Kazakhstan on the World Map: A Nation of Vast Landscapes and Strategic Importance
Related Articles: Kazakhstan on the World Map: A Nation of Vast Landscapes and Strategic Importance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Kazakhstan on the World Map: A Nation of Vast Landscapes and Strategic Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Kazakhstan on the World Map: A Nation of Vast Landscapes and Strategic Importance
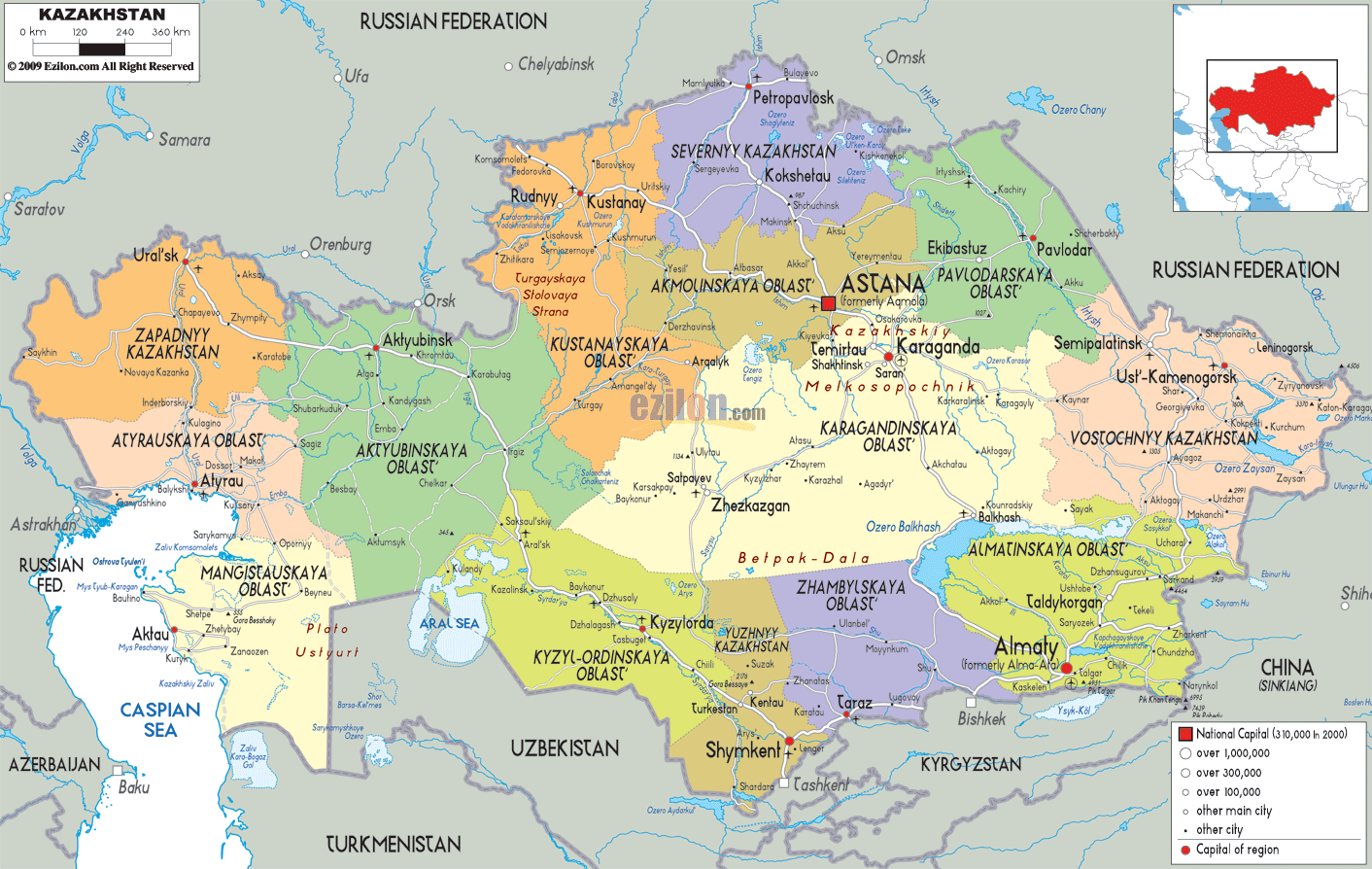
Kazakhstan, a vast and landlocked nation nestled in Central Asia, occupies a prominent position on the world map. Its strategic location, spanning over 2.7 million square kilometers, makes it a crucial link between Europe and Asia, influencing trade routes and geopolitical dynamics. This article delves into the complexities of Kazakhstan’s geography, history, culture, and its significance in the global landscape.
A Tapestry of Landscapes:
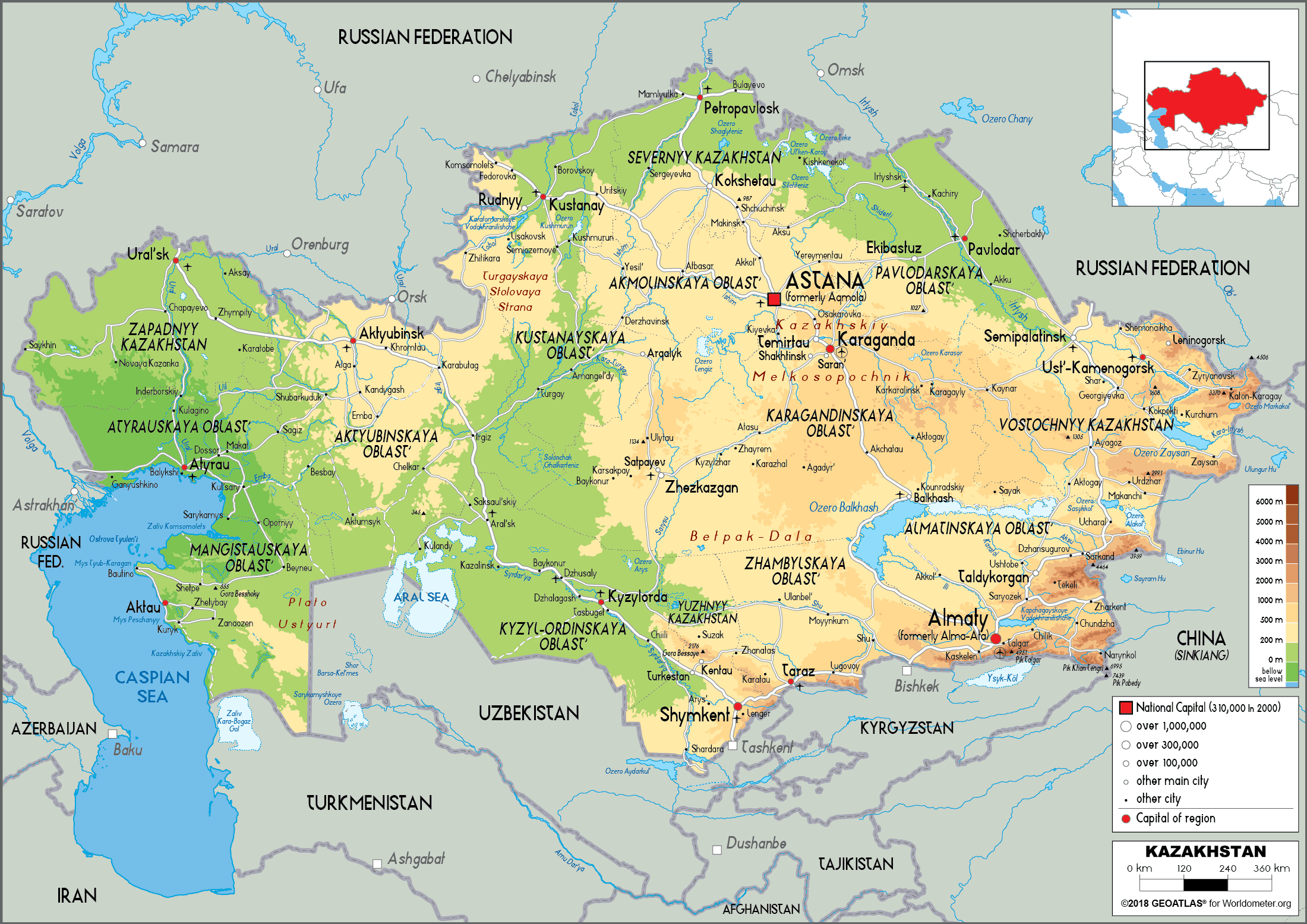
Kazakhstan’s topography is a testament to its immense size and diverse geological history. The country is characterized by vast steppes, rolling hills, and towering mountain ranges. The majestic Tian Shan Mountains, a formidable barrier separating Kazakhstan from China, dominate the southeast, while the Altai Mountains mark the eastern border with Russia and Mongolia. The vast, flat plains of the Kazakh Steppe, known for its nomadic history, stretch across the northern and western regions.
The country’s diverse geography also includes vast deserts, such as the Kyzylkum Desert in the southwest and the Betpak-Dala Desert in the central region. The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland body of water, forms its western boundary, providing access to vital maritime trade routes. This unique combination of landscapes contributes to Kazakhstan’s ecological richness, hosting a wide range of flora and fauna, including endangered species like the snow leopard and the saiga antelope.
A History of Nomadic Culture and Imperial Influence:
Kazakhstan’s history is deeply intertwined with the nomadic cultures of the Eurasian steppes. For centuries, the land was inhabited by nomadic tribes, most notably the Kazakhs, who developed a unique culture centered on horse-riding, livestock herding, and a strong sense of community. This nomadic heritage continues to influence Kazakh identity and traditions, shaping its artistic expressions, musical traditions, and social structure.
However, Kazakhstan’s history also reflects the influence of powerful empires. It was part of the Silk Road, the ancient trade route connecting East and West, facilitating cultural exchange and economic prosperity. In the 18th century, the Kazakh Khanate, a loose confederation of tribes, fell under the influence of the Russian Empire. This period marked a significant shift in Kazakhstan’s political landscape, leading to its eventual incorporation into the Soviet Union in 1936.
The Legacy of Soviet Rule and the Path to Independence:
The Soviet era significantly shaped Kazakhstan’s social, economic, and political landscape. Industrialization, particularly in the mining and energy sectors, transformed the country’s economic profile. However, this development came at a cost, with forced collectivization of agriculture and suppression of cultural identity impacting the Kazakh people. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 brought independence to Kazakhstan, ushering in a new era of political and economic transformation.
A Nation in Transition: Economic Growth and Challenges:
Since gaining independence, Kazakhstan has embarked on a path of economic diversification and modernization. The country has leveraged its vast natural resources, particularly oil and gas, to fuel economic growth. It has also invested in infrastructure development, attracting foreign investment and fostering a growing manufacturing sector. However, Kazakhstan faces several challenges, including economic diversification, social inequality, and environmental concerns.
Geopolitical Significance and International Relations:
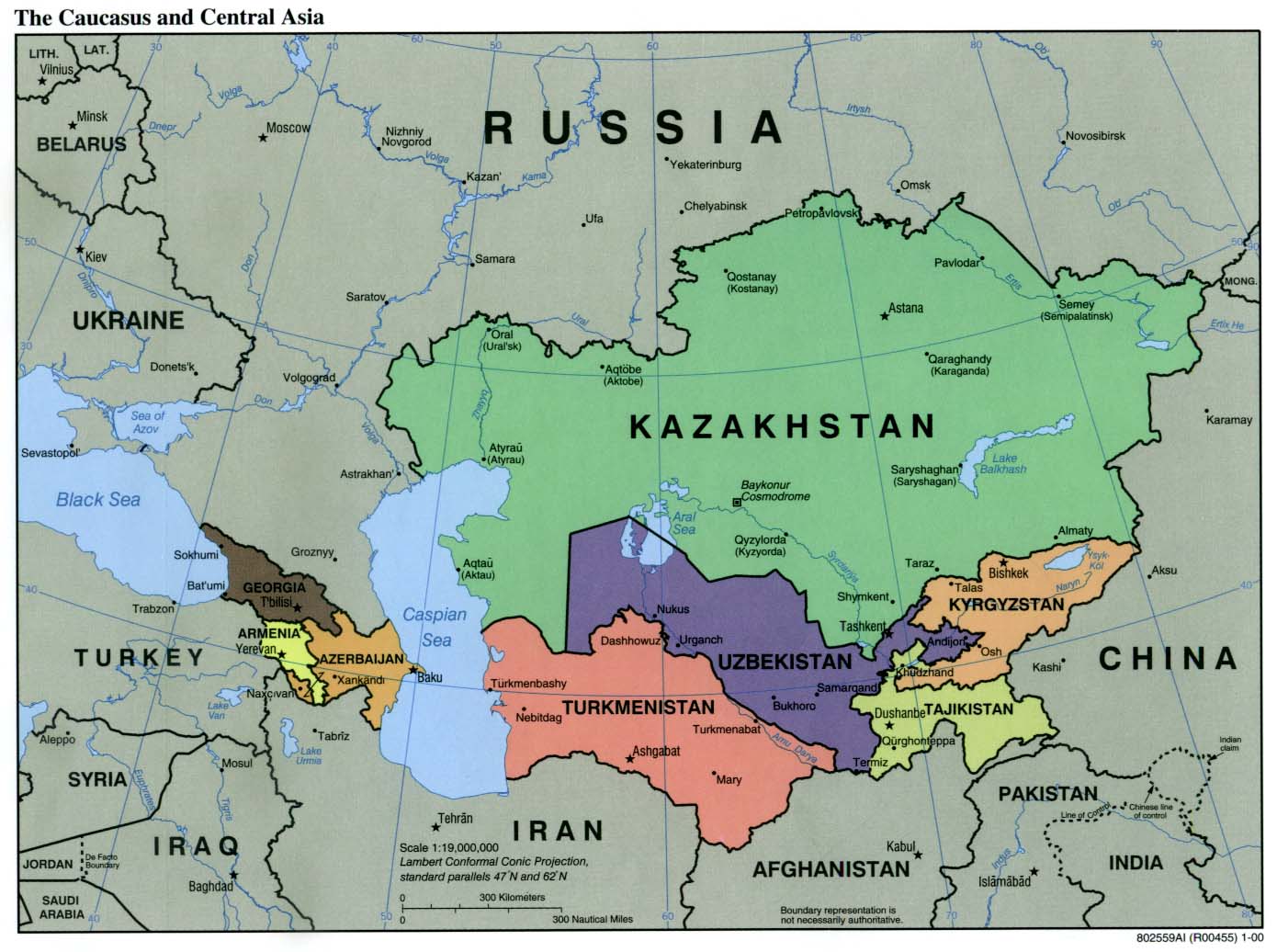
Kazakhstan’s strategic location at the crossroads of Eurasia makes it a significant player in regional and global affairs. The country plays a vital role in promoting regional stability and cooperation, actively engaging in multilateral organizations like the United Nations, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, and the Eurasian Economic Union. It has also fostered close relations with key international partners, including Russia, China, and the United States.
Cultural Heritage and Artistic Expressions:
Kazakhstan boasts a rich cultural heritage, deeply rooted in its nomadic past and influenced by its diverse history. Traditional music, dance, and crafts are integral to Kazakh identity, reflecting the spirit of the steppes and the resilience of its people. Modern Kazakh art, literature, and music are increasingly gaining international recognition, showcasing the country’s evolving cultural landscape.
FAQs about Kazakhstan:
- What is Kazakhstan’s population? Kazakhstan has a population of approximately 19 million people.
- What languages are spoken in Kazakhstan? The official language is Kazakh, while Russian is widely spoken, particularly in urban areas.
- What is the main religion in Kazakhstan? Islam is the dominant religion in Kazakhstan, with a significant percentage of the population adhering to Sunni Islam.
- What is Kazakhstan’s main industry? Kazakhstan is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas, which are its main exports.
- What are some popular tourist destinations in Kazakhstan? Popular tourist destinations include Almaty, the former capital, known for its stunning mountains and ski resorts; Astana, the modern capital, with its unique architecture; and the Bayanaul National Park, a natural wonder with picturesque lakes and forests.
Tips for Visiting Kazakhstan:
- Learn a few basic Kazakh phrases: Even a few words will show respect for the local culture.
- Be prepared for a wide range of temperatures: Kazakhstan experiences extreme temperature variations, so pack accordingly.
- Try traditional Kazakh cuisine: Explore local dishes like beshbarmak (meat and noodles), plov (rice pilaf), and shashlik (grilled meat).
- Visit historical sites: Explore ancient burial mounds, Silk Road trading posts, and Soviet-era monuments.
- Respect local customs and traditions: Dress modestly when visiting religious sites and be mindful of cultural sensitivities.
Conclusion:
Kazakhstan, a nation of vast landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture, holds a significant place on the world map. Its strategic location, diverse resources, and evolving economic landscape make it a key player in regional and global affairs. As the country continues its journey of development and modernization, its importance in the global context is likely to grow, solidifying its position as a bridge between East and West.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Kazakhstan on the World Map: A Nation of Vast Landscapes and Strategic Importance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!