Mapping Environmental Justice in Kazakhstan: A Vital Tool for Sustainable Development
Related Articles: Mapping Environmental Justice in Kazakhstan: A Vital Tool for Sustainable Development
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping Environmental Justice in Kazakhstan: A Vital Tool for Sustainable Development. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Environmental Justice in Kazakhstan: A Vital Tool for Sustainable Development
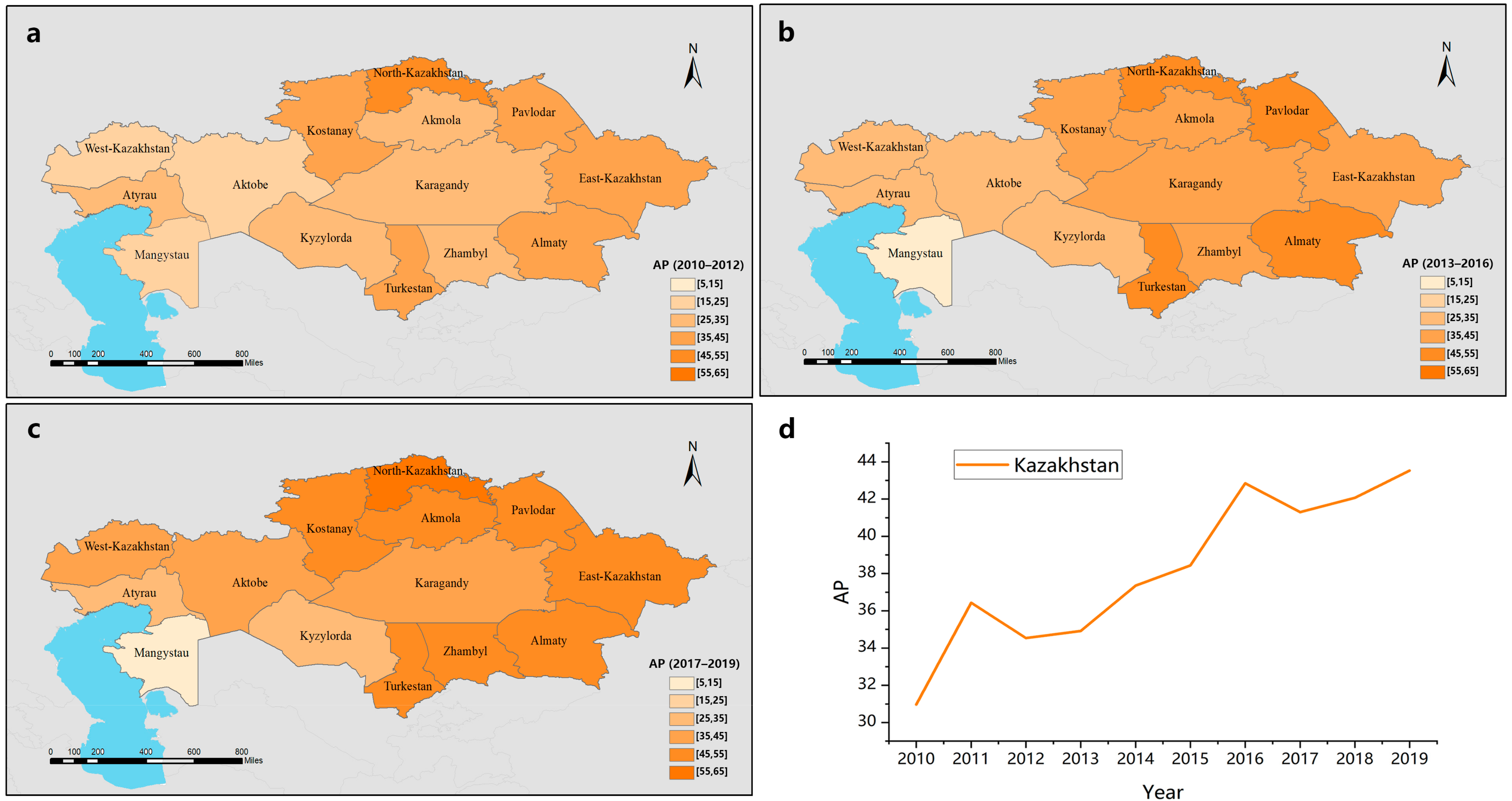
Kazakhstan, a vast nation spanning Central Asia, faces a complex tapestry of environmental challenges. From the shrinking Aral Sea to the impacts of oil and gas extraction, the country grapples with issues that disproportionately affect vulnerable communities. This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the spatial distribution of environmental burdens and benefits, which is where an Environmental Justice Map (EJM) becomes a crucial tool for equitable development.
Understanding the Concept of Environmental Justice
Environmental justice, at its core, advocates for the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people regardless of race, color, national origin, or income with respect to the development, implementation, and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations, and policies. This concept recognizes that environmental hazards and benefits are often unequally distributed, with marginalized communities frequently bearing a heavier burden of pollution and environmental degradation.
The Role of an Environmental Justice Map in Kazakhstan
An EJM for Kazakhstan would serve as a visual representation of environmental justice concerns across the country. It would provide a platform for visualizing:
- Environmental Hazards: Mapping the locations of polluting industries, hazardous waste sites, air and water pollution hotspots, and areas affected by resource extraction.
- Vulnerable Communities: Identifying areas with high concentrations of marginalized populations, such as ethnic minorities, low-income communities, and indigenous groups.
- Environmental Benefits: Mapping areas with access to clean air and water, green spaces, and natural resources.
- Policy Implementation: Visualizing the effectiveness of environmental regulations and policies in protecting vulnerable communities.
Benefits of an EJM for Kazakhstan
The development and utilization of an EJM in Kazakhstan would yield numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Awareness: The map would serve as a powerful tool for raising awareness about environmental justice issues and the unequal distribution of environmental burdens.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By providing a visual representation of environmental disparities, the EJM would empower policymakers, researchers, and activists to make informed decisions regarding environmental regulations, resource allocation, and development projects.
- Community Engagement: The map could facilitate community involvement in environmental decision-making processes, ensuring that the voices of vulnerable communities are heard.
- Improved Environmental Protection: By identifying areas where environmental risks are concentrated, the EJM would help target environmental protection efforts and resources more effectively.
- Promoting Sustainable Development: The map would contribute to a more sustainable development model that prioritizes environmental justice and equitable access to environmental benefits.
Challenges and Considerations in Developing an EJM
The creation of a comprehensive and accurate EJM for Kazakhstan presents several challenges:
- Data Availability: Access to reliable and comprehensive data on environmental hazards, vulnerable communities, and environmental benefits is crucial.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from various sources and ensuring consistency in data formats and definitions is a complex task.
- Community Engagement: Active participation and input from local communities are vital for ensuring the map accurately reflects their experiences and concerns.
- Technical Expertise: Developing and maintaining a robust and user-friendly EJM requires technical expertise in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and data analysis.
- Resource Allocation: Developing and maintaining an EJM requires financial resources and dedicated personnel.
FAQs about an Environmental Justice Map in Kazakhstan
1. What types of data would be included in an EJM for Kazakhstan?
An EJM for Kazakhstan would include data on various factors, such as:
- Environmental Hazards: Air pollution levels, water contamination, hazardous waste sites, mining operations, oil and gas extraction sites, and industrial emissions.
- Vulnerable Communities: Demographics (ethnicity, income levels, age, gender), health statistics, access to healthcare, and proximity to environmental hazards.
- Environmental Benefits: Access to clean water and air, green spaces, protected areas, and natural resources.
- Policy Implementation: Location of environmental regulations, enforcement actions, and compliance data.
2. How would an EJM be used to promote environmental justice in Kazakhstan?
An EJM could be used to:
- Identify Environmental Disparities: Highlight areas where environmental hazards are concentrated and vulnerable communities are disproportionately affected.
- Target Environmental Protection Efforts: Focus resources on areas with the greatest need for environmental protection.
- Empower Communities: Provide communities with the information they need to advocate for their environmental rights.
- Hold Polluters Accountable: Use data from the map to monitor compliance with environmental regulations and hold polluters accountable.
3. What are the potential limitations of an EJM?
While an EJM is a valuable tool, it has limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the map depends on the quality and availability of data.
- Data Bias: The map may reflect existing data biases, which can perpetuate existing inequalities.
- Interpretation: The interpretation of data presented on the map can be subjective and influenced by individual perspectives.
Tips for Developing an Effective EJM for Kazakhstan
- Collaborative Approach: Involve stakeholders from government agencies, NGOs, research institutions, and local communities in the development process.
- Data Quality: Prioritize data accuracy and ensure consistency across data sources.
- Community Engagement: Actively seek input from local communities and incorporate their perspectives into the map.
- Transparency and Accessibility: Make the map publicly accessible and provide clear explanations of the data and methodology used.
- Regular Updates: Ensure the map is regularly updated with new data to reflect changing environmental conditions and policy developments.
Conclusion
An Environmental Justice Map for Kazakhstan presents a powerful tool for fostering a more equitable and sustainable future. By visualizing the spatial distribution of environmental burdens and benefits, the EJM can raise awareness, inform decision-making, empower communities, and drive progress towards environmental justice. Implementing such a map requires a collaborative effort, robust data, and ongoing engagement with communities. By embracing the potential of this innovative approach, Kazakhstan can take a significant step towards a more just and sustainable future for all its citizens.


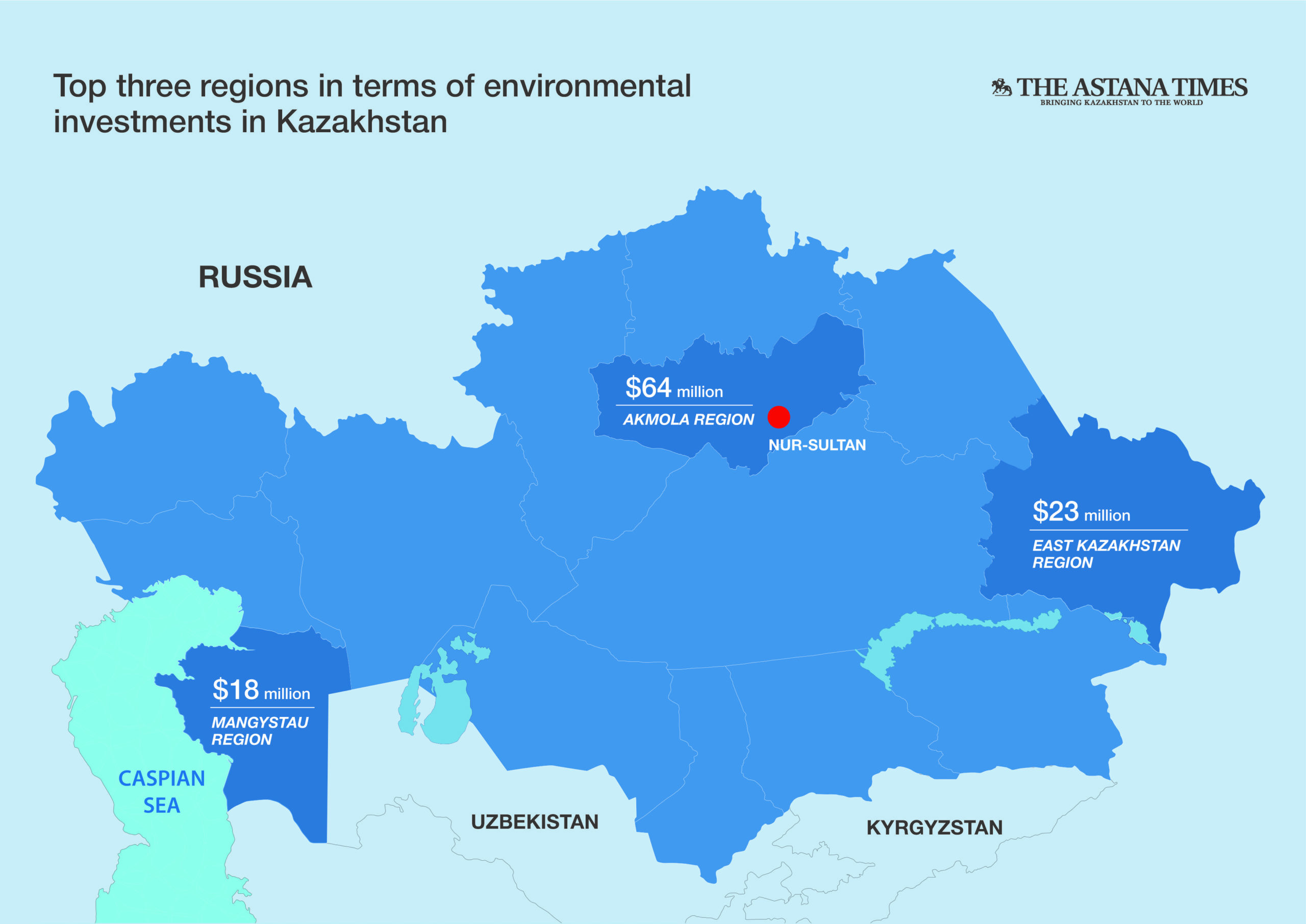
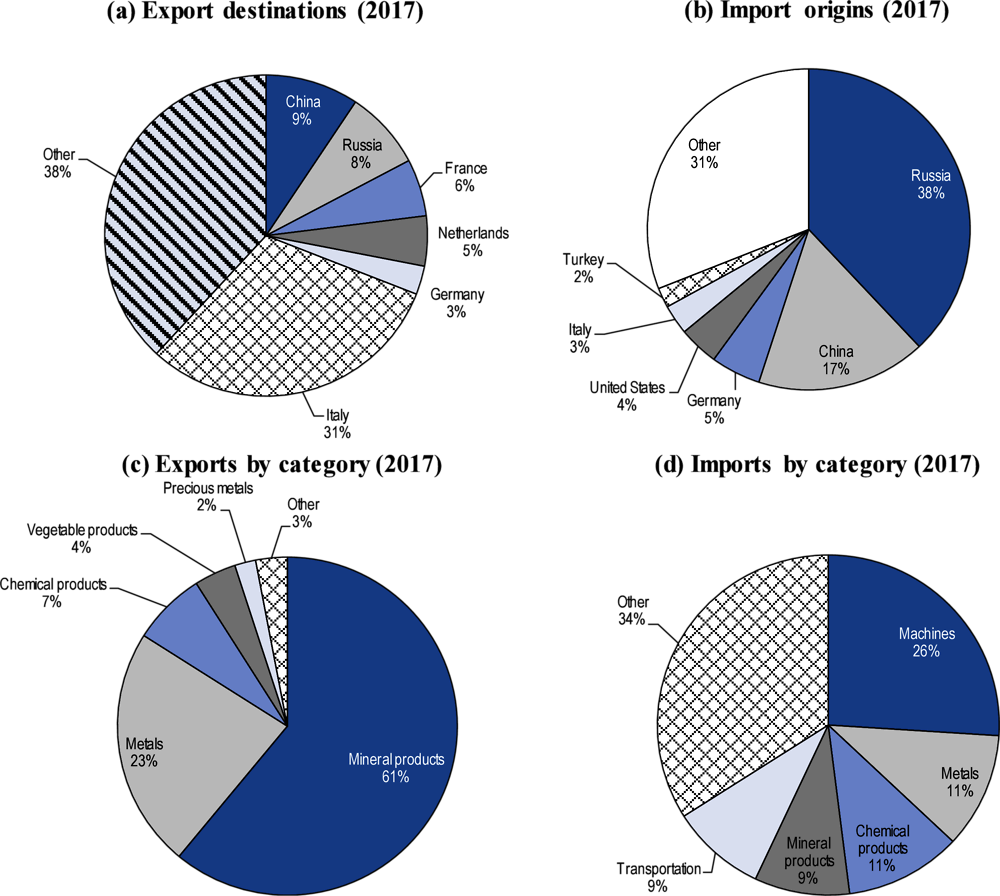

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Environmental Justice in Kazakhstan: A Vital Tool for Sustainable Development. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!