North Korea’s Geographic Position: A Strategic Crossroads
Related Articles: North Korea’s Geographic Position: A Strategic Crossroads
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to North Korea’s Geographic Position: A Strategic Crossroads. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
North Korea’s Geographic Position: A Strategic Crossroads

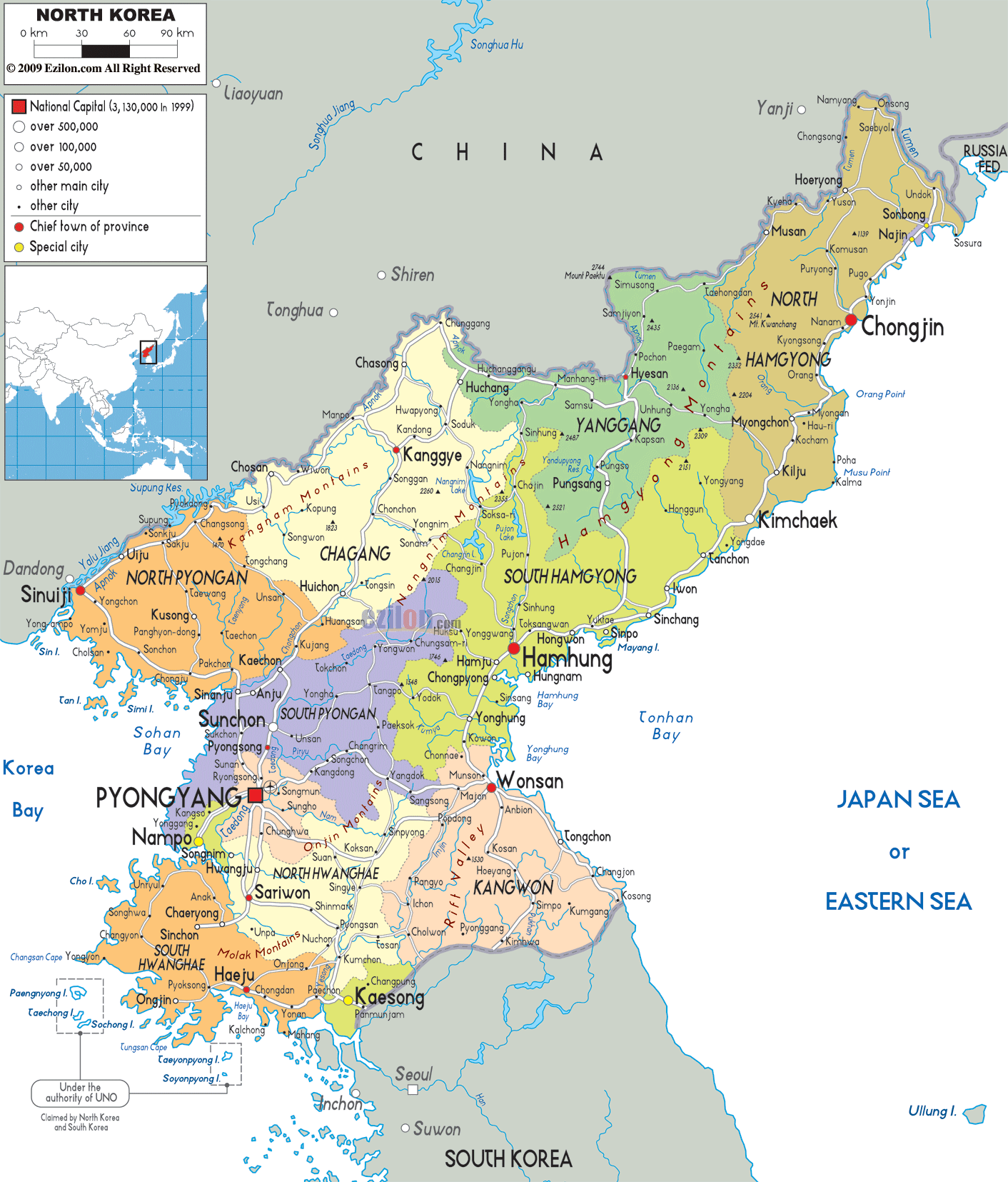
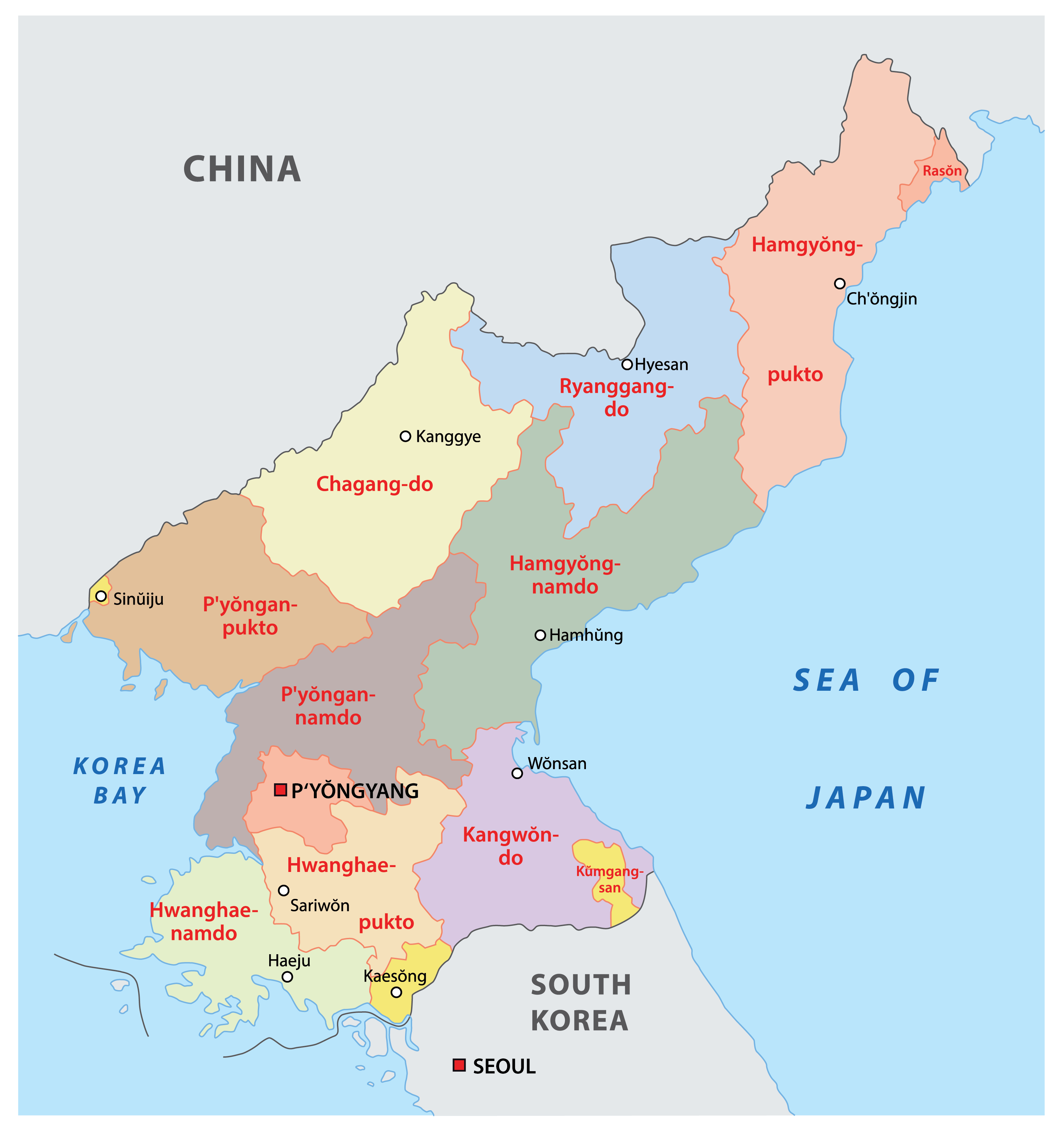
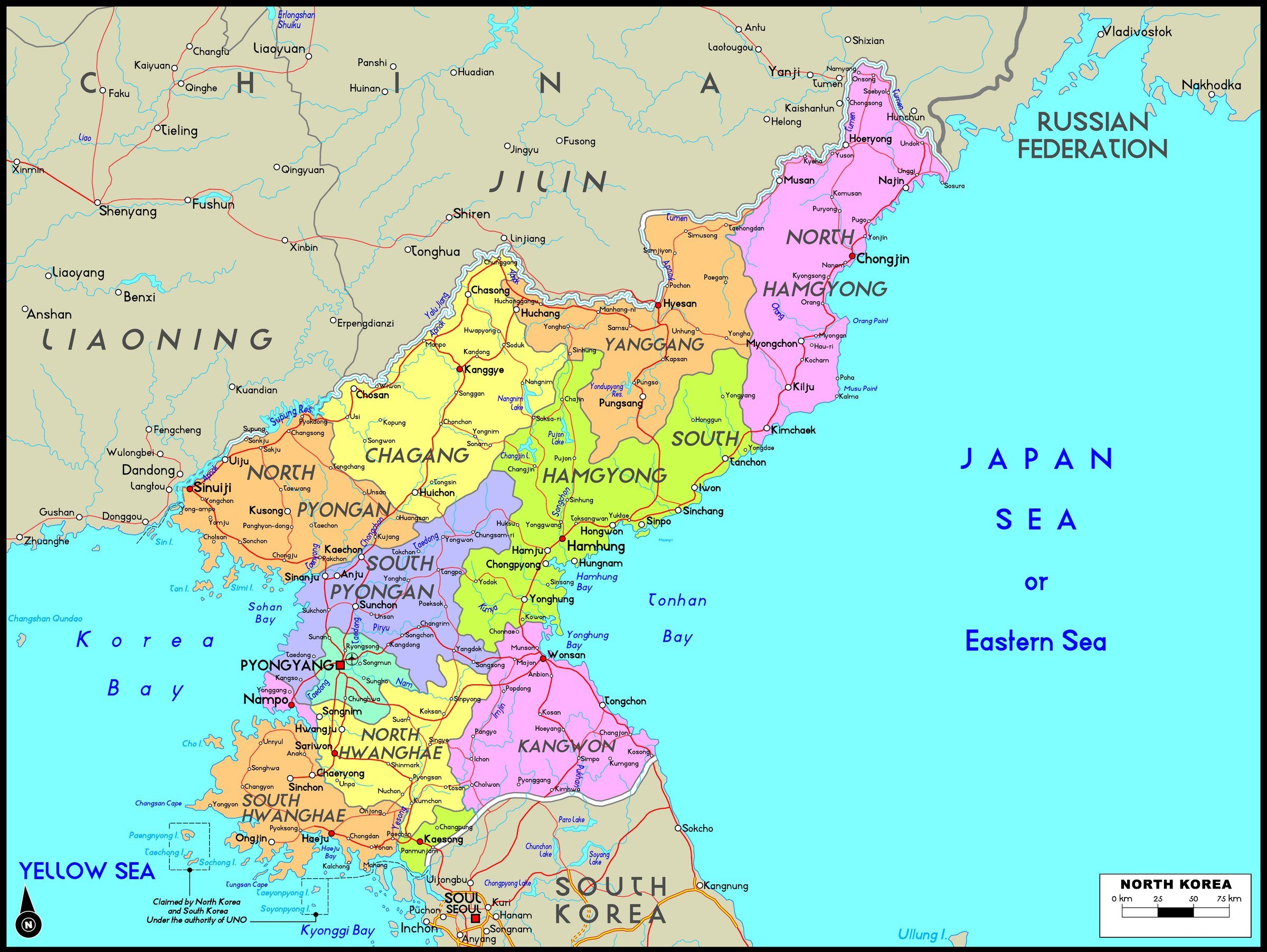
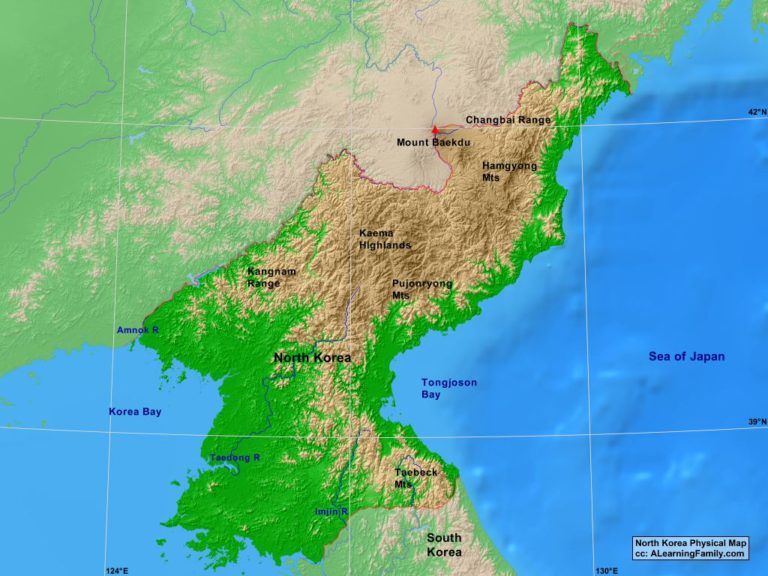
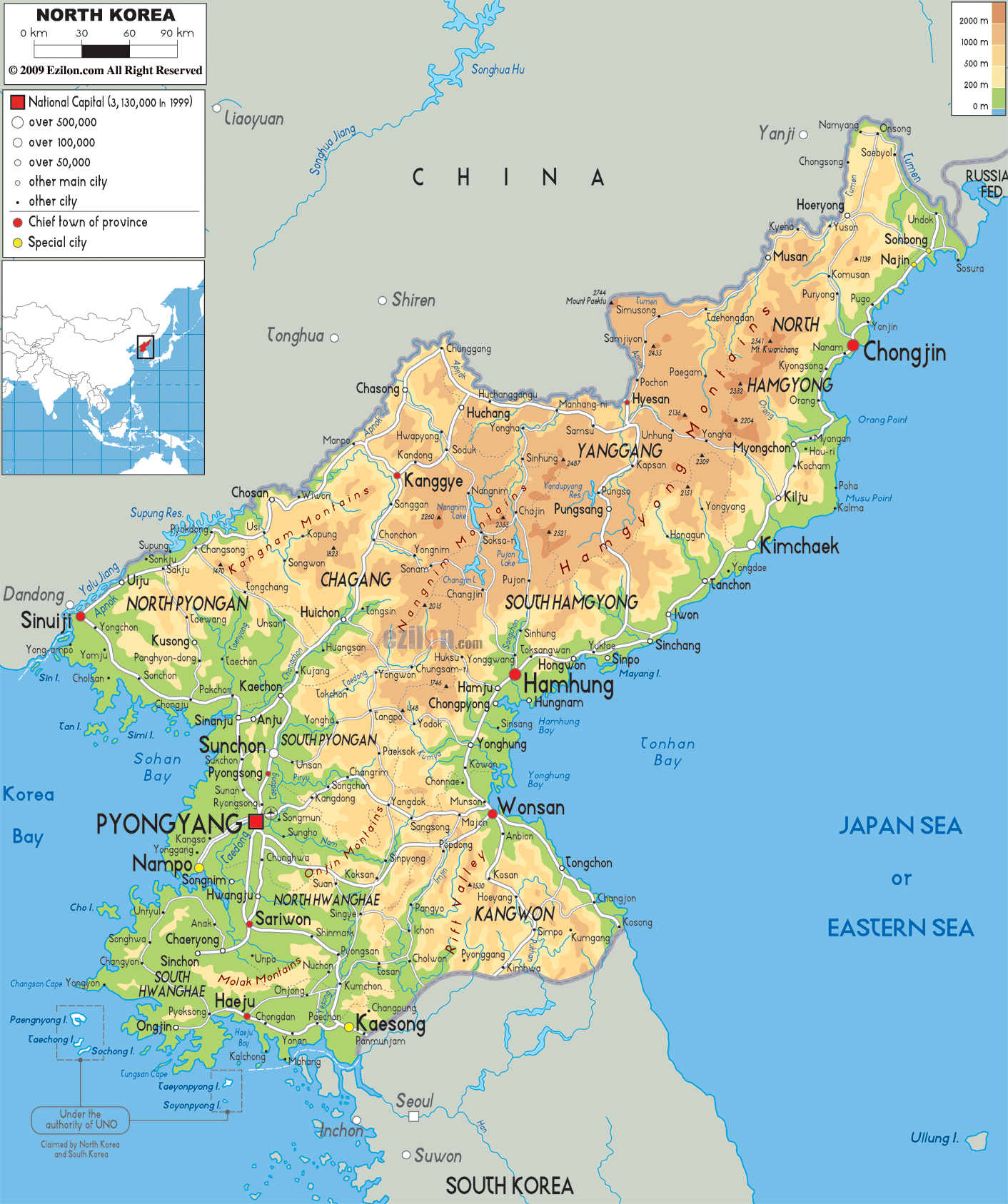
North Korea, officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), occupies a unique and strategically significant location on the Korean Peninsula, nestled within Northeast Asia. Its geographical position has profoundly shaped its history, politics, and international relations.
A Peninsula at the Heart of East Asia:
North Korea shares a land border with China to the north and with Russia to the northeast, making it a vital link between these two major powers. Its eastern coastline faces the Sea of Japan, while the west faces the Yellow Sea, connecting it to South Korea and the wider East Asian maritime network. This strategic location places North Korea at the crossroads of major shipping routes and trade networks, making it a crucial player in regional dynamics.
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ): A Symbolic Divide:
The Korean Peninsula is divided by the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), a heavily fortified border that runs across the 38th parallel. This line, established after the Korean War (1950-1953), serves as a stark reminder of the peninsula’s division and the ongoing tensions between North and South Korea. The DMZ, a 4km-wide buffer zone, is one of the most heavily militarized borders in the world, further emphasizing the geopolitical complexities of the region.
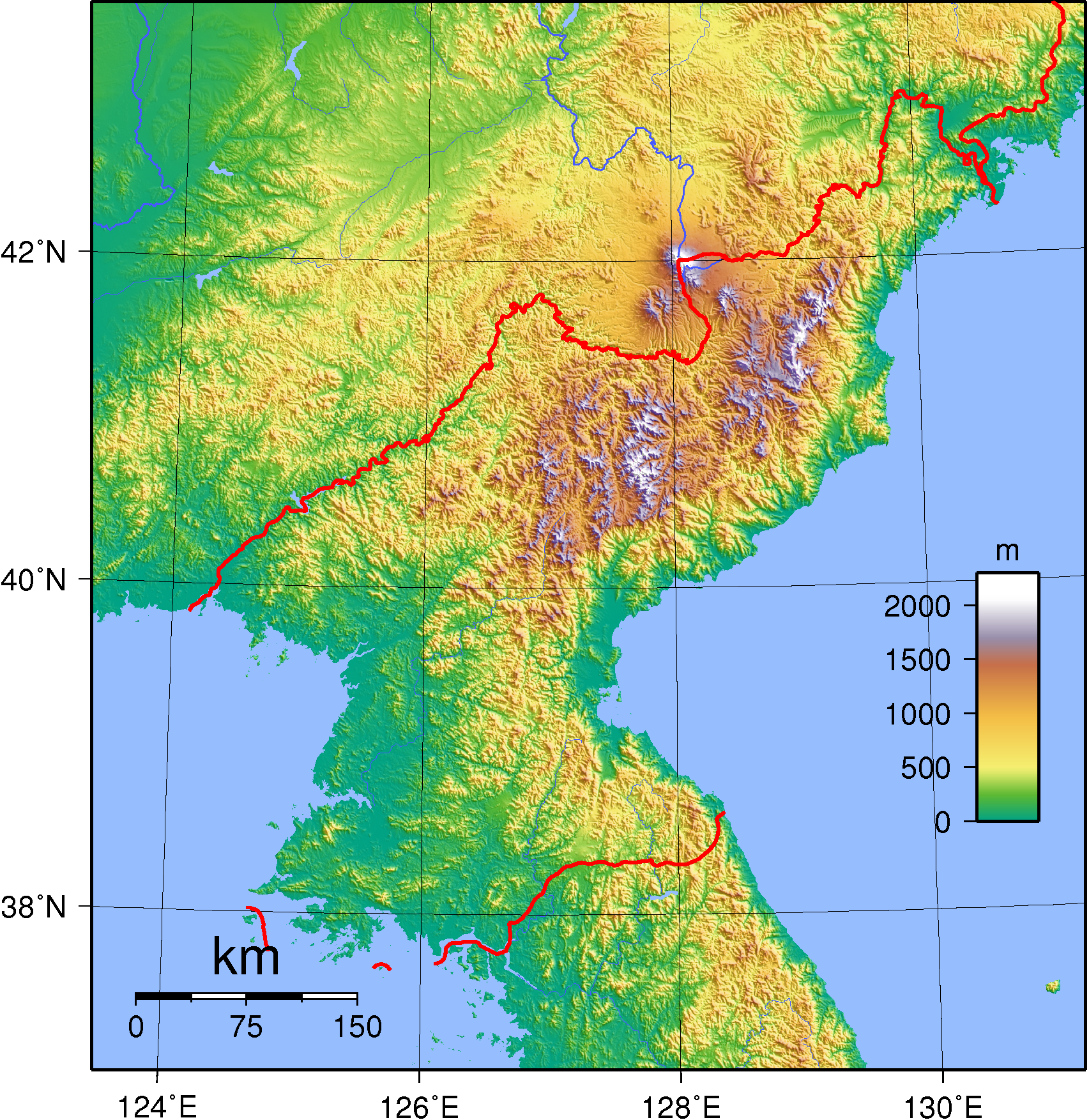
Mountainous Terrain and Limited Resources:
North Korea’s terrain is predominantly mountainous, with the Taebaeksan mountain range dominating the country’s eastern portion. This mountainous landscape has historically limited communication and transportation, contributing to the country’s isolation and the development of distinct regional identities.
Despite its strategic location, North Korea faces significant resource constraints. Its mineral resources, while present, are often limited or difficult to extract. The country’s reliance on agriculture, heavily impacted by its mountainous terrain and erratic weather patterns, further underscores its economic vulnerabilities.
Strategic Implications of North Korea’s Location:
North Korea’s geographic position has numerous strategic implications, both for the country itself and for the wider region:
- Regional Security: The DMZ and the ongoing tensions between North and South Korea create a volatile security environment in Northeast Asia. North Korea’s military capabilities, including its nuclear weapons program, have raised concerns among its neighbors and the international community.
- Economic Potential: Despite its challenges, North Korea’s location holds significant economic potential. Its proximity to major economic powers like China, South Korea, and Japan, coupled with its access to vital sea lanes, provides opportunities for trade and investment.
- Geopolitical Influence: North Korea’s strategic location allows it to play a role in regional power dynamics. Its relationships with China and Russia, coupled with its potential to disrupt stability in Northeast Asia, give it a degree of geopolitical influence.
Challenges and Opportunities:
North Korea’s location presents both challenges and opportunities. While its strategic position offers potential for economic development and regional influence, it also exposes the country to geopolitical risks and economic vulnerabilities.
Challenges:
- Political Isolation: North Korea’s isolationist policies and its authoritarian regime have hampered its economic development and its integration into the global community.
- Economic Constraints: The country’s limited resources, underdeveloped infrastructure, and inefficient economic system have hindered its ability to achieve sustainable economic growth.
- Security Threats: North Korea’s nuclear weapons program and its aggressive military posture have created significant security threats in the region, leading to international sanctions and diplomatic tensions.
Opportunities:
- Economic Cooperation: North Korea’s location provides opportunities for economic cooperation with neighboring countries, particularly China and South Korea.
- Regional Integration: The country’s strategic position could enable it to play a more active role in regional organizations and initiatives, promoting cooperation and stability.
- Resource Development: North Korea possesses untapped resources that could be developed to generate economic growth and improve the standard of living for its population.
Conclusion:
North Korea’s geographic location on the Korean Peninsula, nestled within Northeast Asia, is a defining factor in its history, politics, and international relations. Its strategic position at the crossroads of major powers and shipping routes presents both challenges and opportunities. While the country faces significant economic and political constraints, its location offers potential for economic development, regional integration, and a more constructive role in international affairs.
FAQs:
Q: What is the significance of the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) in North Korea?
A: The DMZ, a heavily fortified border that runs across the 38th parallel, symbolizes the division of the Korean Peninsula and the ongoing tensions between North and South Korea. It is one of the most militarized borders in the world, highlighting the region’s geopolitical complexities.
Q: What are the main challenges faced by North Korea due to its location?
A: North Korea faces challenges such as political isolation, economic constraints, and security threats stemming from its nuclear weapons program and its aggressive military posture. Its mountainous terrain and limited resources also contribute to its economic vulnerabilities.
Q: What are the potential opportunities for North Korea stemming from its location?
A: North Korea’s location offers potential for economic cooperation with neighboring countries, regional integration, and the development of its untapped resources. Its strategic position could enable it to play a more active and constructive role in international affairs.
Tips:
- Focus on regional dynamics: Understanding North Korea’s location requires understanding the broader geopolitical context of Northeast Asia.
- Consider historical context: North Korea’s history and its relationship with its neighbors are crucial factors in understanding its current situation.
- Recognize the complexities: North Korea’s location presents both challenges and opportunities, and its future remains uncertain.
Conclusion:
North Korea’s geographic position is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications. Understanding its location requires considering its historical context, its regional dynamics, and its potential for both challenges and opportunities. As the world navigates the complexities of Northeast Asia, understanding North Korea’s strategic location remains crucial for promoting regional stability and fostering international cooperation.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into North Korea’s Geographic Position: A Strategic Crossroads. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!