Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values
Related Articles: Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values
- 3.1 Understanding the Foundation: Keys and Values
- 3.2 The Power of Associative Arrays: A Deeper Dive
- 3.3 Implementation and Usage: Bringing Maps to Life
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Essential Operations and Features
- 3.5 Real-World Applications: Unlocking the Power of Maps
- 3.6 FAQ: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Map Utilization
- 3.8 Conclusion: Mastering the Power of Key-Value Pairs
- 4 Closure
Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values
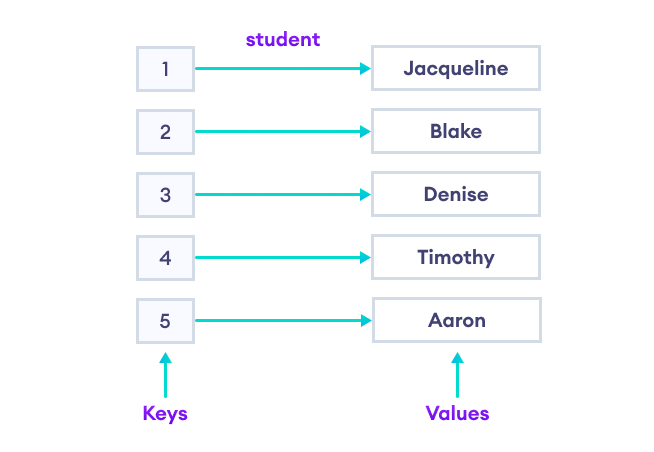
In the world of programming, efficient data organization is paramount. C++ offers a powerful tool for this purpose: the map container. Maps provide a structured way to store and retrieve data, enabling developers to access specific information quickly and easily. This article delves into the core concepts of map key-value pairs, exploring their functionality, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding the Foundation: Keys and Values
At its essence, a map in C++ is a collection of key-value pairs. Each pair comprises two elements:
- Key: A unique identifier that acts as a reference point for accessing the associated value. Keys are typically of a specific data type, ensuring efficient retrieval.
- Value: The data associated with the key. Values can be of any data type, allowing for flexible storage of diverse information.
The key-value pairing system allows for direct access to values based on their corresponding keys, making maps highly efficient for searching and retrieval operations.
The Power of Associative Arrays: A Deeper Dive
Maps in C++ are essentially associative arrays. Unlike traditional arrays, where elements are accessed by their index, maps leverage keys for accessing values. This association between keys and values grants maps several advantages:
-
Dynamic Size: Unlike arrays with a fixed size,
mapscan dynamically grow or shrink as needed, accommodating variable data amounts. -
Unique Keys: Each key within a
mapmust be unique, ensuring that every value is associated with a distinct identifier. This uniqueness guarantees efficient data access. -
Ordered Retrieval:
Mapsin C++ maintain their elements in a sorted order based on their keys. This ordering allows for predictable iteration and retrieval of data.
Implementation and Usage: Bringing Maps to Life
C++ offers the std::map container, a standard library implementation of associative arrays. To utilize maps, developers must include the map header file:
#include <map>Here’s a simple example demonstrating the creation and usage of a map to store student names and their corresponding grades:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
int main()
// Create a map to store student names and grades
std::map<std::string, int> studentGrades;
// Insert key-value pairs into the map
studentGrades["Alice"] = 90;
studentGrades["Bob"] = 85;
studentGrades["Charlie"] = 95;
// Access and print the grade for a specific student
std::cout << "Alice's grade: " << studentGrades["Alice"] << std::endl;
return 0;
This code snippet showcases the fundamental operations of maps:
-
Creation: A
mapis declared with the desired key and value data types. -
Insertion: Key-value pairs are added to the
mapusing the[]operator. -
Retrieval: Values are accessed based on their corresponding keys using the
[]operator.
Beyond the Basics: Essential Operations and Features
The std::map container offers a rich set of operations and functionalities for managing key-value pairs:
-
insert(): Adds a new key-value pair to themap. -
erase(): Removes a specific key-value pair from themap. -
find(): Searches for a specific key and returns an iterator to its corresponding value. -
count(): Determines if a specific key exists within themap. -
empty(): Checks if themapis empty. -
size(): Returns the number of key-value pairs in themap. -
begin()andend(): Return iterators to the first and last elements of themap, respectively.
These operations provide developers with comprehensive control over map data, enabling efficient manipulation and retrieval of information.
Real-World Applications: Unlocking the Power of Maps
Maps in C++ find widespread application across diverse programming domains, including:
-
Data Management:
Mapsexcel in storing and managing data, such as user profiles, inventory details, and configuration settings. Their efficient retrieval capabilities make them ideal for lookup operations. -
Dictionaries and Translation:
Mapscan represent dictionaries or translation tables, associating words or phrases with their corresponding translations or definitions. -
Game Development:
Mapscan store game objects and their attributes, facilitating efficient access to information about entities within the game world. -
Network Programming:
Mapscan be used to store network connections and associated data, enabling efficient communication management. -
Database Interactions:
Mapscan be used to represent data retrieved from databases, providing a structured representation for processing and manipulation.
These are just a few examples of the numerous applications where maps demonstrate their versatility and efficiency in handling data.
FAQ: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can keys in a map be of different data types?
A: No, all keys in a map must be of the same data type. This ensures consistent and efficient data retrieval based on key comparisons.
Q: What happens if I try to insert a duplicate key into a map?
A: If a duplicate key is inserted, the existing value associated with that key will be overwritten by the new value.
Q: Are maps sorted based on keys by default?
A: Yes, std::map maintains its elements in a sorted order based on their keys. This ordering allows for predictable iteration and retrieval of data.
Q: How can I iterate through all the elements of a map?
A: You can iterate through a map using iterators provided by begin() and end(). These iterators allow you to access each key-value pair in the sorted order of the map.
Q: What are the differences between std::map and std::unordered_map?
A: While both are associative containers, std::map maintains elements in a sorted order based on their keys, while std::unordered_map does not. This difference impacts the efficiency of insertion, retrieval, and iteration operations. std::unordered_map is generally faster for these operations, but it does not guarantee a specific order for its elements.
Tips for Effective Map Utilization
- Choose the Right Data Types: Select appropriate data types for keys and values based on the nature of your data.
-
Use Iterators for Efficient Access: Utilize iterators to efficiently traverse and access elements within a
map. -
Consider
std::unordered_mapfor Performance: If order is not crucial,std::unordered_mapcan offer better performance for insertion, retrieval, and deletion operations. -
Utilize the
find()Operation for Efficient Lookup: Leverage thefind()operation to efficiently search for specific keys within amap. - Avoid Unnecessary Operations: Optimize code by avoiding redundant insertions or deletions, minimizing the overhead associated with these operations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Power of Key-Value Pairs
Maps in C++ offer a powerful and versatile tool for managing and accessing data. Their key-value pairing system enables efficient retrieval, while their dynamic nature allows for flexibility in handling variable data volumes. Understanding the fundamentals of maps, their operations, and their applications empowers developers to build robust and efficient data-driven solutions. By leveraging the capabilities of maps, programmers can create applications that efficiently store, retrieve, and manipulate information, enhancing the overall functionality and performance of their programs.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Data with C++ Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Keys and Values. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!