Navigating the World of Automation: A Comprehensive Look at Keyence’s Z-Map Technology
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Automation: A Comprehensive Look at Keyence’s Z-Map Technology
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Automation: A Comprehensive Look at Keyence’s Z-Map Technology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Automation: A Comprehensive Look at Keyence’s Z-Map Technology
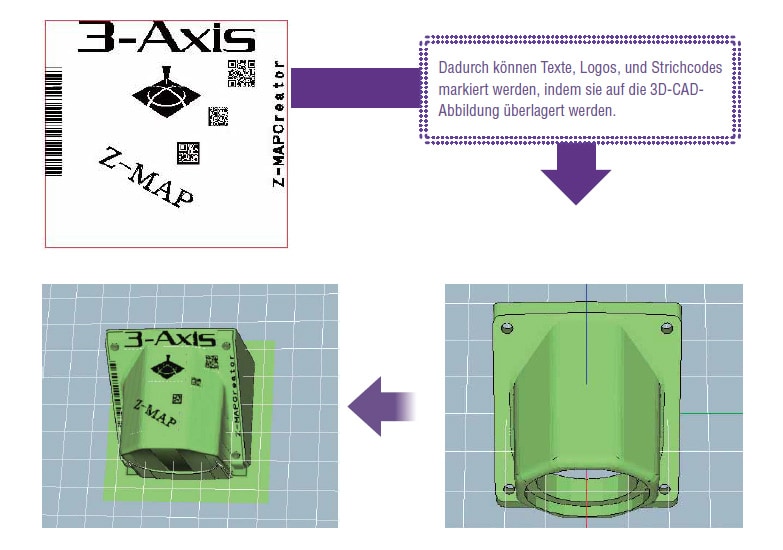
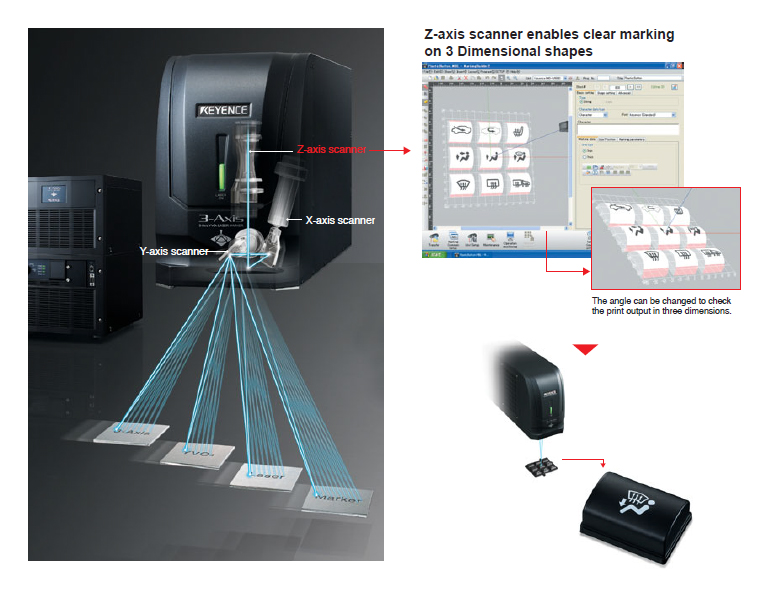
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation, achieving optimal efficiency and precision is paramount. This pursuit has led to the development of innovative technologies that streamline processes, enhance quality control, and ultimately drive productivity. Keyence, a global leader in automation solutions, has made significant contributions in this domain, particularly with its groundbreaking Z-Map technology.
Unveiling the Essence of Z-Map:
Z-Map, a proprietary technology developed by Keyence, is a powerful tool for capturing and analyzing three-dimensional (3D) data of objects. This technology utilizes a unique combination of high-resolution imaging, advanced algorithms, and sophisticated data processing techniques to create detailed, accurate, and comprehensive 3D models of objects. These models serve as the foundation for a wide range of applications within industrial automation, offering a transformative approach to various challenges.
How Z-Map Works:
Z-Map technology relies on the principle of structured light projection. A specialized projector emits a pattern of light onto the object being scanned. This light pattern is then captured by a high-resolution camera, and advanced algorithms analyze the distortion of the projected pattern to determine the precise shape and dimensions of the object. This process, known as triangulation, enables the creation of a highly accurate 3D model.
Applications of Z-Map Technology:
Z-Map technology finds diverse applications across various industries, revolutionizing processes and enabling unprecedented levels of efficiency and accuracy. Some key applications include:
- 3D Inspection and Quality Control: Z-Map enables detailed inspection of complex objects, identifying defects, deviations from specifications, and ensuring consistent product quality. This is crucial in industries like automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, where even minute imperfections can have significant consequences.
- Reverse Engineering: By capturing the precise 3D geometry of existing objects, Z-Map facilitates reverse engineering. This allows for the creation of digital models for 3D printing, CAD design, or manufacturing tooling, streamlining the design and production processes.
- Robotics and Automation: Z-Map plays a critical role in robotic applications, providing precise object recognition and localization. This enables robots to perform complex tasks with greater accuracy and autonomy, such as picking and placing objects, assembling components, and performing intricate operations.
- 3D Measurement and Dimensional Analysis: Z-Map technology enables accurate measurement of objects, providing precise dimensions and geometric data. This is essential for tasks like part dimensioning, tool path generation, and process optimization.
- Virtual Prototyping and Simulation: Z-Map data can be used to create virtual prototypes, allowing for simulations and testing of designs before physical production. This enables early detection of potential issues, optimization of designs, and reduction in development time and costs.
Benefits of Z-Map Technology:
The application of Z-Map technology brings numerous benefits to industrial operations, significantly enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. These benefits include:
- Improved Accuracy and Precision: Z-Map technology delivers exceptionally accurate and precise 3D data, enabling meticulous inspection, measurement, and analysis. This eliminates human error and ensures consistent quality control throughout production processes.
- Enhanced Productivity: Z-Map’s ability to automate tasks, such as inspection and measurement, significantly reduces manual labor and cycle times. This frees up human resources for more complex and value-adding activities, boosting overall productivity.
- Reduced Costs: By minimizing defects and rework, Z-Map technology contributes to lower manufacturing costs. It also streamlines processes, reduces lead times, and optimizes resource utilization, further contributing to cost savings.
- Increased Flexibility: Z-Map technology allows for the rapid and efficient adaptation to changes in product design or manufacturing requirements. This flexibility ensures that businesses can quickly respond to market demands and adapt to evolving production needs.
- Improved Safety: By automating hazardous or repetitive tasks, Z-Map technology enhances workplace safety. It also provides accurate data for risk assessment and mitigation, minimizing the potential for accidents and injuries.
Keyence Z-Map: FAQs
1. What are the limitations of Z-Map technology?
While Z-Map technology offers exceptional accuracy and versatility, it does have certain limitations. It is generally suitable for objects with a defined surface and may struggle with highly reflective or transparent materials. Additionally, the size and complexity of the object can influence the accuracy and resolution of the generated 3D model.
2. How does Z-Map compare to other 3D scanning technologies?
Z-Map technology stands out for its high accuracy, resolution, and speed. Compared to other 3D scanning technologies like laser scanning or structured light scanning, Z-Map offers a more robust and reliable solution for industrial applications. It excels in capturing detailed 3D data, particularly for complex objects with intricate features.
3. What are the different types of Z-Map sensors available?
Keyence offers a range of Z-Map sensors designed for various applications and object sizes. These sensors differ in their scanning range, resolution, and accuracy, allowing users to choose the most suitable sensor for their specific needs.
4. How can I integrate Z-Map technology into my existing systems?
Keyence provides comprehensive support for integrating Z-Map technology into existing systems. They offer software tools, application programming interfaces (APIs), and technical expertise to ensure seamless integration with automation systems, robotic platforms, and other industrial equipment.
5. What are the future trends in Z-Map technology?
Keyence continues to innovate and enhance Z-Map technology. Future trends include advancements in sensor technology, increased resolution and accuracy, and the development of more sophisticated algorithms for data processing and analysis. These advancements will further expand the capabilities of Z-Map technology, enabling even more complex and sophisticated applications in industrial automation.
Keyence Z-Map: Tips
- Identify the Right Sensor: Choose a Z-Map sensor that aligns with the size, complexity, and material properties of the objects being scanned. Consider factors like scanning range, resolution, and accuracy when selecting the most suitable sensor.
- Optimize Scanning Conditions: Ensure optimal lighting conditions and minimize external disturbances to achieve the best possible scanning results. Properly position the sensor and the object to avoid shadows and reflections that can affect data accuracy.
- Calibrate Regularly: Regularly calibrate the Z-Map sensor to maintain accuracy and consistency in measurements. This ensures reliable and repeatable results over time.
- Utilize Software Tools: Leverage Keyence’s software tools for data processing, analysis, and visualization. These tools enable efficient manipulation and interpretation of Z-Map data, facilitating decision-making and process optimization.
- Explore Advanced Applications: Explore the potential of Z-Map technology beyond traditional applications. Consider its use in areas like virtual reality, augmented reality, and advanced robotics, unlocking new possibilities in industrial automation.
Conclusion:
Keyence’s Z-Map technology represents a significant advancement in industrial automation, empowering businesses to achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy, efficiency, and productivity. By capturing precise 3D data, Z-Map enables detailed inspection, accurate measurement, and efficient automation, transforming various processes across industries. As technology continues to evolve, Z-Map will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of industrial automation, driving innovation and unlocking new possibilities in the pursuit of a more efficient and productive world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Automation: A Comprehensive Look at Keyence’s Z-Map Technology. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!