Navigating the Landscape: Exploring Free Alternatives to Nearmap for Aerial Imagery
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Exploring Free Alternatives to Nearmap for Aerial Imagery
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Exploring Free Alternatives to Nearmap for Aerial Imagery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Exploring Free Alternatives to Nearmap for Aerial Imagery

Nearmap, a leading provider of high-resolution aerial imagery and 3D models, has become an invaluable tool for various sectors, including construction, real estate, and insurance. However, the cost associated with Nearmap’s services can be a significant barrier for some users, particularly those seeking occasional access or working with limited budgets. Fortunately, a range of free and affordable alternatives exist, offering comparable functionalities for specific use cases.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these alternatives, exploring their strengths, limitations, and suitability for different needs. By understanding the diverse landscape of free aerial imagery resources, users can make informed decisions and select the most appropriate solution for their requirements.
Understanding the Need for Free Alternatives
The demand for free alternatives to Nearmap stems from the growing accessibility and affordability of aerial imagery technology. Advancements in drone technology, satellite imaging, and open-source data platforms have democratized access to high-resolution imagery, empowering individuals and organizations with limited resources to leverage this powerful tool.
Key Considerations for Selecting an Alternative
Before exploring specific alternatives, it is crucial to define the specific requirements and use cases for aerial imagery. Several factors influence the selection process, including:
- Spatial Resolution: The level of detail required for the imagery. Higher resolution imagery is ideal for detailed analysis, while lower resolution imagery may suffice for broader overview purposes.
- Temporal Resolution: The frequency of image updates. Some platforms offer frequent updates, while others provide historical archives.
- Coverage Area: The geographic extent of the required imagery. Some platforms offer global coverage, while others focus on specific regions.
- Data Format: The desired format for the imagery, such as GeoTIFF, JPEG, or KML.
- Data Access: The ease of accessing and downloading the imagery. Some platforms offer seamless online access, while others may require specific software or tools.
- Licensing and Usage Rights: The permitted use of the imagery, including commercial and non-commercial applications.
A Comprehensive Overview of Free Alternatives
1. Open-Source Platforms:
- USGS EarthExplorer: This platform offers a vast repository of freely accessible satellite imagery from various sensors, including Landsat, Sentinel, and MODIS. It provides a user-friendly interface for searching, downloading, and visualizing imagery. However, the spatial resolution of the imagery can be limited, and the data may not be updated frequently.
- Planet Labs Explore: Planet Labs provides a free tier that offers access to a limited selection of their high-resolution satellite imagery. While the free tier offers a good starting point, it has restrictions on the amount of data and the frequency of updates.
- Sentinel Hub: This platform offers free access to Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data, providing high-resolution imagery with frequent updates. It also includes tools for data processing and analysis, making it suitable for various applications.
2. Government Agencies and Institutions:
- National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA): NGA provides access to a wide range of geospatial data, including aerial imagery, through its Geospatial Information Access (GIA) portal. The data is typically high-resolution and updated frequently, making it a valuable resource for various applications.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): NASA’s Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) offers a vast collection of satellite imagery and data, including images from Landsat, MODIS, and other sensors. The data is freely accessible and can be used for research, education, and commercial purposes.
- European Space Agency (ESA): ESA provides access to a range of satellite imagery and data, including Sentinel data, through its Earth Observation Portal. The data is freely accessible and can be used for various applications.
3. Commercial Platforms with Free Trials:
- Google Earth Pro: Google Earth Pro offers a free trial period that allows users to access high-resolution imagery, 3D models, and historical data. While the trial period is limited, it provides a valuable opportunity to explore the platform’s capabilities.
- Bing Maps: Bing Maps offers a free tier that provides access to aerial imagery and 3D models. While the resolution and coverage may not be as extensive as other platforms, it offers a convenient option for basic mapping needs.
4. Specialized Platforms:
- DroneDeploy: DroneDeploy offers a free plan that allows users to process and analyze aerial imagery captured using drones. While the free plan has limitations on the amount of data and features, it provides a good starting point for users exploring drone-based aerial imagery.
- Pix4Dmapper: Pix4Dmapper offers a free trial that allows users to process and analyze aerial imagery captured using drones or cameras. The trial period provides access to the platform’s advanced features, including 3D modeling and orthomosaic creation.
5. Online Image Repositories:
- Wikimedia Commons: Wikimedia Commons hosts a vast collection of freely licensed images, including aerial photographs and satellite imagery. The collection is diverse and covers various geographic locations and time periods.
- Flickr: Flickr offers a vast collection of user-uploaded images, including aerial photographs and satellite imagery. While the quality and licensing of images can vary, it offers a valuable resource for finding specific imagery.
FAQs by Nearmap Free Alternative
Q: What are the key advantages of using free alternatives to Nearmap?
A: Free alternatives offer several advantages, including:
- Cost-Effectiveness: They eliminate the subscription fees associated with Nearmap, making aerial imagery accessible to users with limited budgets.
- Flexibility: They provide access to a diverse range of data sources, allowing users to select the most appropriate imagery for their specific needs.
- Open Access: Many platforms offer open access to their data, promoting collaboration and innovation in various fields.
Q: What are the limitations of using free alternatives to Nearmap?
A: Free alternatives also have certain limitations, including:
- Data Quality: The quality of the imagery can vary significantly depending on the source and the data acquisition techniques.
- Data Availability: The availability of imagery may be limited by factors such as geographic coverage, temporal resolution, and data licensing restrictions.
- Data Processing: Some platforms require specialized software or tools for data processing and analysis, which may not be readily available to all users.
Q: How do I choose the best free alternative for my specific needs?
A: The best free alternative depends on the specific requirements of your project. Consider the following factors:
- Spatial resolution: The level of detail required for the imagery.
- Temporal resolution: The frequency of image updates.
- Coverage area: The geographic extent of the required imagery.
- Data format: The desired format for the imagery.
- Data access: The ease of accessing and downloading the imagery.
- Licensing and usage rights: The permitted use of the imagery.
Tips by Nearmap Free Alternative
- Explore multiple platforms: Utilize the free trial periods offered by various platforms to evaluate their capabilities and suitability for your needs.
- Leverage open-source tools: Utilize open-source software and tools for data processing and analysis to enhance your workflow and reduce costs.
- Understand licensing restrictions: Carefully review the licensing terms and conditions of each platform before using the imagery for any purpose.
Conclusion by Nearmap Free Alternative
The availability of free and affordable alternatives to Nearmap has significantly democratized access to aerial imagery, empowering individuals and organizations with limited resources to leverage this powerful tool. By carefully considering the specific requirements of your project and exploring the diverse range of alternatives, you can find the most suitable solution for your needs and unlock the potential of aerial imagery for various applications.
Remember, the best approach is to experiment with different platforms, compare their capabilities, and choose the option that best aligns with your specific requirements, budget, and desired outcomes. By embracing the vast world of free alternatives, you can navigate the landscape of aerial imagery and unlock its power for your projects.
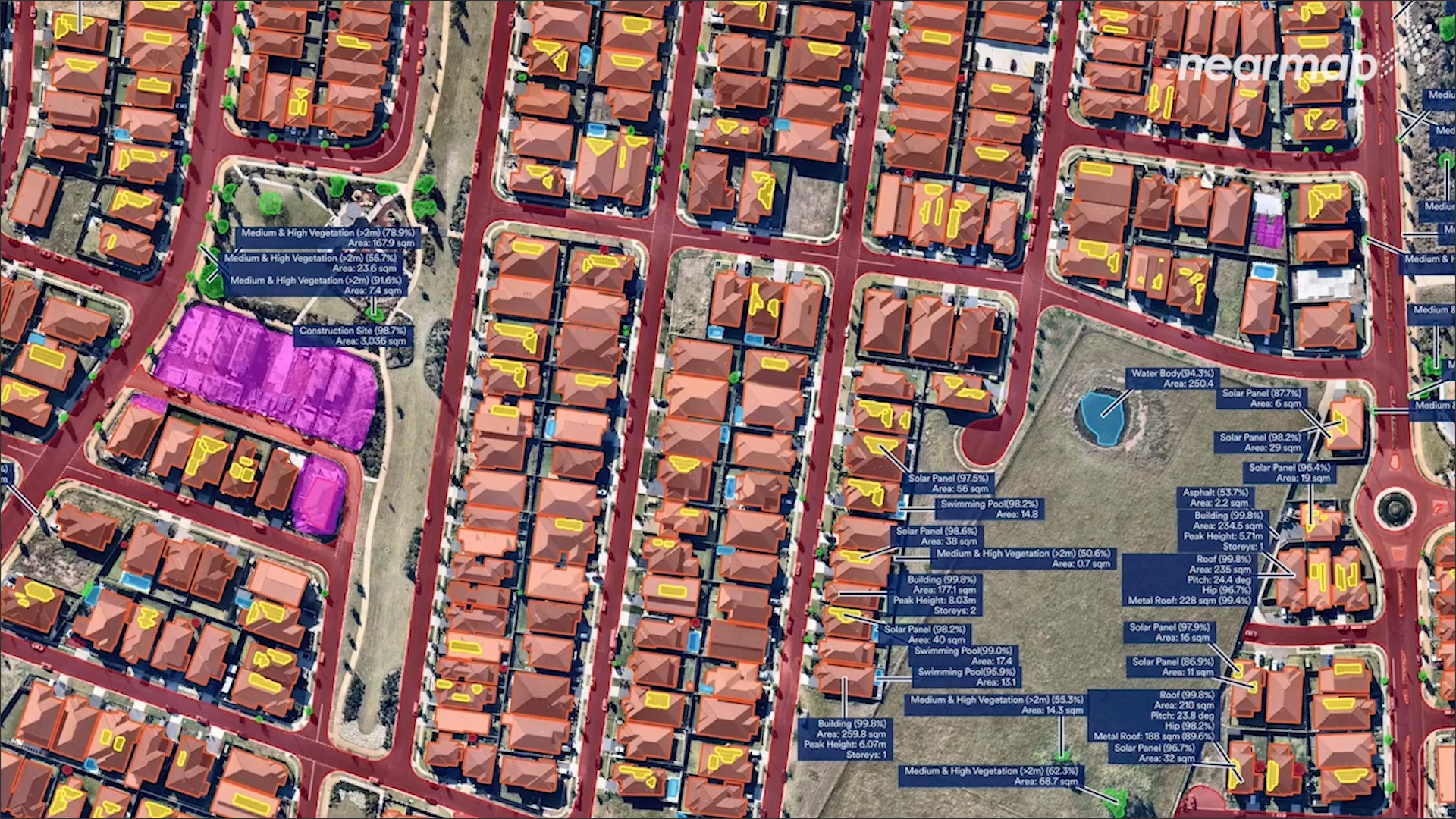







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Exploring Free Alternatives to Nearmap for Aerial Imagery. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!