Navigating the Landscape of South Korea: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of South Korea: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of South Korea: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of South Korea: A Comprehensive Exploration

South Korea, a vibrant nation nestled on the Korean Peninsula, boasts a diverse geography that has shaped its history, culture, and development. Understanding the country’s physical landscape is crucial for appreciating its unique character and appreciating the interconnectedness of its various regions. This exploration delves into the key geographical features of South Korea, analyzing their influence on the nation’s socio-economic landscape and providing insights into the intricate relationship between its natural environment and human activity.
A Tapestry of Mountains and Coastlines:
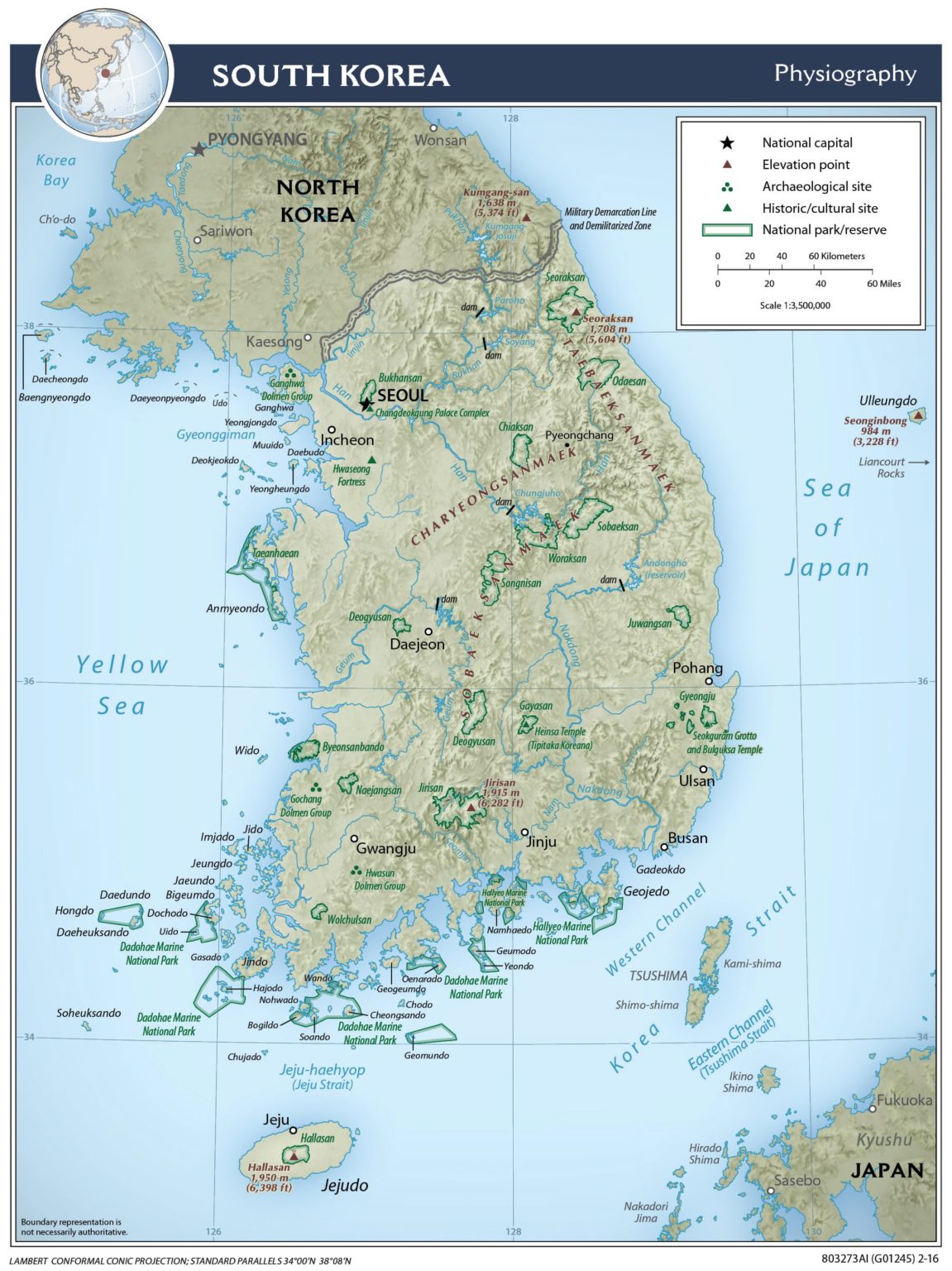
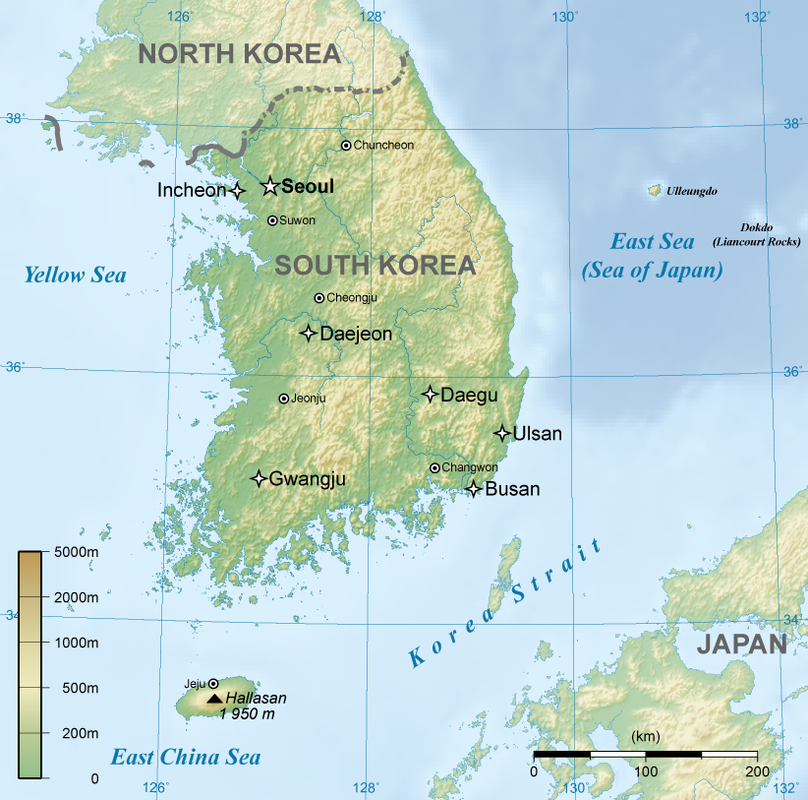
South Korea’s topography is dominated by mountains, with over 70% of its landmass covered by hills and peaks. The Taebaek Mountains, a significant mountain range stretching across the peninsula, are a defining feature, influencing the flow of rivers and the distribution of rainfall. The mountainous terrain has historically played a crucial role in shaping Korean culture, influencing traditional settlements, transportation routes, and agricultural practices.
The coastline, encompassing over 2,400 kilometers, is another prominent feature. The Yellow Sea and the East Sea (Sea of Japan) border the western and eastern coasts, respectively, offering diverse coastal environments ranging from sandy beaches to rocky cliffs. These coastlines have been instrumental in South Korea’s economic development, supporting a thriving fishing industry and facilitating international trade.
Navigating the River Systems:
The nation’s network of rivers, originating from the Taebaek Mountains, plays a vital role in its water resources and transportation infrastructure. The Han River, flowing through Seoul, is the longest and most significant river in South Korea, serving as a critical source of water for the capital city and its surrounding areas. Other major rivers, including the Nakdong, Geum, and Yeongsan rivers, contribute significantly to irrigation, hydropower generation, and transportation.
Distinct Regional Variations:
South Korea’s diverse topography gives rise to distinct regional variations in climate, resources, and economic activities. The northern regions, characterized by mountainous terrain and colder temperatures, are primarily focused on forestry and agriculture. The central region, dominated by the Han River basin, is the most densely populated and economically active area, housing major cities like Seoul and its surrounding metropolitan areas. The southern region, with its warmer climate and coastal plains, is known for its agricultural production, particularly rice cultivation and fruit farming.
The Impact of Geography on Development:
South Korea’s geography has significantly influenced its development trajectory. The mountainous terrain, while challenging for transportation and infrastructure development, has provided ample natural resources, including forests, minerals, and hydroelectric potential. The coastline has facilitated trade and economic growth, while the river systems have served as vital transportation routes and sources of water for agriculture and industry.
However, the mountainous terrain has also posed challenges, particularly in terms of accessibility and land availability for urban development. The country’s vulnerability to natural disasters, such as typhoons and landslides, is also influenced by its geography.
Understanding the Interplay of Nature and Culture:
South Korea’s geography has deeply intertwined with its culture, shaping its traditions, art, and lifestyle. The mountainous terrain has fostered a sense of isolation and community, while the coastal regions have influenced culinary traditions and recreational activities. The country’s artistic expressions, from traditional landscape paintings to contemporary photography, often reflect the beauty and grandeur of its natural environment.
Exploring the Geographic Significance of Key Cities:
Seoul: The capital city of South Korea, situated in the Han River basin, is the country’s economic and cultural hub. Its strategic location, surrounded by mountains and accessible by river, has made it a focal point of Korean history and development.
Busan: Located on the southeastern coast, Busan is South Korea’s second-largest city and a major port city. Its coastal location has played a significant role in its economic success, making it a center for shipping, fishing, and manufacturing.
Gyeongju: Located in the southeastern region, Gyeongju is a historic city renowned for its ancient Silla Kingdom ruins. Its location in a fertile valley, surrounded by mountains, contributed to its prosperity during the Silla period.
Jeju Island: A volcanic island off the southern coast, Jeju Island is known for its unique natural beauty and diverse ecosystem. Its volcanic origins and subtropical climate have made it a popular tourist destination.
The Importance of Geographic Literacy:
Understanding South Korea’s geography is essential for appreciating its cultural diversity, economic development, and historical significance. It allows for a deeper understanding of the country’s strengths and challenges, informing policies and initiatives aimed at sustainable development and resource management.
FAQs on the Geography of South Korea:
1. What is the highest mountain in South Korea?
The highest mountain in South Korea is Mount Hallasan, located on Jeju Island, with an elevation of 1,950 meters.
2. What are the major rivers in South Korea?
The major rivers in South Korea include the Han River, Nakdong River, Geum River, and Yeongsan River.
3. What is the climate like in South Korea?
South Korea experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The northern regions experience colder winters and shorter summers, while the southern regions have milder winters and longer summers.
4. What are the major natural resources found in South Korea?
South Korea’s natural resources include forests, minerals, and hydroelectric potential.
5. How does South Korea’s geography influence its agricultural production?
South Korea’s mountainous terrain limits arable land, but the country’s diverse climate and river systems support a variety of agricultural activities, including rice cultivation, fruit farming, and livestock raising.
Tips for Exploring the Geography of South Korea:
1. Visit National Parks: South Korea boasts numerous national parks, offering opportunities to experience its diverse landscapes, from mountains and forests to coastlines and wetlands.
2. Explore Coastal Regions: Visit coastal cities like Busan and Jeju Island to experience the beauty of South Korea’s coastlines and learn about its fishing industry and maritime traditions.
3. Hike in the Mountains: Embark on hiking trails in the Taebaek Mountains to appreciate the grandeur of South Korea’s mountainous terrain and enjoy breathtaking views.
4. Discover Traditional Villages: Visit traditional Korean villages, often located in mountainous areas, to gain insights into the relationship between geography and traditional Korean architecture and lifestyle.
5. Learn about the Impact of Geography on Development: Visit museums and cultural centers to learn about the historical and contemporary influence of geography on South Korea’s economic development and cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
South Korea’s geography, a tapestry of mountains, coastlines, rivers, and diverse regional variations, has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and development. From the mountainous terrain that has influenced traditional settlements and transportation routes to the coastlines that have facilitated trade and economic growth, the country’s physical landscape has played a crucial role in shaping its identity. Understanding the interplay of nature and culture in South Korea provides valuable insights into its unique character and the interconnectedness of its various regions, fostering a deeper appreciation for this vibrant and dynamic nation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of South Korea: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!