Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security
Related Articles: Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security
- 3.1 Understanding the DMZ Key Map
- 3.2 Benefits of a DMZ Key Map
- 3.3 Key Components of a DMZ Key Map
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Effective DMZ Key Map Implementation
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security
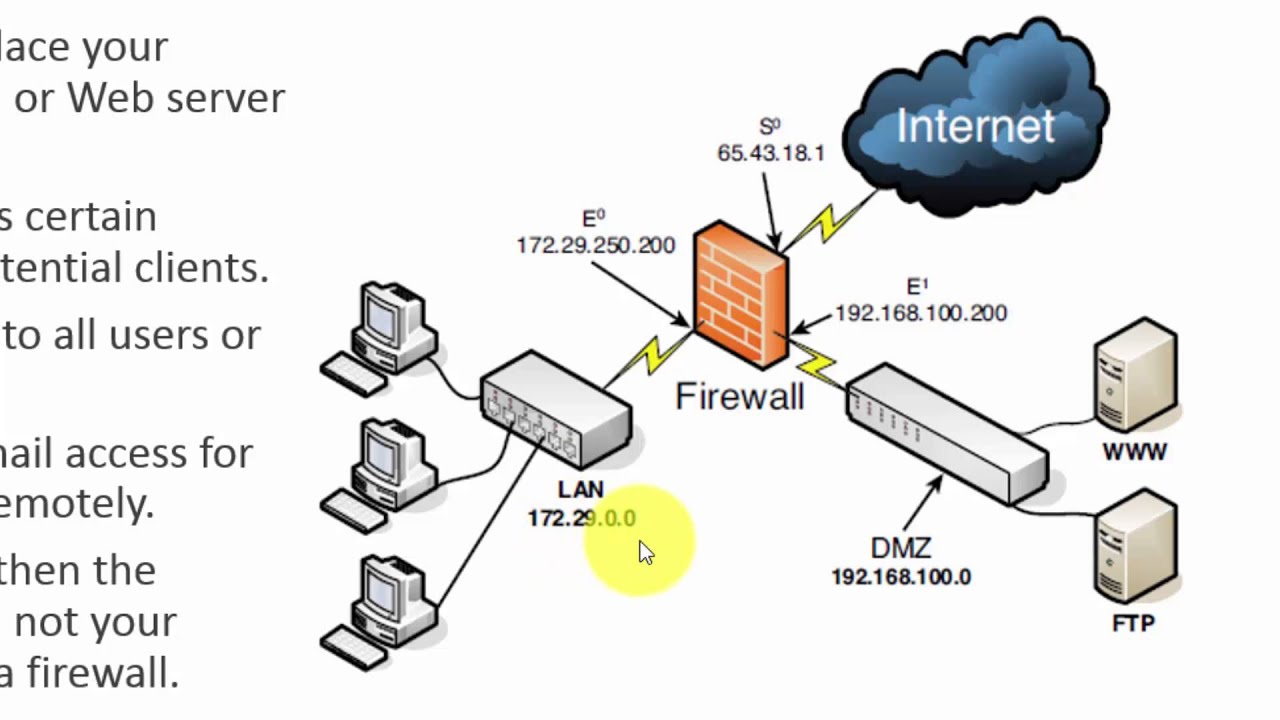
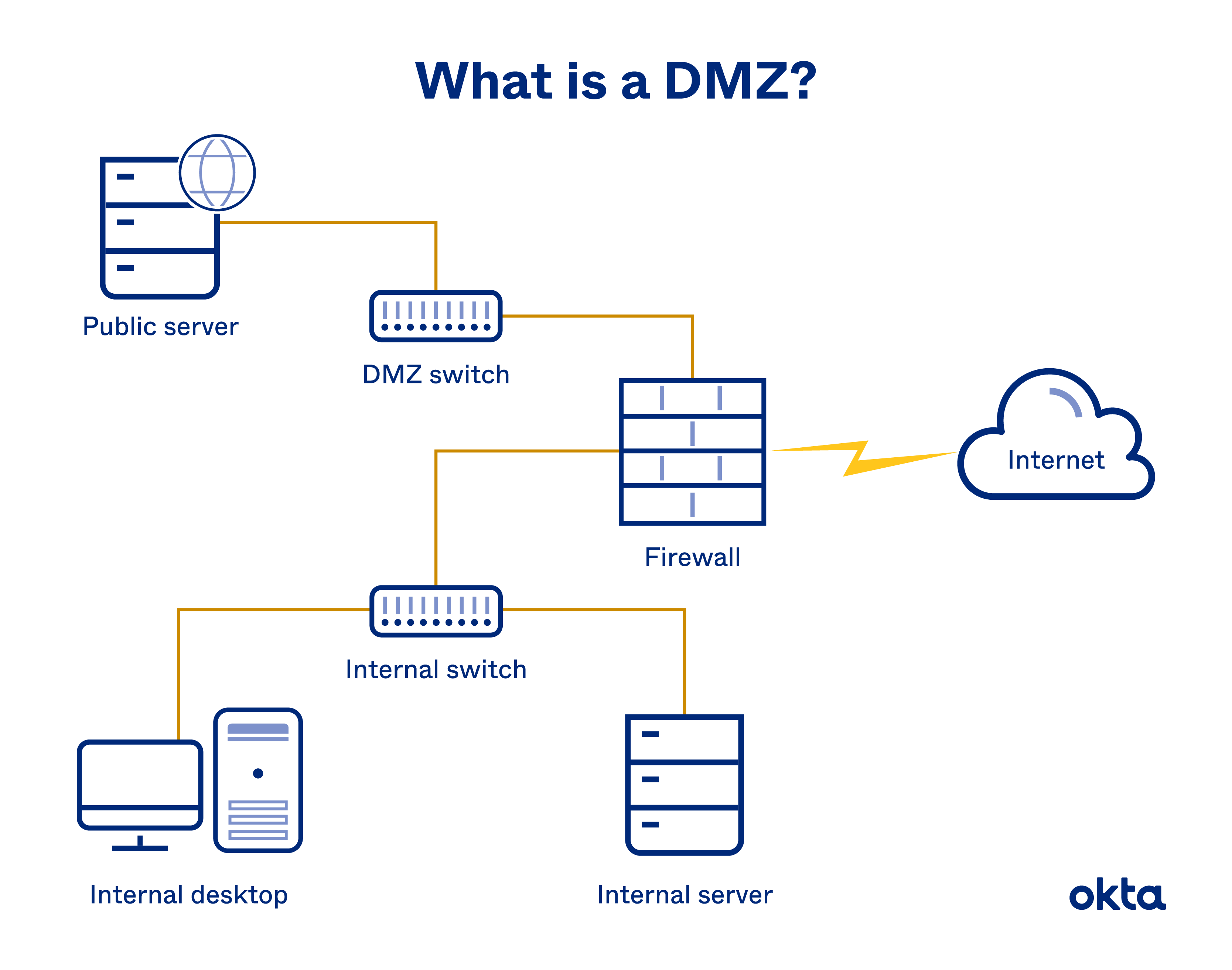
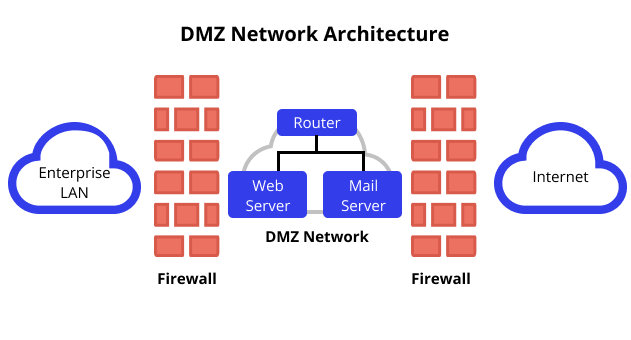
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is a crucial component of modern network security, acting as a buffer zone between the public internet and a private network. Within this zone, specific servers and services are exposed to the internet, allowing for controlled access while protecting the internal network from potential threats. A DMZ key map serves as a visual representation of this zone, outlining the components, connections, and traffic flow within it.
Understanding the DMZ Key Map
A DMZ key map is essentially a diagram that illustrates the layout and configuration of the DMZ. It provides a clear and concise visual representation of:
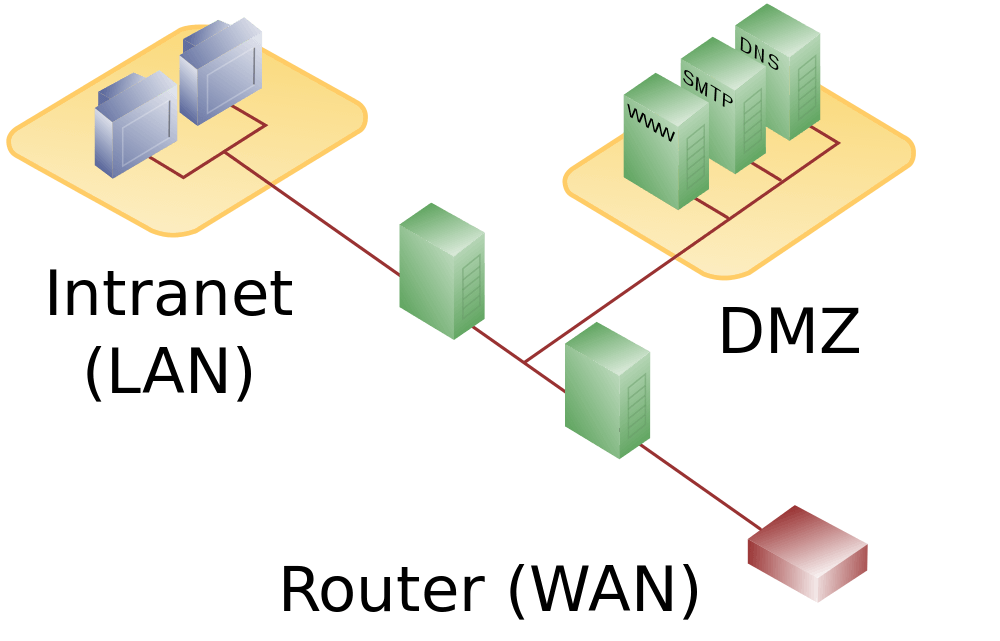
- DMZ Servers: The servers and services hosted within the DMZ, such as web servers, email servers, or databases, are depicted with their respective roles and configurations.
- Network Connections: The map showcases the connections between the DMZ servers, the internal network, and the public internet. This includes firewalls, routers, and other network devices that control traffic flow.
- Traffic Flow: The map highlights the direction and type of traffic permitted between the DMZ and other network segments. This allows for a visual understanding of how data is exchanged within the DMZ environment.
Benefits of a DMZ Key Map
Utilizing a DMZ key map provides numerous advantages for network security and management:
- Enhanced Security: By clearly defining the boundaries and connections within the DMZ, the map facilitates the implementation of robust security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists.
- Improved Visibility: The map offers a comprehensive view of the DMZ infrastructure, allowing network administrators to easily identify potential vulnerabilities and security risks.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: In the event of a security incident or network failure, the map serves as a valuable tool for quickly identifying the affected components and troubleshooting the issue.
- Streamlined Management: The map simplifies the management and maintenance of the DMZ by providing a clear visual representation of its configuration and traffic flow.
- Effective Communication: The map serves as a communication tool, enabling network administrators to effectively convey the DMZ setup to other stakeholders, such as security teams and management.
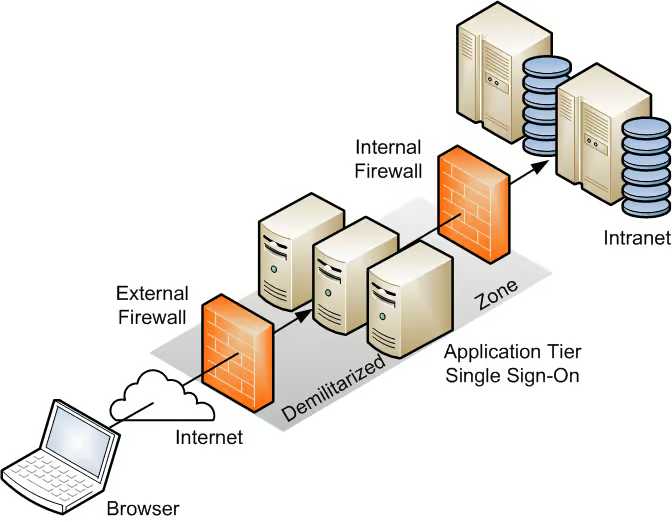
Key Components of a DMZ Key Map
A well-designed DMZ key map typically includes the following essential components:
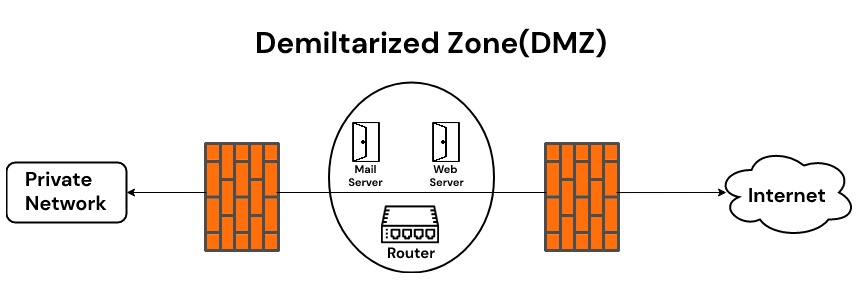
- External Network: Represents the public internet, where external users and services reside.
- Firewall: Acts as the primary security barrier between the DMZ and the external network, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules.
- DMZ Network: Depicts the isolated network segment where DMZ servers and services are hosted.
- DMZ Servers: Illustrates the specific servers and services exposed to the internet, such as web servers, mail servers, or VPN gateways.
- Internal Network: Represents the private network, which houses sensitive data and applications.
- Firewall: Another firewall acts as a barrier between the DMZ and the internal network, further protecting the private network from potential threats.
- Traffic Flow: Arrows indicate the direction and type of traffic permitted between different network segments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the key considerations when designing a DMZ key map?
A: When designing a DMZ key map, it is crucial to consider:
- Security Requirements: The level of security needed for different services and the sensitivity of the data they handle.
- Network Topology: The physical and logical layout of the network, including the placement of firewalls and other security devices.
- Traffic Flow: The types of traffic allowed between different network segments and the associated security policies.
- Scalability: The ability to expand the DMZ infrastructure to accommodate future growth and changes in service requirements.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of my DMZ key map?
A: To ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the DMZ key map, it is essential to:
- Regularly Review and Update: The map should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect any changes in the DMZ configuration, security policies, or network topology.
- Use Standardized Symbols and Notations: Consistent use of symbols and notations ensures clarity and easy understanding of the map.
- Document Configuration Details: Include detailed information about each server, service, and network device within the DMZ.
- Validate the Map: Regularly validate the map against the actual DMZ configuration to ensure its accuracy.
Q: What are the best practices for managing a DMZ key map?
A: Best practices for managing a DMZ key map include:
- Centralized Management: Store the map in a central location accessible to all relevant personnel, such as network administrators and security teams.
- Version Control: Implement version control to track changes made to the map over time.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up the map to ensure its availability in case of data loss or corruption.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training to network administrators and other relevant personnel on the use and interpretation of the DMZ key map.
Tips for Effective DMZ Key Map Implementation
- Use a Clear and Concise Layout: Employ a simple and easy-to-understand layout, using clear symbols and notations.
- Focus on Essential Information: Include only the most relevant information, avoiding unnecessary details that can clutter the map.
- Use Color Coding: Utilize different colors to distinguish different network segments, servers, and services.
- Include Security Controls: Highlight the security controls implemented within the DMZ, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists.
- Document Changes: Keep a detailed record of any changes made to the DMZ key map, including the date, reason, and person responsible for the change.
Conclusion
A DMZ key map is a valuable tool for network administrators, providing a clear and comprehensive visual representation of the DMZ environment. By effectively utilizing a DMZ key map, organizations can enhance their network security, improve visibility, streamline management, and facilitate effective communication. By adhering to best practices and consistently maintaining the map, organizations can ensure its accuracy and effectiveness in protecting their critical data and systems from external threats.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) Key Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!