Kazakhstan’s Mineral Wealth: A Geographic Overview and its Significance
Related Articles: Kazakhstan’s Mineral Wealth: A Geographic Overview and its Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Kazakhstan’s Mineral Wealth: A Geographic Overview and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Kazakhstan’s Mineral Wealth: A Geographic Overview and its Significance

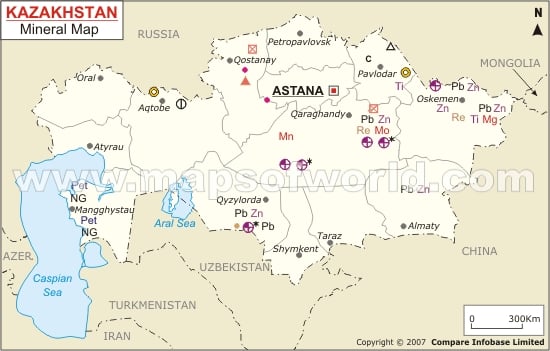
Kazakhstan, a vast landlocked nation in Central Asia, is renowned for its abundant mineral resources. These resources have played a pivotal role in shaping the country’s economy, contributing significantly to its industrial development and global trade. A comprehensive understanding of Kazakhstan’s mineral resources map is crucial for comprehending the nation’s economic potential, environmental considerations, and geopolitical significance.
A Geographic Landscape of Mineral Riches
Kazakhstan’s mineral wealth is geographically diverse, with deposits scattered across its expansive territory. The country’s mineral resources can be broadly categorized into:
-
Energy Resources:
- Oil and Gas: Kazakhstan holds substantial reserves of oil and natural gas, primarily concentrated in the western and southwestern regions. The Caspian Sea basin, particularly the Tengiz and Kashagan fields, are major oil producers. The country’s natural gas reserves are primarily located in the western and northern regions.
- Coal: Kazakhstan possesses significant coal reserves, mainly located in the eastern and southeastern regions. The Karaganda and Ekibastuz coal basins are notable producers.
- Uranium: Kazakhstan is a leading global producer of uranium, with major deposits found in the southeastern regions, notably in the Zhezkazgan and Aktau areas.
-
Metallic Minerals:
- Copper: Kazakhstan is a significant copper producer, with deposits found in the central and eastern regions, particularly in the Zhezkazgan and Balkhash areas.
- Iron Ore: Iron ore deposits are primarily located in the central and eastern regions, with the Sokolov-Sarbai and Lisakovsk mines being notable producers.
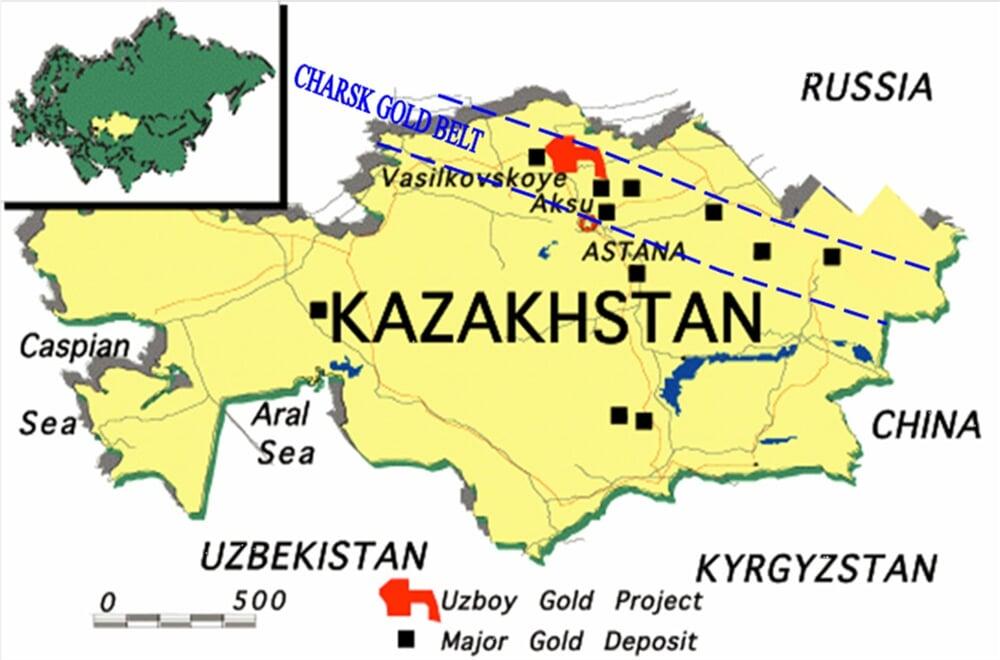
- Gold: Kazakhstan is a major gold producer, with deposits scattered throughout the country, including the Karatau, Kyzylzhar, and Aktobe regions.
- Zinc and Lead: Significant deposits of zinc and lead are found in the eastern and southern regions, notably in the Ridder-Sokolovskoye and Altyn-Topkan areas.
- Aluminum: Kazakhstan possesses bauxite reserves, the raw material for aluminum production, primarily located in the southern regions.
-
Non-Metallic Minerals:
- Phosphate Rock: Kazakhstan has substantial reserves of phosphate rock, a key ingredient in fertilizers, primarily located in the southern and southeastern regions.
- Salt: Salt deposits are found in various regions, including the western and southern parts of the country.
- Chromium: Kazakhstan holds significant deposits of chromium, a crucial component in stainless steel, mainly located in the southern regions.
- Molybdenum: Molybdenum deposits are found in the eastern and southern regions, primarily in the Zhezkazgan and Aktobe areas.
The Importance of Kazakhstan’s Mineral Resources
Kazakhstan’s mineral resources have had a profound impact on its economy and development:
- Economic Growth and Diversification: Mineral extraction and processing constitute a significant portion of Kazakhstan’s GDP, contributing to its overall economic growth. The country’s mineral wealth has facilitated the development of related industries, such as metallurgy, chemicals, and construction materials, contributing to economic diversification.
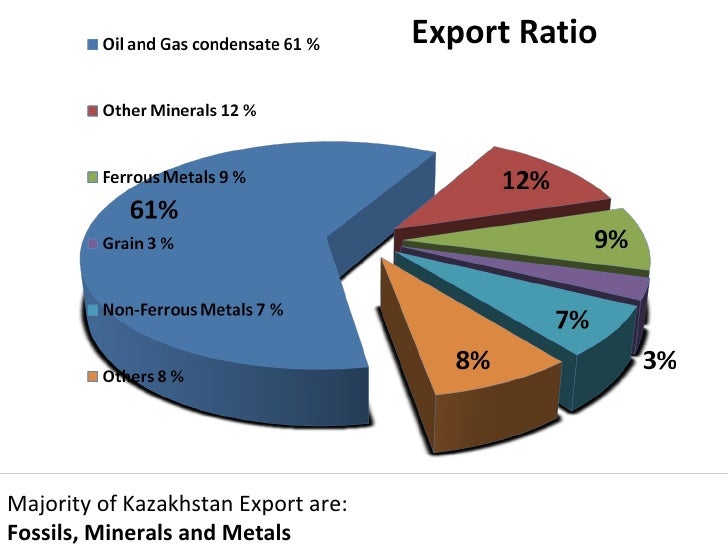
- Export Revenue and Foreign Investment: Kazakhstan’s mineral exports generate substantial revenue, playing a crucial role in balancing the country’s trade deficit. The abundance of mineral resources has attracted significant foreign investment, particularly in the energy and mining sectors.
- Infrastructure Development: The extraction and transportation of minerals have driven the development of infrastructure, including roads, railways, and pipelines, connecting various regions and facilitating trade.
- Employment and Social Welfare: The mining sector provides employment opportunities for a significant portion of the Kazakh workforce, contributing to social welfare and economic stability.
- Technological Advancement: The mining industry in Kazakhstan has driven the adoption of advanced technologies, including automation, remote sensing, and data analytics, contributing to increased efficiency and productivity.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Kazakhstan’s mineral wealth presents significant opportunities, it also poses challenges:
- Environmental Impact: Mining operations can have a negative impact on the environment, including land degradation, water pollution, and air pollution. Sustainable mining practices and environmental regulations are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
- Resource Depletion: The finite nature of mineral resources necessitates responsible management to ensure their long-term sustainability. Diversifying the economy and investing in renewable energy sources are essential steps to mitigate resource depletion.
- Economic Volatility: Global commodity prices can fluctuate significantly, impacting the revenue generated from mineral exports. Diversifying the economy and developing value-added processing industries are crucial to minimize this volatility.
- Political Stability: Political stability is essential for attracting foreign investment and ensuring the smooth functioning of the mining sector. Maintaining a stable political environment is vital for sustainable development.
- Social Impacts: Mining activities can have social impacts on local communities, including displacement, loss of traditional livelihoods, and potential conflicts over resource ownership. Addressing these issues through community engagement and equitable benefit-sharing is crucial.
FAQs about Kazakhstan’s Mineral Resources Map
-
What are the key mineral resources found in Kazakhstan?
- Kazakhstan is rich in energy resources, including oil, natural gas, and coal. It is also a major producer of metallic minerals such as copper, iron ore, gold, zinc, and lead. Non-metallic minerals like phosphate rock, salt, chromium, and molybdenum are also found in significant quantities.
-
What are the major mining regions in Kazakhstan?
- The Caspian Sea basin, particularly the Tengiz and Kashagan fields, are major oil producers. The Karaganda and Ekibastuz coal basins are notable producers of coal. The Zhezkazgan and Balkhash areas are significant copper producers. The Sokolov-Sarbai and Lisakovsk mines are notable iron ore producers. The Karatau, Kyzylzhar, and Aktobe regions are known for gold production.
-
How does Kazakhstan’s mineral wealth contribute to its economy?
- Mineral extraction and processing constitute a significant portion of Kazakhstan’s GDP, driving economic growth and diversifying the economy. Mineral exports generate substantial revenue, attracting foreign investment and supporting infrastructure development.
-
What are the environmental challenges associated with mining in Kazakhstan?
- Mining activities can lead to land degradation, water pollution, and air pollution. Sustainable mining practices and strict environmental regulations are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
-
What are the social impacts of mining in Kazakhstan?
- Mining activities can displace local communities, impact traditional livelihoods, and create conflicts over resource ownership. Addressing these issues through community engagement and equitable benefit-sharing is essential.
Tips for Understanding Kazakhstan’s Mineral Resources Map
- Refer to reliable sources: Use official government websites, reputable research institutions, and international organizations for accurate data and analysis.
- Analyze the geographic distribution: Study the map to identify the locations of major mineral deposits and understand their regional distribution.
- Consider economic factors: Examine the relationships between mineral resources, economic activity, and infrastructure development.
- Assess environmental implications: Evaluate the potential environmental impacts of mining activities and the measures taken to mitigate them.
- Recognize social considerations: Understand the social implications of mining on local communities and the efforts to address them.
Conclusion
Kazakhstan’s mineral resources map is a testament to the country’s vast potential and its role in the global economy. The abundance of energy and mineral resources has been a driving force behind Kazakhstan’s economic growth and industrial development. However, sustainable resource management, environmental protection, and social responsibility are crucial to ensure the long-term benefits of this wealth. By navigating the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, Kazakhstan can continue to harness its mineral resources for sustainable economic growth and social progress.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Kazakhstan’s Mineral Wealth: A Geographic Overview and its Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!