Mapping Kansas: A Comprehensive Exploration of Geographic Information Systems in the Sunflower State
Related Articles: Mapping Kansas: A Comprehensive Exploration of Geographic Information Systems in the Sunflower State
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Kansas: A Comprehensive Exploration of Geographic Information Systems in the Sunflower State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Kansas: A Comprehensive Exploration of Geographic Information Systems in the Sunflower State
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized the way we understand, analyze, and interact with our world. In Kansas, this technology has become an indispensable tool for a diverse range of stakeholders, from government agencies and researchers to businesses and individuals. This article delves into the multifaceted world of Kansas GIS, exploring its applications, benefits, and the crucial role it plays in shaping the state’s future.
Understanding the Foundation: What is GIS?
GIS is a powerful system that integrates various types of data, including maps, satellite imagery, and statistical information, to create a comprehensive understanding of geographic phenomena. This data is analyzed and visualized using specialized software, enabling users to identify patterns, relationships, and trends within geographic contexts.
The Kansas GIS Landscape: A Multifaceted Tool
In Kansas, GIS has become deeply embedded in various sectors, playing a vital role in:
1. Environmental Management and Conservation:
- Resource Management: Kansas GIS maps assist in managing water resources, identifying areas susceptible to drought, and optimizing irrigation systems. They also provide critical insights into soil health, land cover changes, and the distribution of natural resources.
- Wildlife Habitat Management: GIS helps in identifying and monitoring wildlife habitats, predicting species movements, and designing effective conservation strategies. This is particularly relevant for endangered species and migratory birds.
- Disaster Response and Mitigation: GIS plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness by mapping floodplains, identifying evacuation routes, and assessing the impact of natural disasters. It also facilitates the efficient allocation of resources during emergency situations.
2. Infrastructure Development and Planning:
- Transportation Planning: GIS enables efficient planning and management of transportation networks, analyzing traffic flow, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing routes. This includes planning for road construction, public transportation, and infrastructure maintenance.
- Urban Planning and Development: GIS is instrumental in urban planning, helping to identify suitable locations for new developments, assess the impact of proposed projects, and optimize land use. It also facilitates the creation of detailed city maps, zoning plans, and infrastructure layouts.
- Energy and Utilities: GIS aids in planning and managing energy infrastructure, including pipelines, power lines, and wind farms. It also assists in identifying optimal locations for renewable energy projects and optimizing utility network efficiency.
3. Agriculture and Food Production:
- Precision Agriculture: GIS plays a crucial role in precision agriculture, enabling farmers to create detailed maps of their fields, identify areas with varying soil conditions, and optimize fertilizer and pesticide application. This results in increased crop yields and reduced environmental impact.
- Farm Management: GIS assists farmers in managing their land, tracking crop rotations, and monitoring livestock movement. It also helps in identifying areas suitable for different crops and optimizing farm operations.
- Food Safety and Traceability: GIS can be used to track the origin and movement of food products, ensuring safety and transparency throughout the supply chain.
4. Public Health and Safety:
- Disease Surveillance and Prevention: GIS helps in mapping disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk areas, and developing effective public health interventions. It also assists in tracking the spread of infectious diseases and implementing targeted prevention strategies.
- Emergency Response: GIS is essential for coordinating emergency response efforts, mapping evacuation routes, and allocating resources during natural disasters, accidents, and public health emergencies.
- Community Health Assessment: GIS allows for the creation of detailed maps that highlight health disparities, identifying areas with high rates of chronic diseases and implementing targeted community health programs.
5. Education and Research:
- Geographic Education: GIS provides a valuable tool for teaching geography and spatial analysis in classrooms, allowing students to explore geographic data, create maps, and conduct spatial research.
- Scientific Research: GIS is widely used in scientific research, enabling researchers to analyze spatial data, identify patterns, and develop new insights into a wide range of topics, including climate change, biodiversity, and population dynamics.
- Historical Research: GIS assists historians in mapping historical events, tracing population movements, and understanding the spatial dimensions of past societies.
Benefits of GIS in Kansas:
The adoption of GIS in Kansas has yielded numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Decision-Making: GIS provides comprehensive spatial data and analysis tools, enabling informed and data-driven decisions across various sectors.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: GIS streamlines processes, automates tasks, and optimizes resource allocation, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: GIS enables the sharing of spatial data and information, fostering transparency and accountability within government agencies and other organizations.
- Better Communication and Collaboration: GIS facilitates the sharing of spatial data and information among stakeholders, fostering collaboration and communication.
- Cost Savings: GIS can help reduce costs by optimizing resource allocation, improving efficiency, and reducing the need for costly physical surveys.
- Improved Public Safety and Health: GIS contributes to improved public safety and health by enabling efficient emergency response, disease surveillance, and targeted public health interventions.
- Sustainable Development: GIS plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable development by enabling informed land use planning, resource management, and environmental monitoring.
FAQs about Kansas GIS:
1. Where can I access Kansas GIS data?
The Kansas Geographic Information System (KGIS) website, maintained by the Kansas Department of Transportation, provides access to a wide range of spatial data, including maps, imagery, and geographic datasets. Other sources include the Kansas Geological Survey, the Kansas Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism, and various county and municipal websites.
2. What are the different types of GIS software used in Kansas?
Popular GIS software packages used in Kansas include ArcGIS (ESRI), QGIS (open-source), and MapInfo (Pitney Bowes). The choice of software depends on the specific needs and budget of the user.
3. How can I learn more about GIS in Kansas?
Several institutions offer GIS training and education programs in Kansas. These include universities, community colleges, and professional organizations like the Kansas Geographic Alliance and the Kansas Chapter of the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing.
4. What are the future trends in Kansas GIS?
Future trends in Kansas GIS include the integration of cloud computing, mobile GIS, and artificial intelligence (AI). These advancements will enable more powerful data analysis, improved accessibility, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Tips for Using GIS in Kansas:
- Identify your specific needs: Clearly define the objectives and goals of your GIS project to ensure that you choose the right tools and data.
- Access and understand available data: Explore available data sources, including government agencies, research institutions, and private companies.
- Choose appropriate software: Select GIS software that meets your specific needs and budget.
- Develop GIS skills: Invest in training and education to enhance your understanding of GIS concepts and techniques.
- Collaborate with other users: Network with other GIS professionals and organizations to share knowledge and best practices.
Conclusion:
The use of GIS in Kansas is expanding rapidly, transforming the way we manage resources, plan infrastructure, and address critical societal challenges. From promoting sustainable agriculture to improving public health and safety, GIS empowers stakeholders with the tools and insights needed to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and build a more resilient and prosperous future for the Sunflower State. As technology continues to evolve, GIS will play an increasingly important role in shaping Kansas’s landscape and ensuring its continued success.


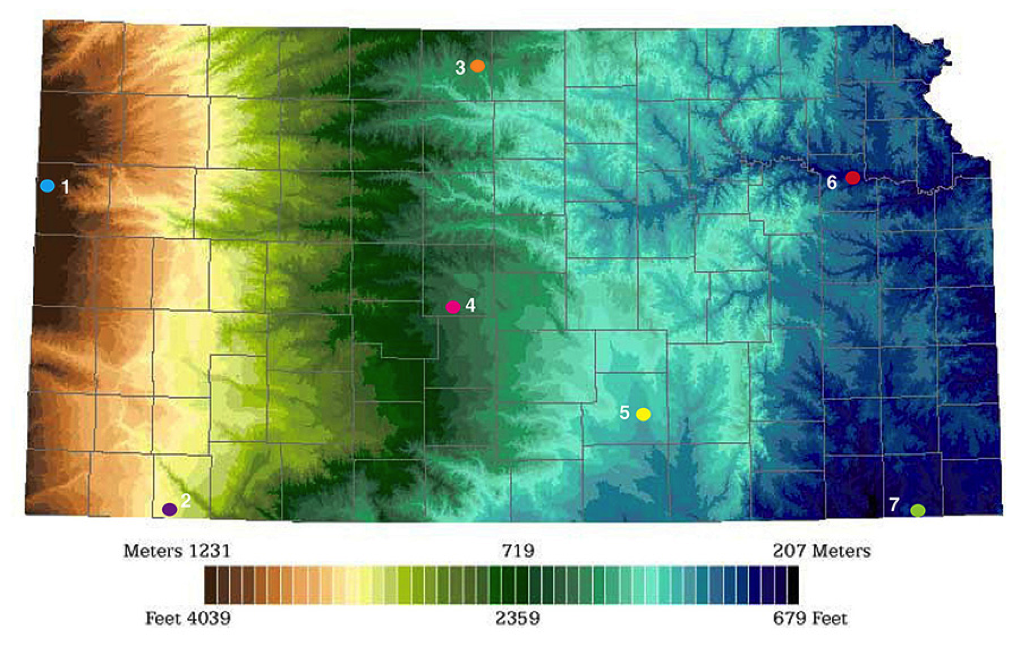
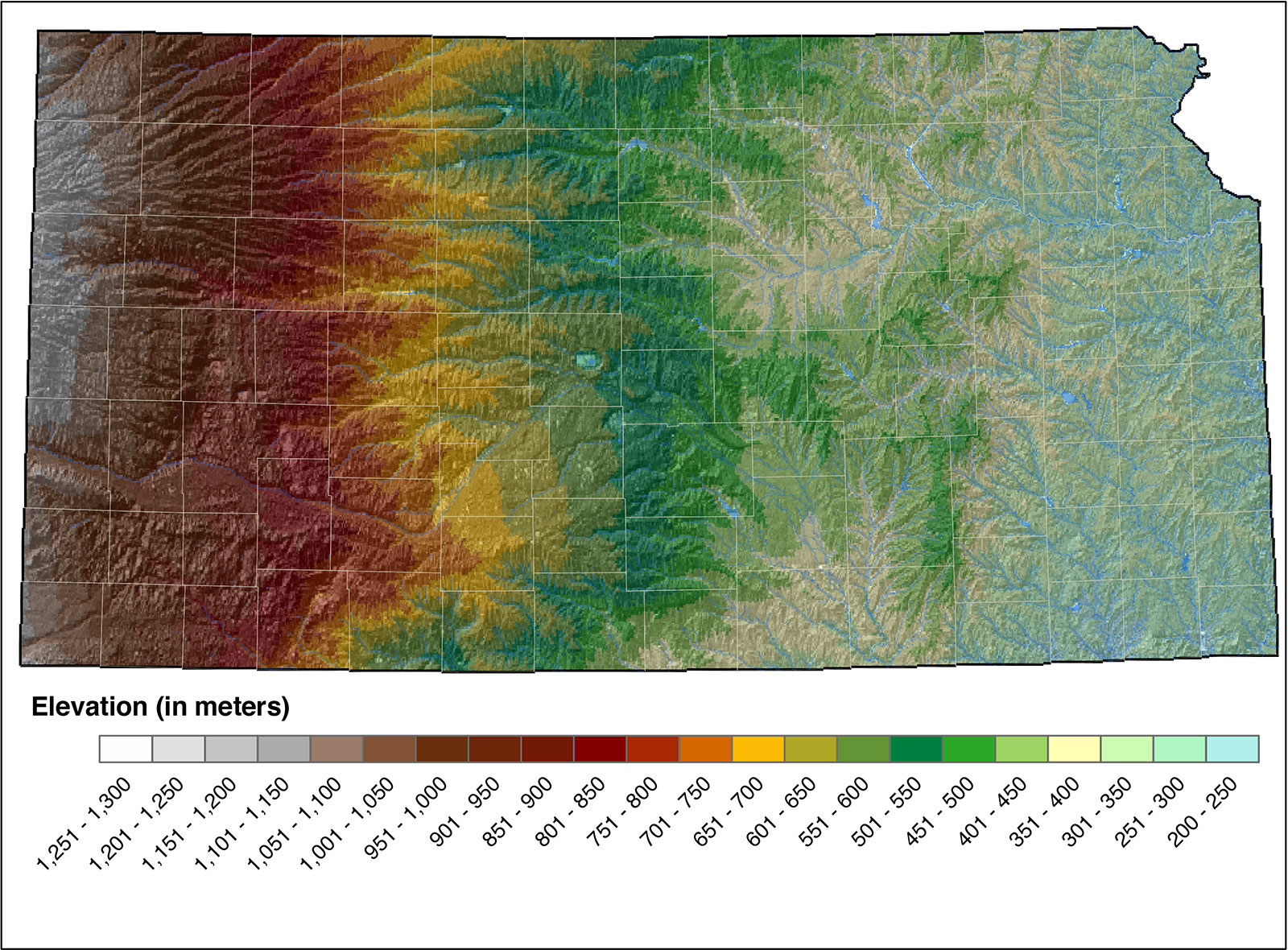

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Kansas: A Comprehensive Exploration of Geographic Information Systems in the Sunflower State. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!