Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Choosing the Best Compass for Map Reading
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Choosing the Best Compass for Map Reading
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Choosing the Best Compass for Map Reading. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Choosing the Best Compass for Map Reading

In the realm of outdoor exploration, navigation is paramount. Whether you’re traversing rugged mountains, navigating dense forests, or simply exploring a new trail, a reliable compass is an indispensable tool. It provides a constant connection to true north, enabling you to pinpoint your position on a map and confidently plan your route. But with an array of compasses available, choosing the right one can be daunting. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of compasses, their functionalities, and essential factors to consider when selecting the best compass for your map reading needs.
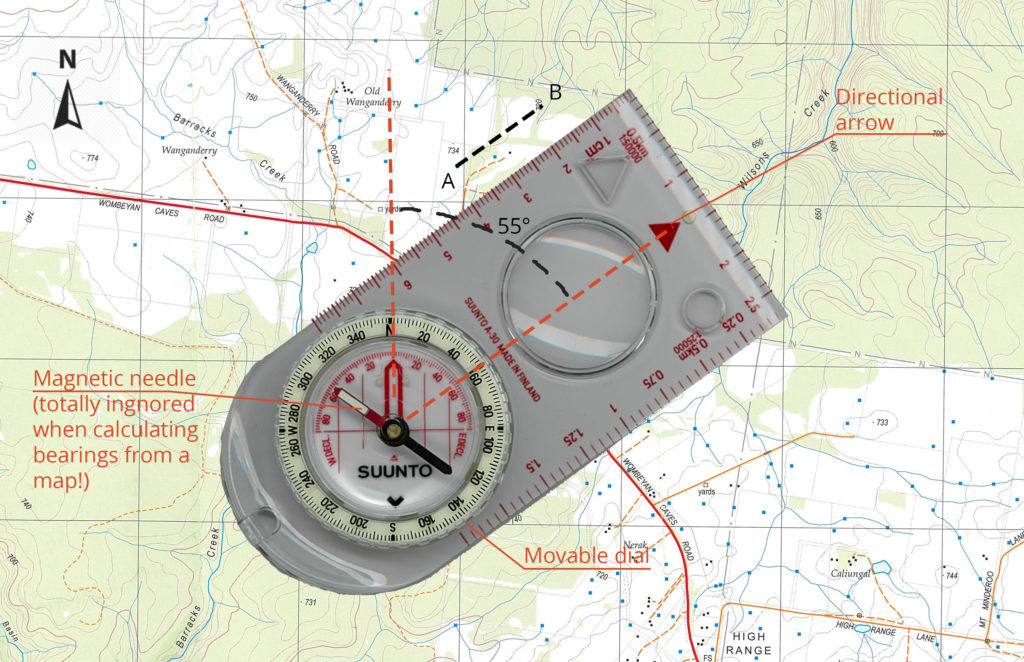
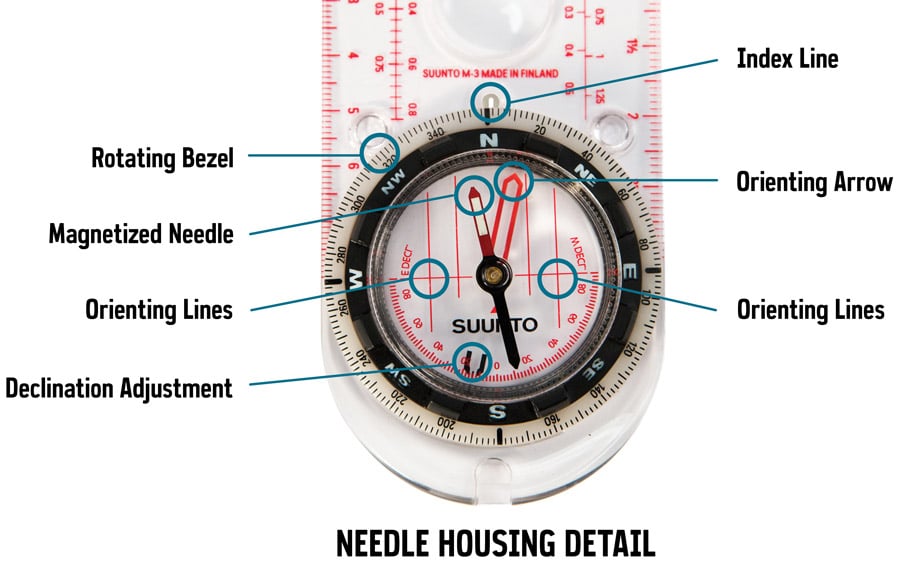
Understanding the Basics: Compass Components and Functionality
At its core, a compass utilizes the Earth’s magnetic field to indicate the direction of magnetic north. This principle is embodied in its fundamental components:
- Compass Needle: The heart of the compass, a magnetized needle that freely rotates to align with the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Compass Housing: A protective casing that houses the needle, often made of durable materials like metal or plastic.
- Compass Baseplate: A flat surface with markings that allow for accurate readings and alignment with maps.
- Compass Sight: A small, movable piece that helps align the compass with a specific landmark or direction.
- Compass Dial: A circular scale with markings that indicate degrees of azimuth, allowing for precise navigation.
Types of Compasses: Navigating the Options
Compasses come in various forms, each designed for specific purposes and levels of precision. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the ideal compass for your needs:
1. Baseplate Compasses:
- Description: These are the most common type of compass, featuring a baseplate for aligning with maps and a rotating bezel for taking bearings.
- Functionality: Baseplate compasses are versatile and suitable for a wide range of activities, from hiking and backpacking to orienteering and general navigation.
- Advantages: Simple design, easy to use, relatively affordable.
- Disadvantages: Can be less precise than other types, particularly in challenging conditions.
2. Lensatic Compasses:
- Description: These compasses feature a built-in magnifying lens that allows for precise readings and accurate alignment with maps.
- Functionality: Lensatic compasses are ideal for precise navigation and demanding situations, often used by military personnel and experienced outdoor enthusiasts.
- Advantages: Enhanced accuracy, magnified readings, durable construction.
- Disadvantages: More expensive than baseplate compasses, can be slightly more complex to use.
3. Wrist Compasses:
- Description: These compasses are designed to be worn on the wrist, providing quick and convenient access to bearings.
- Functionality: Wrist compasses are primarily used for casual navigation and general orientation, offering a convenient alternative to traditional compasses.
- Advantages: Compact size, easy to wear, affordable.
- Disadvantages: Limited accuracy, not suitable for precise navigation.
4. Digital Compasses:
- Description: These compasses integrate electronic sensors to provide digital readings of direction and elevation.
- Functionality: Digital compasses offer advanced features like GPS integration, electronic bearing calculations, and altitude readings.
- Advantages: High accuracy, advanced features, user-friendly interface.
- Disadvantages: Can be more expensive, require batteries, may be less durable than traditional compasses.
Choosing the Right Compass: Essential Factors to Consider
Selecting the best compass involves considering several factors:
1. Accuracy and Precision:
- Accuracy: Refers to the compass’s ability to accurately indicate magnetic north.
- Precision: Relates to the compass’s ability to provide precise readings for bearings and azimuths.
- Considerations: The accuracy and precision of a compass are crucial for reliable navigation, particularly in challenging terrain or low-visibility conditions.
2. Durability and Construction:
- Material: The materials used in the compass’s construction, such as metal or plastic, influence its durability and resistance to wear and tear.
- Waterproof/Water-resistant: This feature is essential for navigating in wet conditions or environments where water exposure is likely.
- Considerations: Choose a compass that can withstand the rigors of your intended use, ensuring it remains functional and reliable in demanding situations.
3. Ease of Use and Functionality:
- User Interface: The compass’s design and layout should be intuitive and user-friendly, facilitating easy and accurate readings.
- Features: Consider features like a magnifying lens, adjustable declination settings, or a built-in mirror, which can enhance navigation capabilities.
- Considerations: Choose a compass that matches your experience level and the complexity of the navigation tasks you anticipate.
4. Size and Weight:
- Compactness: A smaller, lighter compass can be more convenient for carrying, especially on long hikes or backpacking trips.
- Size and Weight Considerations: Balance the need for portability with the size and weight that ensures comfortable use and reliable functionality.
5. Price and Value:
- Price Range: Compasses range in price from affordable options to high-end models with advanced features.
- Value Considerations: Determine your budget and prioritize features that provide the best value for your needs and anticipated use.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Compasses
1. What is declination, and why is it important?
Declination is the angular difference between true north and magnetic north. It varies geographically and over time. Adjusting for declination ensures accurate navigation by aligning the compass with the local magnetic field.
2. How do I calibrate my compass?
Compass calibration involves aligning the compass needle with a known magnetic north reference point. This ensures the compass is functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
3. How do I use a compass to navigate?
Navigating with a compass involves taking bearings, which are measurements of direction relative to magnetic north. These bearings can be used to plot a course on a map, navigate to a specific landmark, or maintain a desired direction.
4. What are some common navigation errors to avoid?
Common navigation errors include misreading the compass, failing to adjust for declination, neglecting to account for terrain features, and neglecting to regularly check your position.
5. Can I use my smartphone as a compass?
While smartphone apps can provide compass functionality, they rely on GPS and magnetic sensors, which can be unreliable in areas with poor signal or magnetic interference. Using a dedicated compass remains the most reliable option for navigation.
Tips for Effective Compass Use:
- Practice Regularly: Familiarity with your compass is essential for accurate and confident navigation. Practice using it in various settings to develop proficiency.
- Maintain Your Compass: Regularly clean and inspect your compass to ensure its accuracy and functionality.
- Use a Map in Conjunction with a Compass: A map provides context and allows you to plot a course and track your progress.
- Consider Terrain Features: Terrain features can influence compass readings, so factor them into your navigation decisions.
- Check Your Bearings Regularly: Periodically recheck your bearings to ensure you are staying on course and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion: Navigating with Confidence
A reliable compass is an essential tool for any outdoor enthusiast, providing a vital link between the physical landscape and a map. By understanding the different types of compasses, their functionalities, and key considerations when choosing one, you can select the best compass for your needs, ensuring accurate and confident navigation in any terrain. Remember, a well-chosen compass is an investment in your safety and enjoyment, empowering you to explore the world with a sense of purpose and direction.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Choosing the Best Compass for Map Reading. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!