The Heart of America: Understanding Kansas’s Geographical Significance
Related Articles: The Heart of America: Understanding Kansas’s Geographical Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Heart of America: Understanding Kansas’s Geographical Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Heart of America: Understanding Kansas’s Geographical Significance

Kansas, often referred to as the "Heartland" or the "Wheat State," occupies a central position within the United States. Its geographic location, nestled amidst the vast plains of the Midwest, plays a crucial role in shaping its identity, economy, and cultural landscape.
A Crossroads of Geography:
Kansas sits at the geographic center of the contiguous United States, a fact reflected in its nickname, "The Wheat State." This central location has historically made Kansas a crucial transportation hub, connecting the East Coast to the West Coast. The state is traversed by major interstate highways and railroad lines, facilitating the movement of goods and people across the country.
A Tapestry of Landscapes:
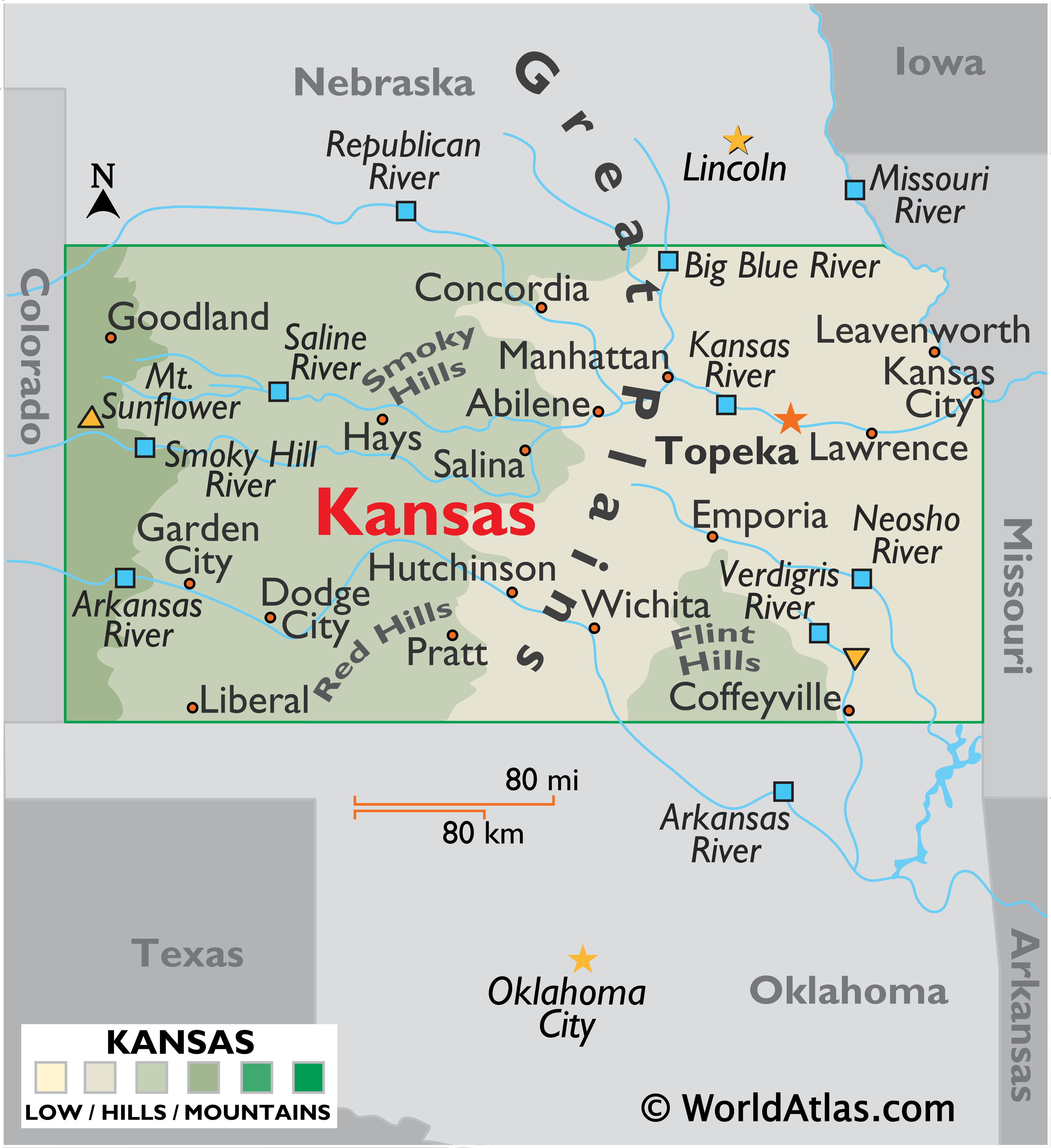
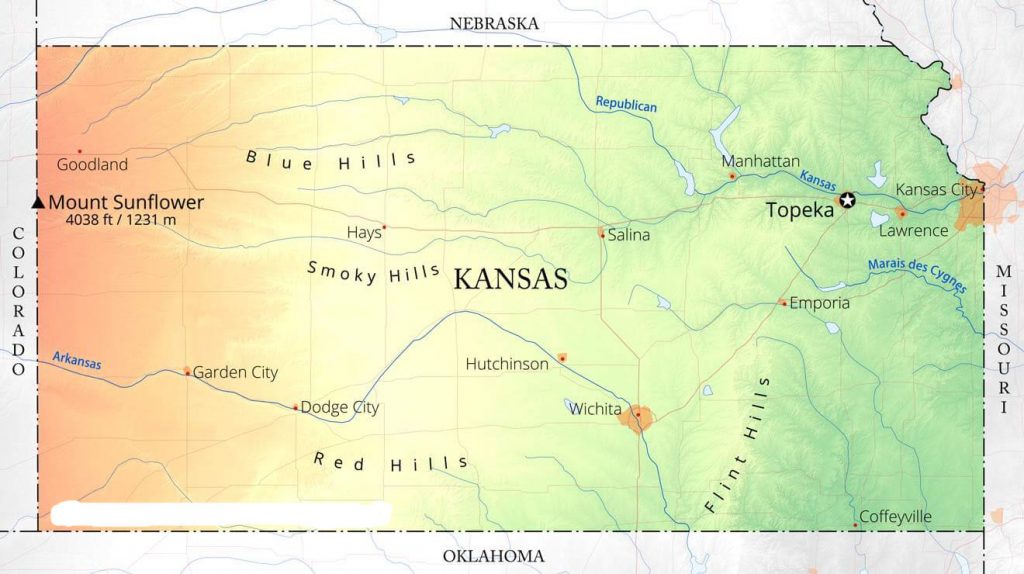
The state’s landscape is characterized by rolling plains, dotted with fertile farmlands and occasional hills. The Flint Hills, a unique ecoregion known for its tallgrass prairie, dominate the eastern part of the state. The western region, influenced by the Great Plains, features more arid conditions with vast expanses of grasslands and canyons.
Location in Relation to Neighboring States:
Kansas shares borders with six states, each contributing to its cultural and economic influence:
- North: Nebraska
- South: Oklahoma
- East: Missouri
- West: Colorado
- Northeast: Iowa
- Southwest: Texas (a small portion)
The Impact of Location:
Kansas’s central location has had a profound impact on its history, economy, and cultural identity:
- Agriculture: The fertile plains of Kansas have made it a major agricultural producer, particularly for wheat, corn, and livestock. Its location within the "Corn Belt" and the "Wheat Belt" has solidified its position as a key player in the global food supply chain.
- Transportation: Its central location has made Kansas a vital transportation hub. Major highways, railroads, and airports connect the state to the rest of the nation, facilitating trade and travel.
- Culture: Kansas’s location has influenced its cultural identity, blending elements of the Midwest, the Great Plains, and the Southwest. The state boasts a rich history of Native American culture, pioneer spirit, and agricultural heritage.
Beyond Geography: A State of Innovation and Diversity:
While its location plays a significant role, Kansas is more than just a geographical point on the map. It is a state brimming with innovation, diversity, and cultural richness.
- Aerospace Industry: Kansas is home to a thriving aerospace industry, with major players like Boeing and Spirit AeroSystems. This industry is fueled by the state’s strategic location, proximity to major aerospace hubs, and skilled workforce.
- Biotechnology: Kansas has emerged as a leader in the biotechnology sector, attracting companies focused on agricultural research and development. The state’s agricultural heritage and strong academic institutions have fueled this growth.
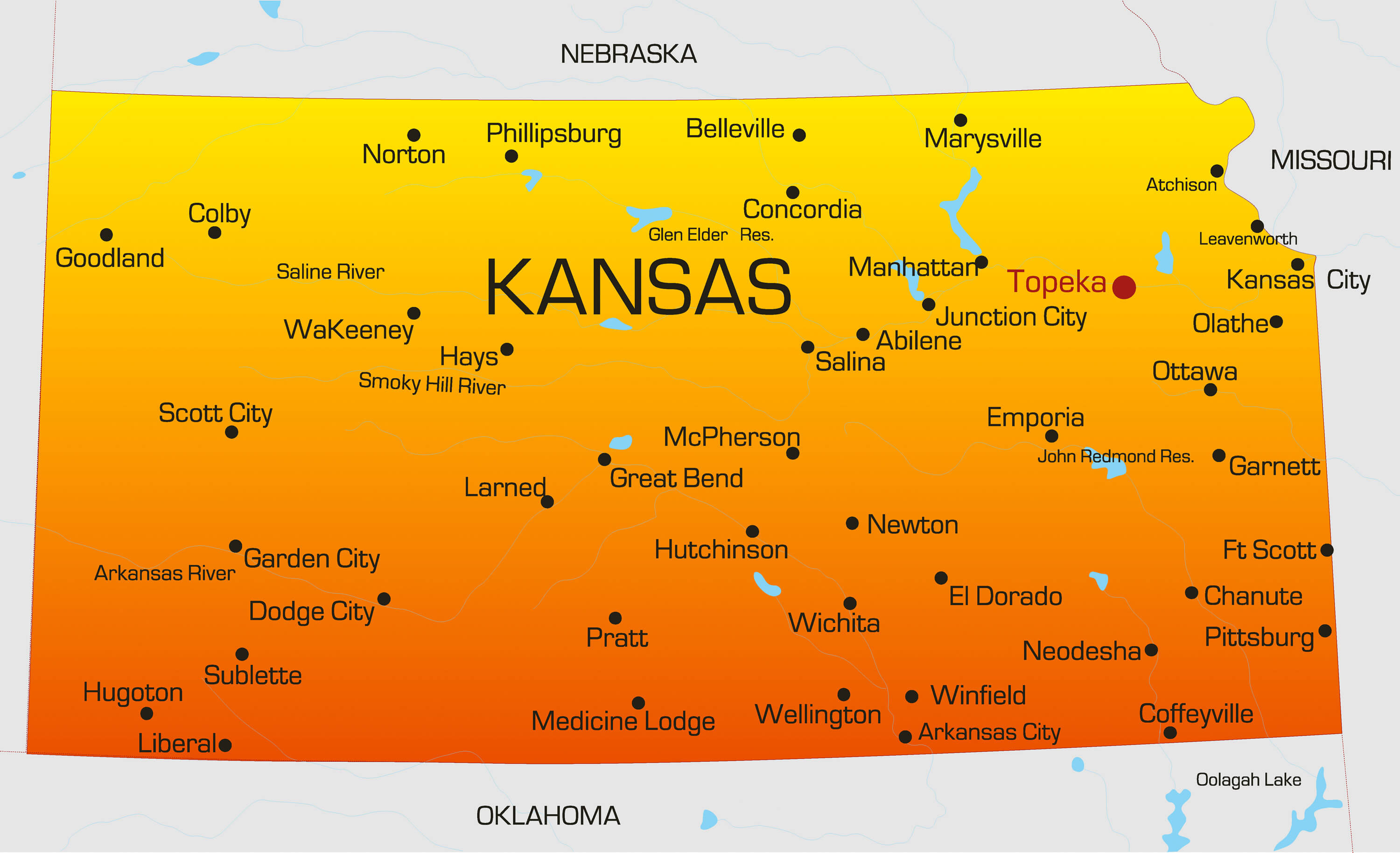
- Cultural Hubs: Kansas boasts vibrant cities like Wichita, Topeka, and Lawrence, each offering unique cultural experiences, museums, theaters, and art galleries.
FAQs:
- Q: Is Kansas considered part of the Midwest or the Great Plains?
A: Kansas is geographically located within both the Midwest and the Great Plains. While its eastern region shares characteristics with the Midwest, its western region is part of the Great Plains.
- Q: What are the major cities in Kansas?
A: The major cities in Kansas are Wichita, Topeka (the state capital), Kansas City (a portion of the city extends into Missouri), and Overland Park.
- Q: What is the climate like in Kansas?
A: Kansas experiences a humid subtropical climate with hot summers and cold winters. The state is prone to extreme weather events, including tornadoes, droughts, and blizzards.
Tips for Exploring Kansas:
- Visit the Flint Hills: Explore the unique tallgrass prairie ecosystem, a national treasure and a testament to Kansas’s natural beauty.
- Explore the Kansas City Art District: Immerse yourself in the vibrant art scene of Kansas City, featuring galleries, studios, and murals.
- Visit the Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve: Discover the vastness and beauty of the Great Plains at this national preserve.
- Experience the Wild West at Dodge City: Step back in time and experience the history of the Wild West at Dodge City, a renowned frontier town.
Conclusion:
Kansas, located at the heart of the United States, embodies the spirit of the American Midwest. Its central location has shaped its history, economy, and cultural identity. From its vast agricultural plains to its thriving cities, Kansas offers a diverse tapestry of experiences, showcasing the beauty, resilience, and innovation of the American heartland.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Heart of America: Understanding Kansas’s Geographical Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!