The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy
Related Articles: The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy
- 3.1 Historical Context: A Legacy of Gerrymandering and Reform
- 3.2 The Current Landscape: A Complex and Evolving System
- 3.3 Understanding the Impact: A Deeper Look at the Map’s Significance
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About the Kentucky Voting Districts Map
- 3.5 Tips: Navigating the Kentucky Voting Districts Map for Informed Participation
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Ensuring Fair and Effective Representation
- 4 Closure
The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy
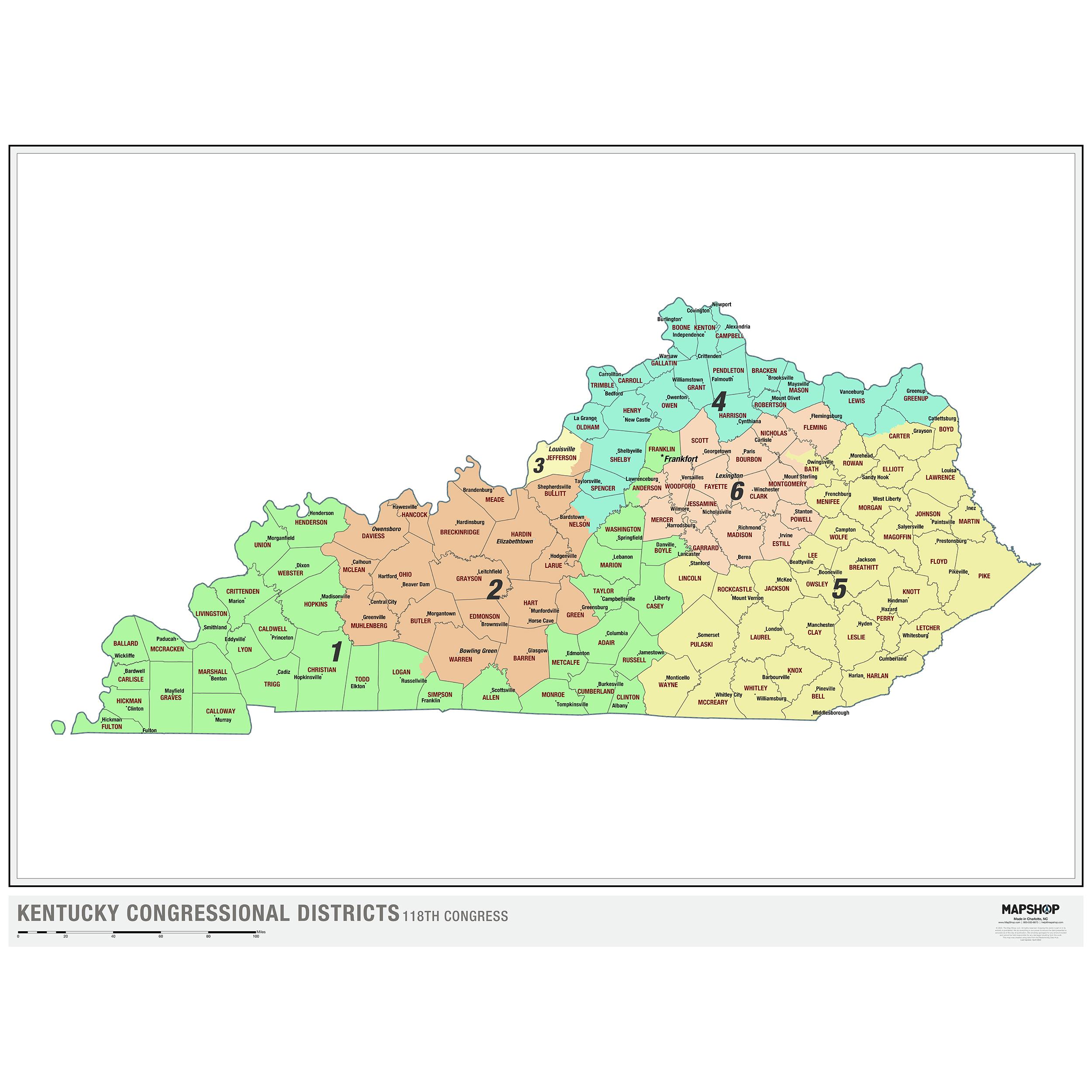
The Kentucky Voting Districts Map, a visual representation of the state’s electoral geography, is a crucial element of the democratic process. It determines the boundaries of legislative and congressional districts, directly impacting the representation of citizens in government. Understanding the map’s intricacies, its historical evolution, and its current impact on the political landscape is essential for informed civic engagement.
Historical Context: A Legacy of Gerrymandering and Reform
Kentucky’s voting districts map has undergone significant transformations over the years, reflecting evolving political dynamics and legal challenges. The history of the map is intricately intertwined with the concept of gerrymandering, a practice aimed at manipulating district boundaries to favor a specific political party or group.
In the early 20th century, Kentucky witnessed blatant gerrymandering, with districts drawn in contorted shapes to concentrate voters from specific demographics in a single area, effectively diluting their voting power. This practice, often criticized for undermining fair representation, led to calls for reform and a shift towards more equitable districting.
The 1960s saw the landmark case of Reynolds v. Sims (1964), which established the "one person, one vote" principle, requiring legislative districts to be roughly equal in population. This ruling significantly impacted the Kentucky map, leading to the redrawing of districts to ensure equal representation based on population.
Further legal challenges and the emergence of sophisticated computer-aided mapping tools brought about new challenges in districting. Concerns about partisan gerrymandering, where districts are drawn to favor one party over another, resurfaced. These concerns led to the passage of the Fair Districts Act of 2018, a bipartisan effort aimed at establishing independent commissions to oversee the redistricting process in Kentucky.
The Current Landscape: A Complex and Evolving System
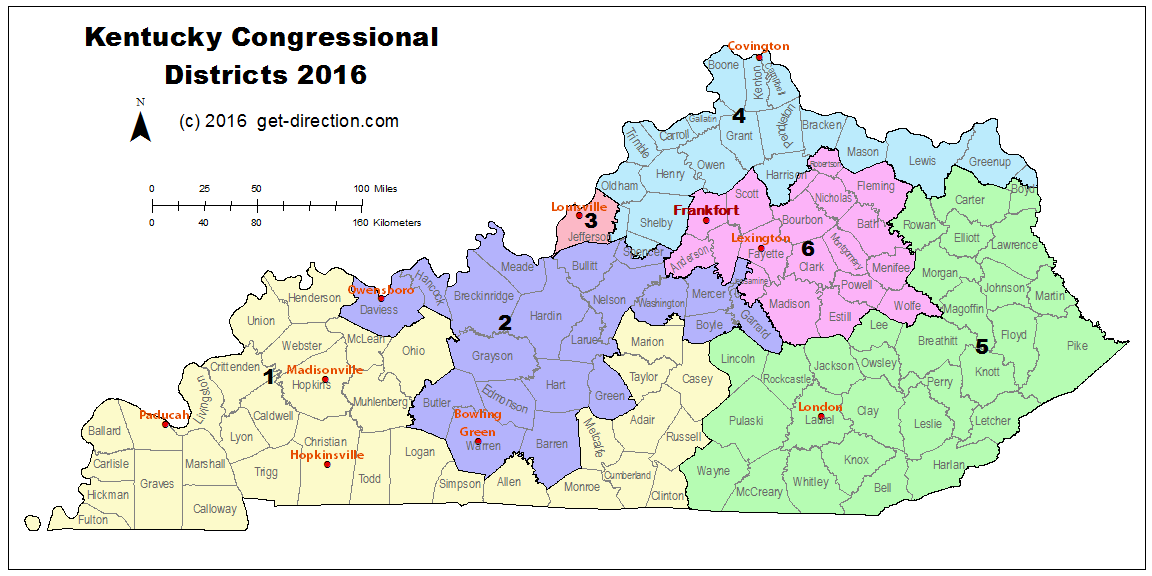
The current Kentucky Voting Districts Map, a product of the 2020 redistricting process, reflects the state’s demographic shifts and the ongoing debate over fair representation. The map consists of 120 legislative districts, encompassing both the state House and Senate, and six congressional districts.
The redistricting process involved several key considerations:
- Population Equality: Districts must be roughly equal in population to ensure that each citizen’s vote carries equal weight.
- Compactness and Contiguity: Districts should be geographically compact and contiguous, minimizing fragmentation and ensuring communities of interest are represented together.
- Minority Representation: The map aims to protect minority voting rights by ensuring that districts are drawn in a way that does not dilute the voting power of minority groups.
- Political Considerations: The redistricting process is inherently political, with both parties seeking to maximize their electoral advantage.
The 2020 map has been the subject of legal challenges, with accusations of partisan gerrymandering. While the legal battles continue, the map remains in effect, impacting the political landscape and the representation of citizens in the Kentucky legislature and Congress.
Understanding the Impact: A Deeper Look at the Map’s Significance
The Kentucky Voting Districts Map plays a crucial role in shaping the state’s political landscape, impacting a wide range of issues, including:
- Electoral Outcomes: The way districts are drawn can influence the outcome of elections, determining which candidates are elected and which party controls the legislature.
- Policy Priorities: The composition of the legislature, determined by the voting districts, influences the policy priorities of the state, affecting issues such as education, healthcare, and economic development.
- Community Representation: The map determines which communities are grouped together within a district, potentially influencing their shared interests and their ability to advocate for their needs.
- Public Engagement: Understanding the map and its implications can empower citizens to participate in the political process and hold their elected officials accountable.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About the Kentucky Voting Districts Map
1. How often are Kentucky voting districts redrawn?
Kentucky voting districts are redrawn every ten years, coinciding with the decennial U.S. Census. This process ensures that districts reflect population changes and maintain equal representation.
2. Who is responsible for redrawing Kentucky voting districts?
The responsibility for redrawing Kentucky voting districts rests with the state legislature. However, the Fair Districts Act of 2018 established independent commissions to oversee the process, aiming to minimize partisan influence.
3. How can I find my Kentucky voting district?
You can find your Kentucky voting district by visiting the Kentucky Secretary of State’s website or contacting your local county clerk’s office.
4. What are the criteria used to draw Kentucky voting districts?
The criteria used to draw Kentucky voting districts include population equality, compactness, contiguity, minority representation, and consideration of communities of interest.
5. How can I get involved in the redistricting process?
You can get involved in the redistricting process by attending public hearings, submitting testimony, and advocating for fair representation.
Tips: Navigating the Kentucky Voting Districts Map for Informed Participation
- Become familiar with the map: Take the time to understand the boundaries of your district and the communities it encompasses.
- Research your elected officials: Learn about the representatives who represent your district and their voting records.
- Engage in public discourse: Participate in discussions about redistricting and advocate for fair representation.
- Stay informed about legal challenges: Follow legal challenges related to the map and understand their potential impact.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Ensuring Fair and Effective Representation
The Kentucky Voting Districts Map, though often overlooked, is a vital tool for ensuring fair and effective representation in the state’s political system. Understanding its history, its current configuration, and its impact on the political landscape empowers citizens to participate in the democratic process and hold their elected officials accountable. By engaging with the map and advocating for fair representation, citizens can contribute to a more inclusive and responsive government, reflecting the diverse voices and interests of all Kentuckians.



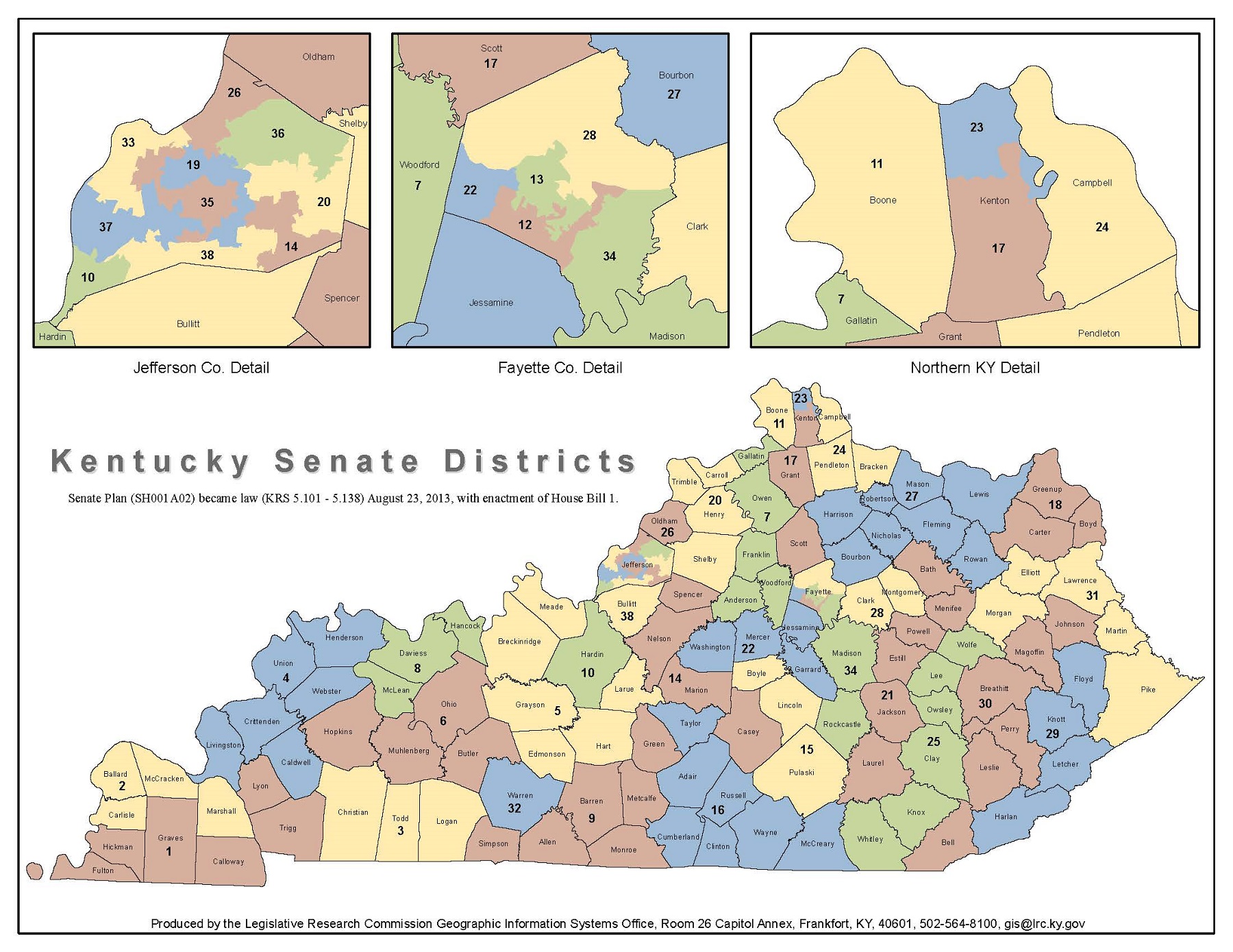
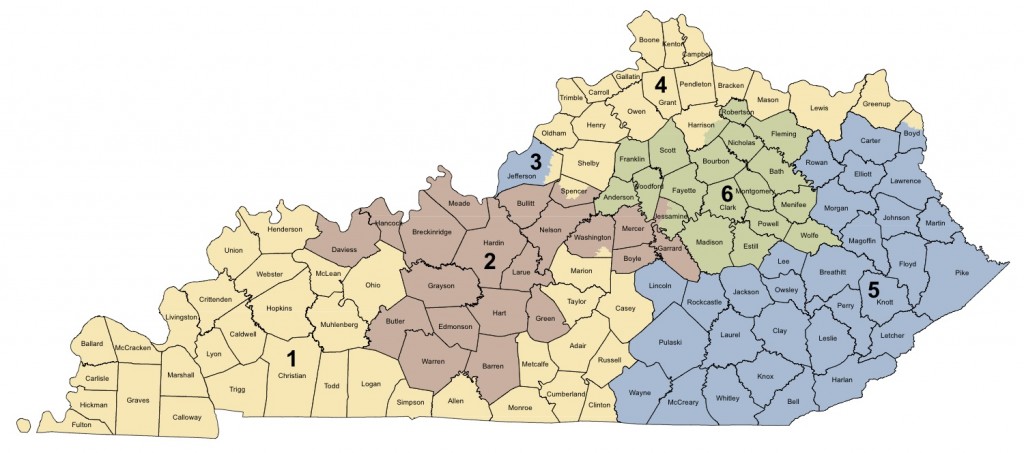

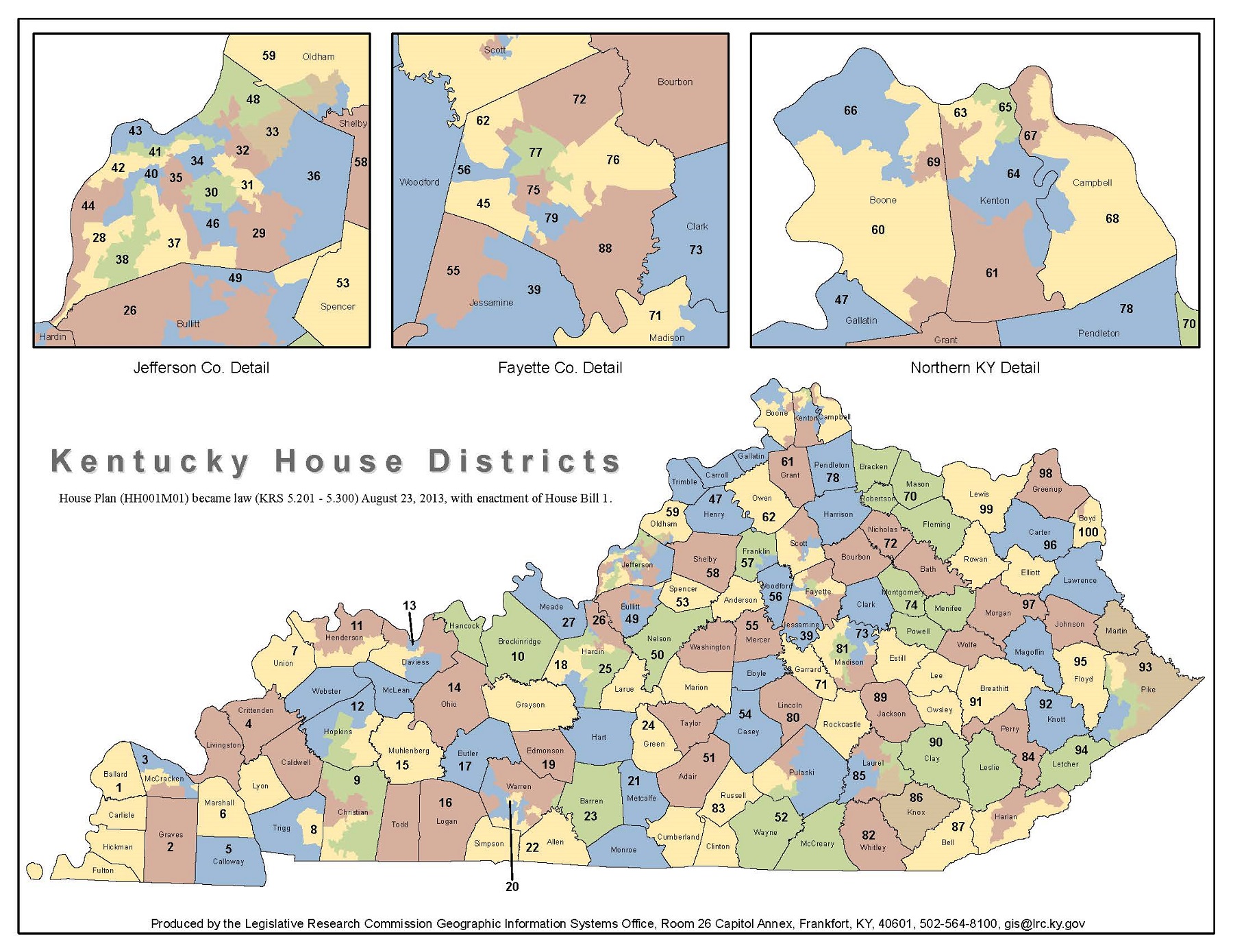
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Kentucky Voting Districts Map: A Vital Tool for Democracy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!