The Geopolitical Landscape of North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads
Related Articles: The Geopolitical Landscape of North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Geopolitical Landscape of North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geopolitical Landscape of North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads
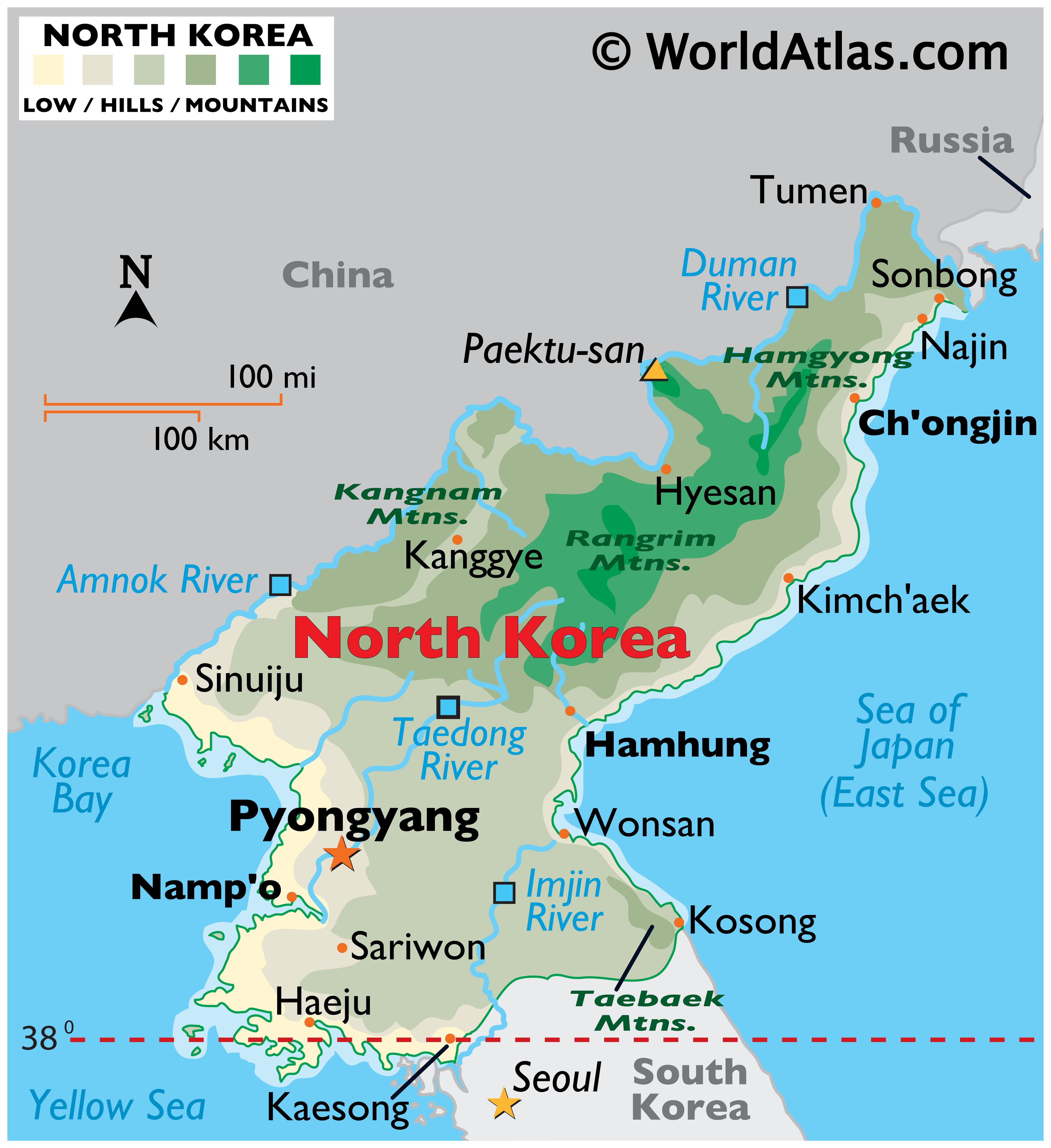
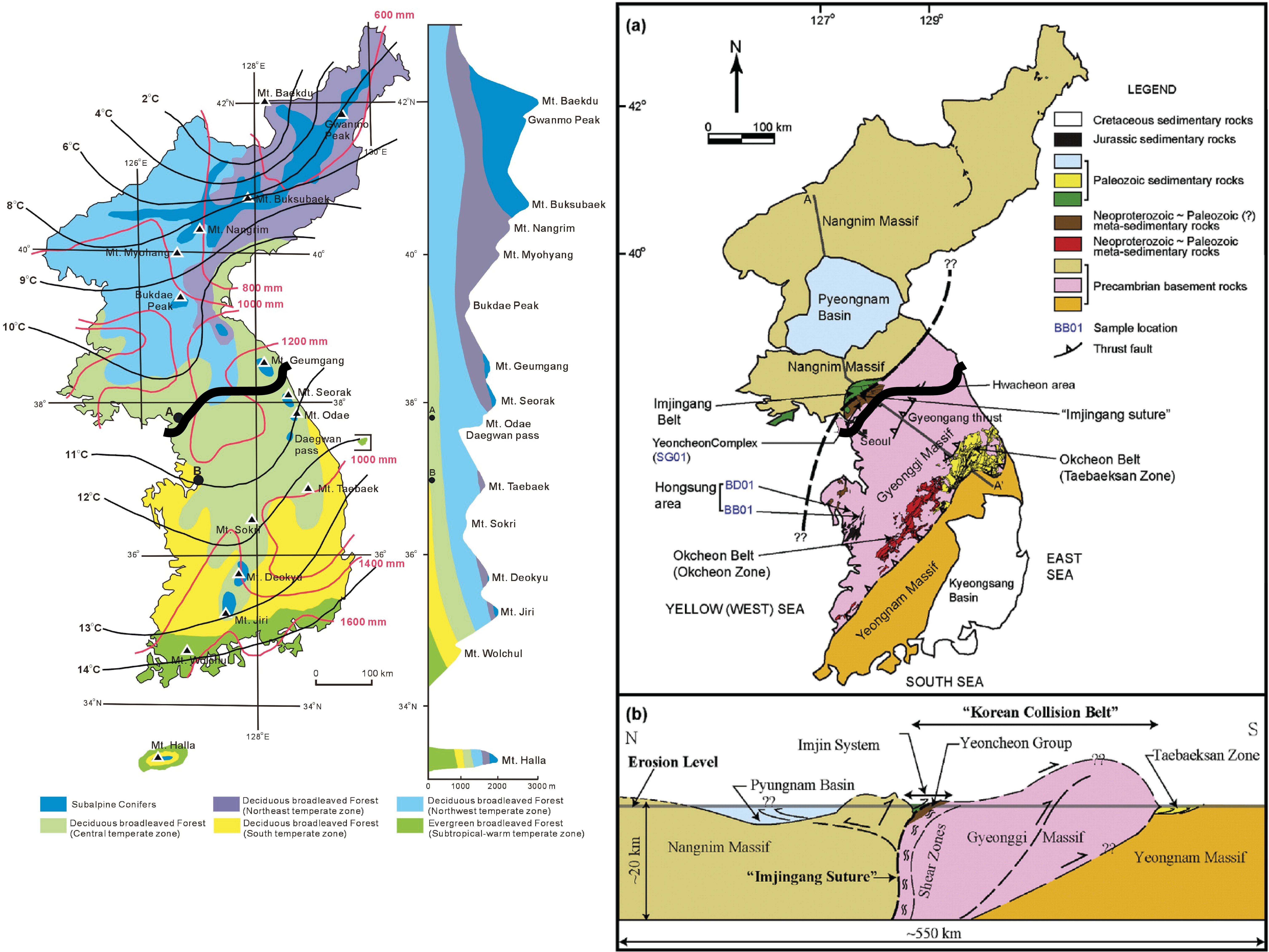
North Korea, officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), occupies a strategically significant location on the Korean Peninsula, a narrow landmass jutting out from the eastern edge of the Asian mainland. Its position, nestled between powerful neighbors and bordering crucial maritime routes, has shaped its history and continues to influence its present.
A Peninsula Divided:
The Korean Peninsula, historically a unified entity, was divided into North Korea and South Korea following World War II. The 38th parallel, a line of latitude, became the arbitrary border separating the two nations. North Korea, occupying the northern portion, shares land borders with China and Russia to the north, while South Korea, to the south, is separated from its northern counterpart by a heavily fortified demilitarized zone (DMZ).
Strategic Location:
North Korea’s geographical positioning grants it access to vital sea routes. The Yellow Sea, to the west, connects it to the Pacific Ocean, while the Sea of Japan (East Sea) lies to the east. This strategic location has historically facilitated trade and interaction with neighboring countries, but it has also attracted geopolitical attention, particularly during periods of regional tension.
Mountains and Terrain:
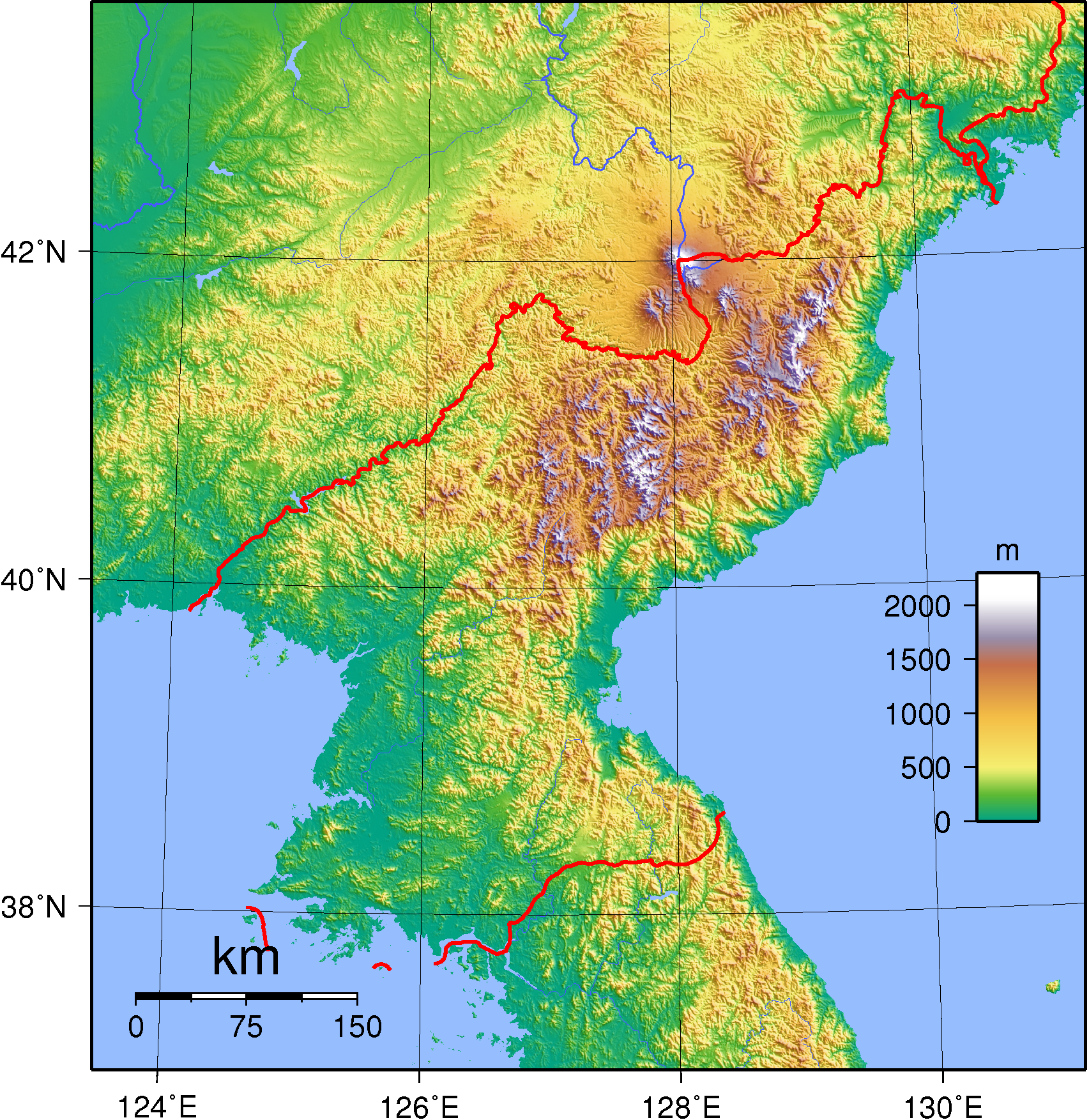
North Korea is a mountainous country, with the Taebaeksan mountain range dominating its landscape. The rugged terrain, characterized by steep slopes and narrow valleys, presents challenges for transportation and communication. However, it also provides natural barriers, contributing to the country’s relative isolation.
Climate and Resources:
North Korea experiences a temperate climate, with four distinct seasons. The country possesses a variety of natural resources, including minerals, coal, iron ore, and timber. However, the exploitation of these resources has been hampered by political and economic constraints.
A Country in Transition:
Despite its geographic advantages, North Korea faces significant challenges. Its closed political system and isolation have hindered economic development and limited its international engagement. The country’s nuclear program has sparked international condemnation and sanctions, further isolating it from the global community.
The Path Forward:
North Korea’s future hinges on its willingness to engage with the international community and pursue a path of peace and economic development. Its strategic location offers potential for regional cooperation and integration, but it requires a shift in policy and a commitment to dialogue.
Understanding North Korea’s Geography:
Comprehending North Korea’s geographical context is crucial for understanding its history, its present, and its potential future. Its location, its terrain, its resources, and its relationship with its neighbors all play a role in shaping its destiny.
FAQs
Q: What are the major cities in North Korea?
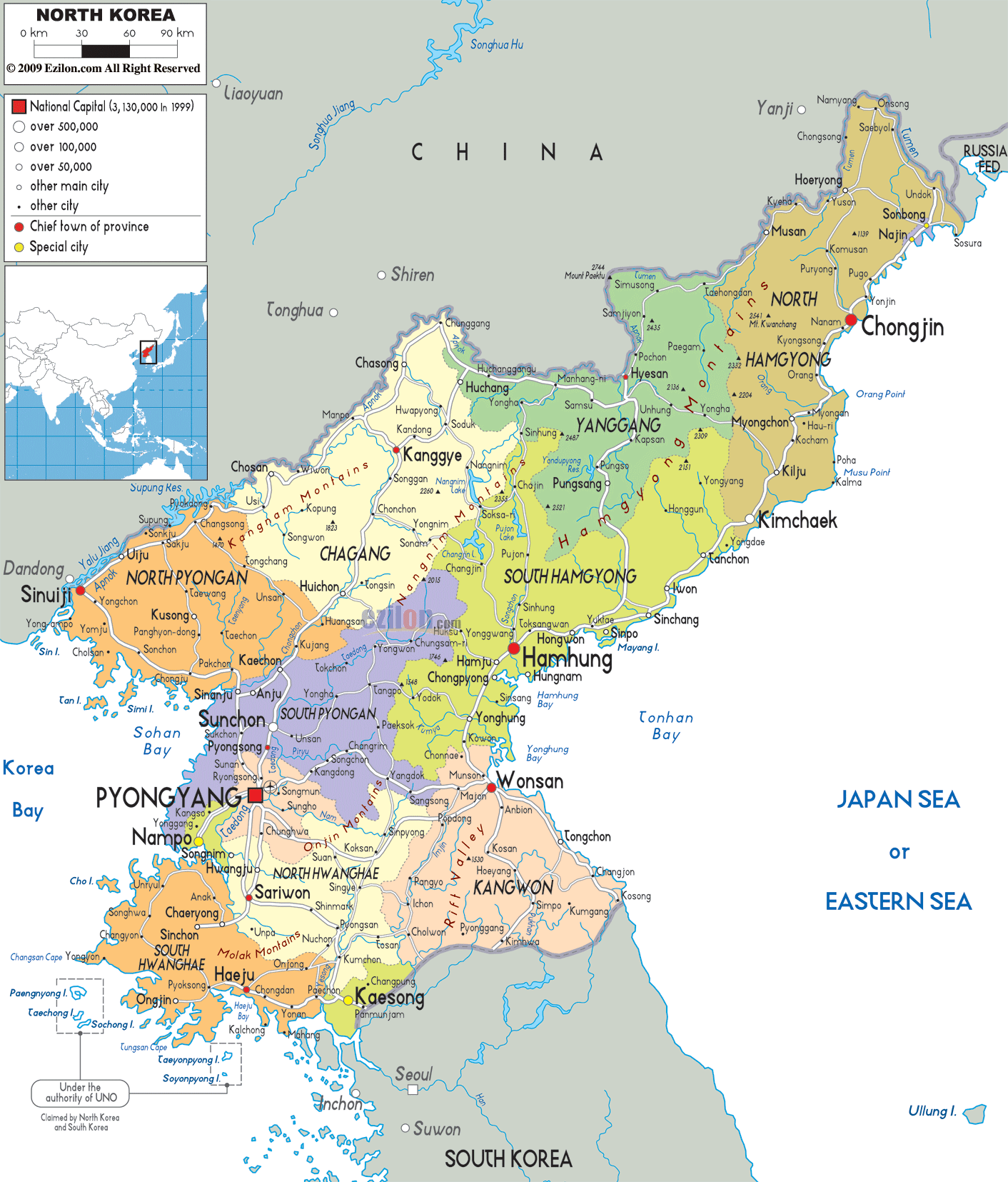
A: Pyongyang, the capital, is the largest and most important city. Other major cities include Chongjin, Hamhung, Wonsan, and Kaesong.
Q: What is the climate like in North Korea?
A: North Korea experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. Winters are cold and dry, while summers are hot and humid.
Q: What are the main industries in North Korea?
A: North Korea’s economy is heavily reliant on its mineral resources, including coal, iron ore, and graphite. The country also has industries in manufacturing, agriculture, and fishing.
Q: What is the political system in North Korea?
A: North Korea is a one-party state ruled by the Workers’ Party of Korea. The country is led by a Supreme Leader, currently Kim Jong-un.
Q: What is the relationship between North Korea and its neighbors?
A: North Korea has complex relationships with its neighbors. It has a strong alliance with China and Russia, but relations with South Korea have been strained for decades.
Tips
- Use reliable sources: When researching North Korea, rely on credible sources such as academic journals, reputable news outlets, and government reports.
- Consider different perspectives: North Korea is a complex country with a diverse range of viewpoints. Explore different perspectives to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Focus on historical context: North Korea’s history has shaped its present and its potential future. Gain an understanding of its past to better comprehend its current situation.
Conclusion
North Korea’s geographical position on the Korean Peninsula has profoundly influenced its history and continues to shape its present. Its strategic location, its challenging terrain, and its complex relationship with its neighbors all contribute to its unique identity. While the country faces significant challenges, its potential for regional cooperation and economic development remains. Understanding North Korea’s geography is essential for navigating the complexities of its present and envisioning its future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geopolitical Landscape of North Korea: A Nation at the Crossroads. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!