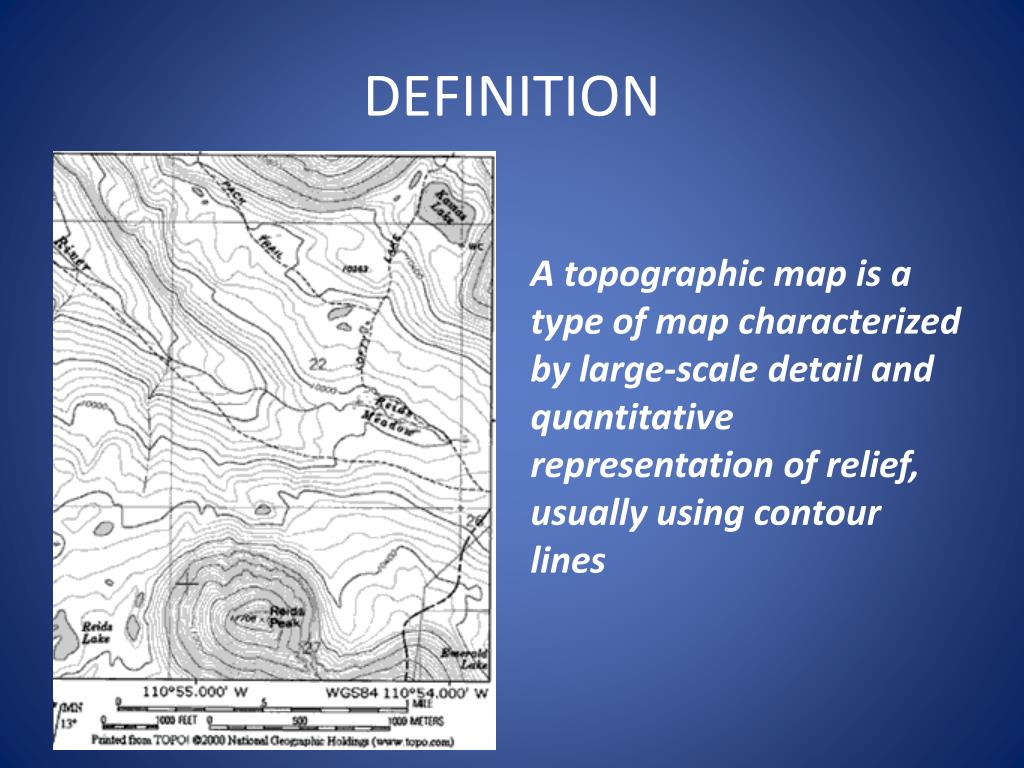
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps and their Significance
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps and their Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps and their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps and their Significance

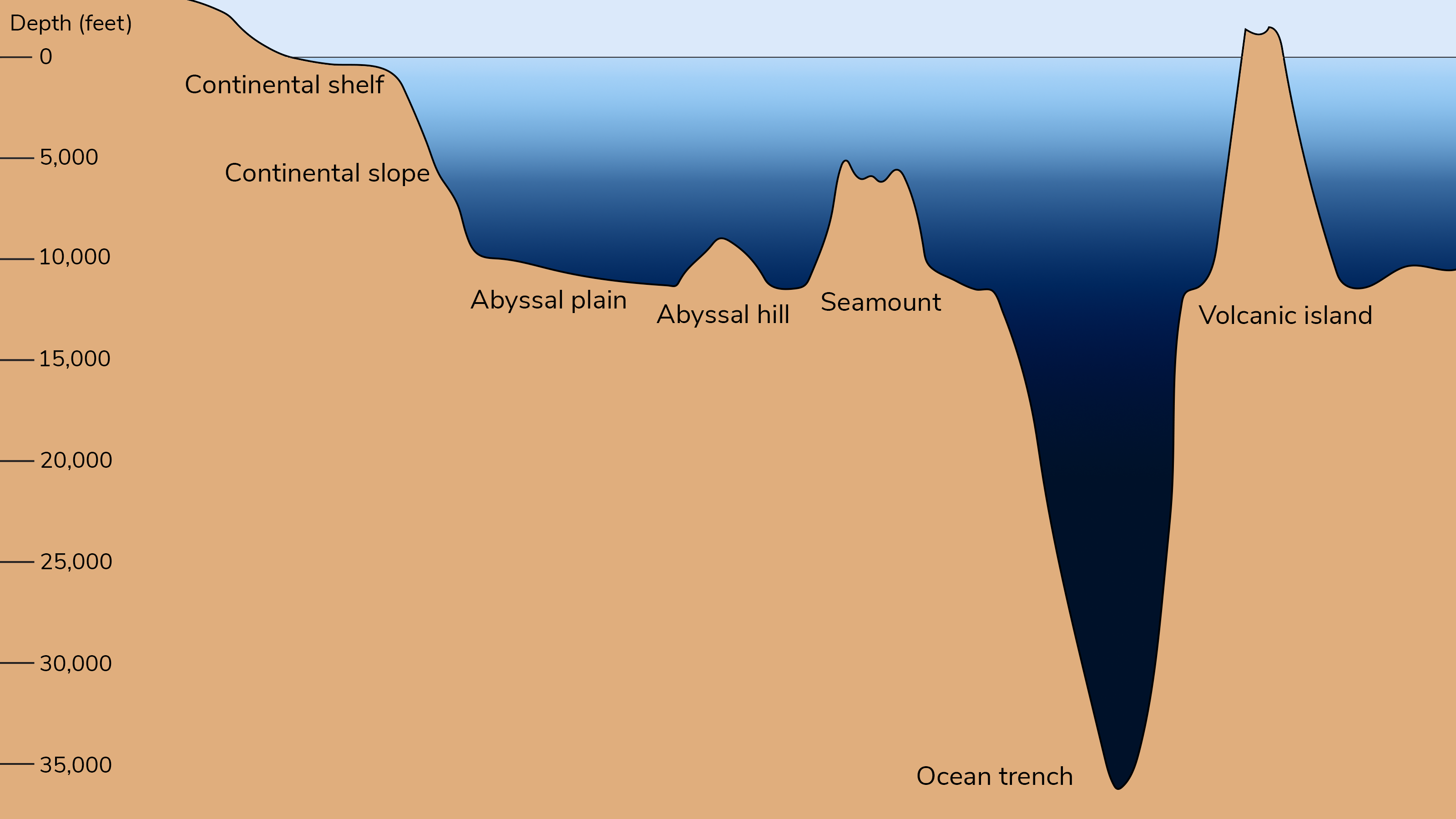
The Earth’s surface is far from uniform. It is a tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus, each with its unique elevation. Capturing this intricate landscape on a flat surface requires specialized cartographic techniques, and one such technique utilizes topographic maps. These maps are not simply visual representations of landforms; they are powerful tools for understanding and navigating the three-dimensional world.
The Essence of Elevation: A Visual Language of Contour Lines
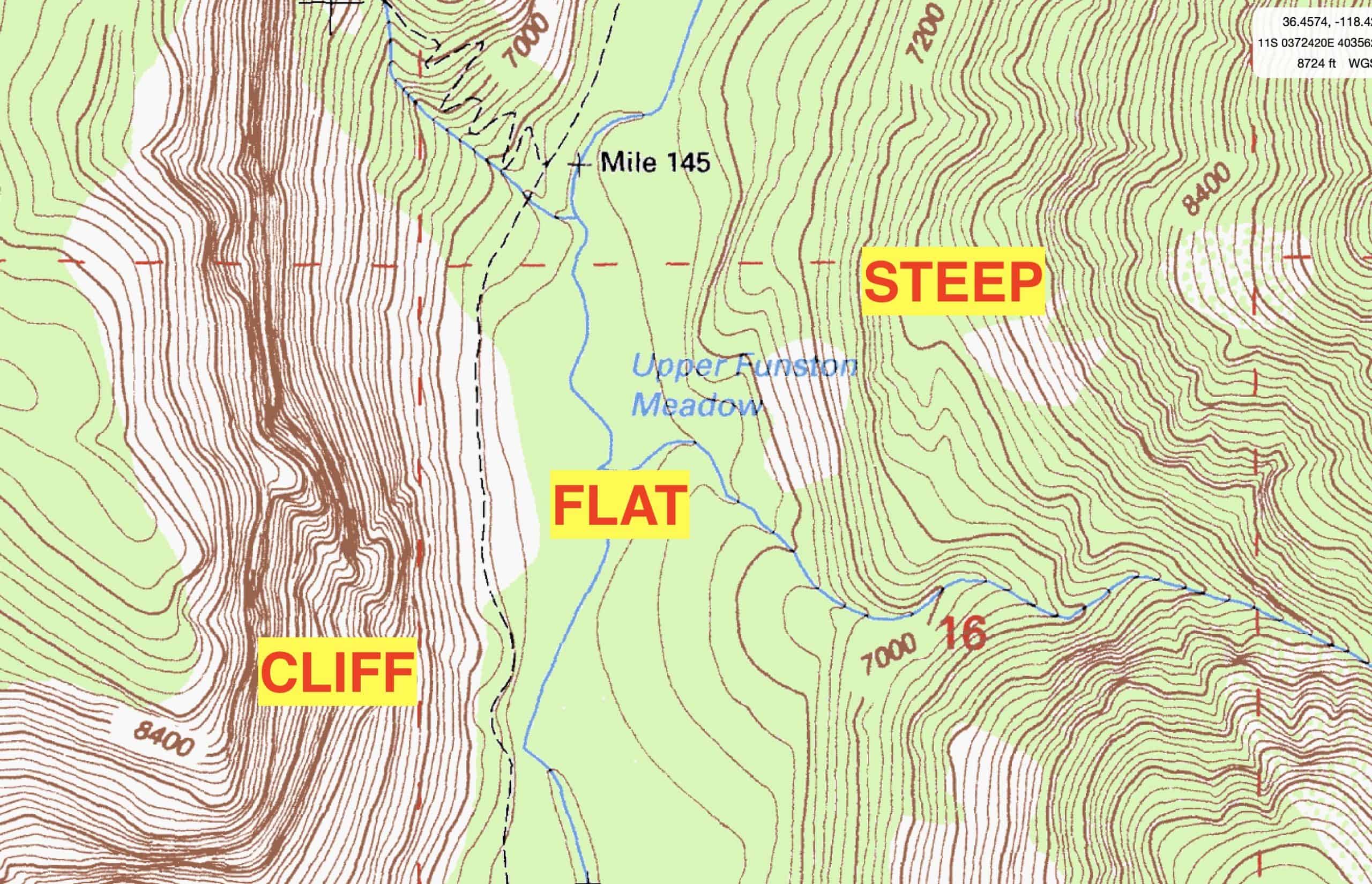
Topographic maps utilize a system of contour lines to depict elevation. Each contour line connects points of equal elevation, forming a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. Imagine slicing through a landscape with horizontal planes at regular intervals. The intersection of each plane with the terrain would create a contour line on the map.
The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope. Conversely, widely spaced contour lines indicate a gentler incline. This visual language allows map readers to understand the terrain’s gradient, identify peaks and valleys, and even estimate the relative difficulty of traversing a particular route.
Beyond Elevation: A Comprehensive View of the Landscape
Topographic maps offer much more than just elevation data. They often include additional information crucial for understanding the environment, including:
- Hydrographic features: Rivers, lakes, and streams are depicted with blue lines, revealing drainage patterns and water sources.
- Land use: Areas marked for different purposes, such as agriculture, urban development, or forests, are indicated with symbols and colors.
- Cultural features: Roads, bridges, buildings, and other man-made structures are displayed, providing a context for human activity within the landscape.
- Elevation values: Specific elevations are often indicated on the map, providing precise numerical data for key points.
This comprehensive information makes topographic maps invaluable tools for various applications, including:
- Navigation: Hikers, climbers, and explorers rely on topographic maps for planning routes, identifying potential hazards, and navigating challenging terrain.
- Urban planning: Planners use topographic maps to understand the topography of a site, assess potential drainage issues, and design infrastructure that integrates with the existing landscape.
- Environmental studies: Researchers and scientists utilize topographic maps to analyze landforms, understand ecological processes, and monitor environmental changes.
- Military operations: Topographic maps are essential for military planning, providing crucial information about terrain, potential cover, and routes of movement.
Types of Topographic Maps: A Spectrum of Detail
Topographic maps exist at various scales, each offering a specific level of detail and serving different purposes:
- Large-scale maps: These maps cover smaller areas with high detail, often used for local planning, hiking, and detailed environmental studies.
- Medium-scale maps: These maps offer a balance between detail and coverage, suitable for regional planning, recreational activities, and general navigation.
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover vast areas with less detail, primarily used for overview purposes, regional planning, and broad environmental analysis.
Beyond Traditional Maps: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs)
While traditional paper topographic maps remain valuable, technology has ushered in a new era of elevation data representation. Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) are digital representations of the Earth’s surface, providing precise elevation data for every point within a specified area. These models are created using various techniques, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and laser scanning.
DEMs offer several advantages over traditional maps:
- High accuracy: DEMs provide precise elevation data, allowing for detailed analysis and modeling.
- Flexibility: DEMs can be easily manipulated and analyzed using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, facilitating complex spatial analysis and visualization.
- Accessibility: DEMs are readily available online, making them accessible for various applications.
FAQs Regarding Topographic Maps and Elevation Data
1. How are contour lines generated?
Contour lines are created by intersecting a series of horizontal planes with the terrain. Each plane represents a specific elevation, and the intersection points are connected to form a contour line.
2. How do I read a topographic map?
Understanding contour lines is key to reading topographic maps. The closer the lines are together, the steeper the slope. Wider spacing indicates a gentler incline. Look for specific elevation values indicated on the map to gain a precise understanding of the terrain.
3. What are the benefits of using topographic maps?
Topographic maps offer a comprehensive understanding of the landscape, including elevation, landforms, water features, and cultural elements. They are crucial for navigation, planning, environmental studies, and various other applications.
4. How do digital elevation models differ from traditional topographic maps?
DEMs are digital representations of the Earth’s surface, providing precise elevation data for every point within an area. They offer higher accuracy, flexibility, and accessibility compared to traditional maps.
5. Where can I find topographic maps and DEMs?
Topographic maps are available from government agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and private publishers. DEMs can be accessed through online repositories like the National Elevation Dataset (NED) and various GIS software platforms.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
- Study the map legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used on the map to interpret information accurately.
- Understand the scale: Determine the map’s scale to accurately estimate distances and terrain features.
- Pay attention to contour lines: Use the spacing and direction of contour lines to understand the terrain’s gradient and potential hazards.
- Consider the map’s purpose: Choose a map appropriate for your specific needs, whether for hiking, planning, or research.
- Utilize technology: Integrate topographic maps with GPS devices or mapping apps for enhanced navigation and data visualization.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Earth’s Topography
Topographic maps and digital elevation models are invaluable tools for understanding and interacting with the Earth’s three-dimensional landscape. They provide a visual language for interpreting elevation, revealing the intricacies of terrain and guiding us through the complexities of our physical environment. From planning outdoor adventures to managing urban infrastructure, these maps empower us to navigate, analyze, and ultimately understand the world around us with greater clarity and precision.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps and their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!