The Essential Role of Map Keys in Geographic Representation
Related Articles: The Essential Role of Map Keys in Geographic Representation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Essential Role of Map Keys in Geographic Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Role of Map Keys in Geographic Representation
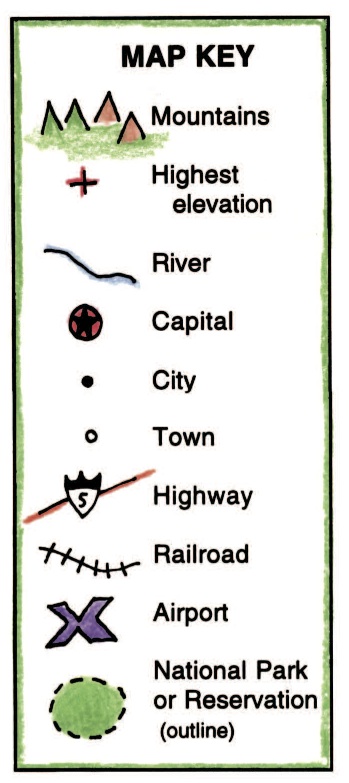
Maps, as visual representations of geographical space, are powerful tools for conveying information and fostering understanding. However, their effectiveness hinges on a crucial element: the map key, also known as a legend. This seemingly simple component plays a vital role in bridging the gap between visual symbols and their real-world counterparts, enabling readers to decipher the information encoded within the map.
Understanding the Purpose of a Map Key
A map key acts as a translator, providing a concise and standardized guide to the symbols, colors, patterns, and other visual elements used on the map. It essentially acts as a glossary, explaining the meaning of each element and ensuring consistency throughout the map’s representation. Without a clear and comprehensive map key, the map’s information becomes ambiguous, potentially leading to misinterpretations and misunderstandings.
Key Components of a Map Key
A well-constructed map key typically includes the following components:
- Symbols: These represent specific features on the map, such as roads, rivers, cities, or land use types. Symbols can vary in shape, size, and color, allowing for differentiation between different categories.
- Colors: Colors are frequently used to distinguish different features or categories on a map. For example, blue might represent water bodies, green might represent forests, and red might represent roads. The choice of colors should be consistent and adhere to established conventions whenever possible.
- Patterns: Patterns, such as hatching, dots, or stripes, can be used in conjunction with colors or symbols to further differentiate features. For instance, different types of roads might be represented by different hatch patterns.
- Scale: The scale of a map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This is crucial for understanding the relative sizes of features and distances between them.
- North Arrow: A north arrow indicates the direction of true north, providing orientation for the map’s user.
- Text: Text labels are used to identify specific features, such as city names, road names, or geographical names.
Importance of Clarity and Consistency
The clarity and consistency of a map key are paramount to its effectiveness. The symbols, colors, and patterns used should be easily recognizable and distinguishable. The text should be clear, concise, and legible. The overall layout of the key should be well-organized and visually appealing, facilitating easy comprehension.
Benefits of a Comprehensive Map Key
A well-designed map key provides numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Comprehension: The key acts as a bridge between the visual language of the map and the reader’s understanding, facilitating accurate interpretation of the information presented.
- Increased Accessibility: A comprehensive key makes the map accessible to a wider audience, including those who may not be familiar with standard map symbols or conventions.
- Improved Communication: A clear and consistent key ensures that the map’s message is communicated effectively and unambiguously.
- Reduced Misinterpretations: By providing a clear explanation of symbols and conventions, the key minimizes the potential for misinterpretations and misunderstandings.
- Increased Trustworthiness: A well-constructed map key enhances the credibility and trustworthiness of the map, as it demonstrates a commitment to clarity and accuracy.
Types of Map Keys
Map keys can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Simple Keys: These keys typically use a limited number of symbols and colors to represent a small number of features. They are often found on simple maps, such as those depicting a local neighborhood or a specific route.
- Complex Keys: These keys use a wider range of symbols, colors, patterns, and text labels to represent a larger number of features. They are commonly found on more detailed maps, such as those depicting entire countries or continents.
FAQs About Map Keys
1. Why are map keys important?
Map keys are crucial for translating the visual elements of a map into meaningful information. They ensure that readers can correctly interpret the symbols, colors, and patterns used, preventing misunderstandings and promoting accurate understanding.
2. How can I create an effective map key?
An effective map key should be clear, concise, and consistent. Use recognizable symbols, distinct colors, and legible text. Organize the key logically and make sure it is easily accessible to the reader.
3. What are some common map key conventions?
Common conventions include using blue for water bodies, green for vegetation, brown for mountains, and red for roads. However, these conventions can vary depending on the map’s purpose and the specific features being represented.
4. Can map keys be used for different types of maps?
Yes, map keys are essential for all types of maps, regardless of their scale, purpose, or subject matter. From simple neighborhood maps to complex global maps, a clear and comprehensive key is crucial for effective communication.
5. Are there any online resources for creating map keys?
Numerous online tools and resources are available for creating map keys. These tools can help you design professional-looking keys with a variety of symbols, colors, and patterns.
Tips for Creating Effective Map Keys
- Keep it simple: Avoid using too many symbols, colors, or patterns, as this can overwhelm the reader.
- Use familiar symbols: Choose symbols that are readily recognizable and easy to understand.
- Employ contrasting colors: Use colors that are easily distinguishable from each other, ensuring that different features are clearly differentiated.
- Provide clear labels: Use concise and legible text labels to identify each symbol, color, or pattern.
- Organize logically: Arrange the key in a way that is easy to navigate and understand.
- Test your key: Show your key to others and ask for feedback to ensure it is clear and effective.
Conclusion
The map key, often overlooked, plays a critical role in the effectiveness of any map. It acts as the essential bridge between the visual language of the map and the reader’s understanding, ensuring accurate interpretation and fostering comprehension. By adhering to principles of clarity, consistency, and accessibility, mapmakers can create keys that empower readers to fully engage with the information presented, unlocking the vast potential of visual geographical representation.
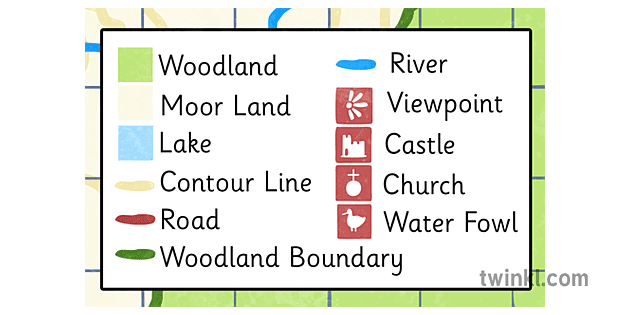




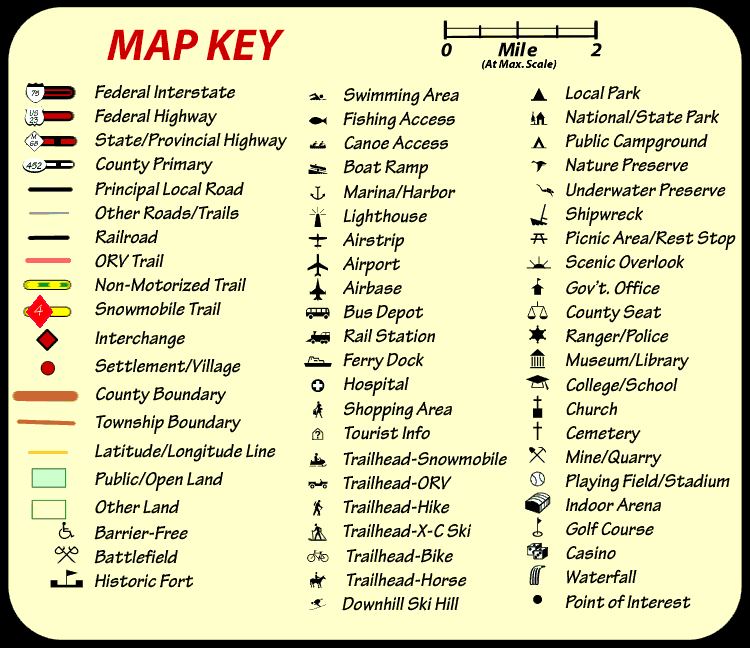

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Role of Map Keys in Geographic Representation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!