The Korean Peninsula: A Geographic Overview and Its Significance
Related Articles: The Korean Peninsula: A Geographic Overview and Its Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Korean Peninsula: A Geographic Overview and Its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Korean Peninsula: A Geographic Overview and Its Significance
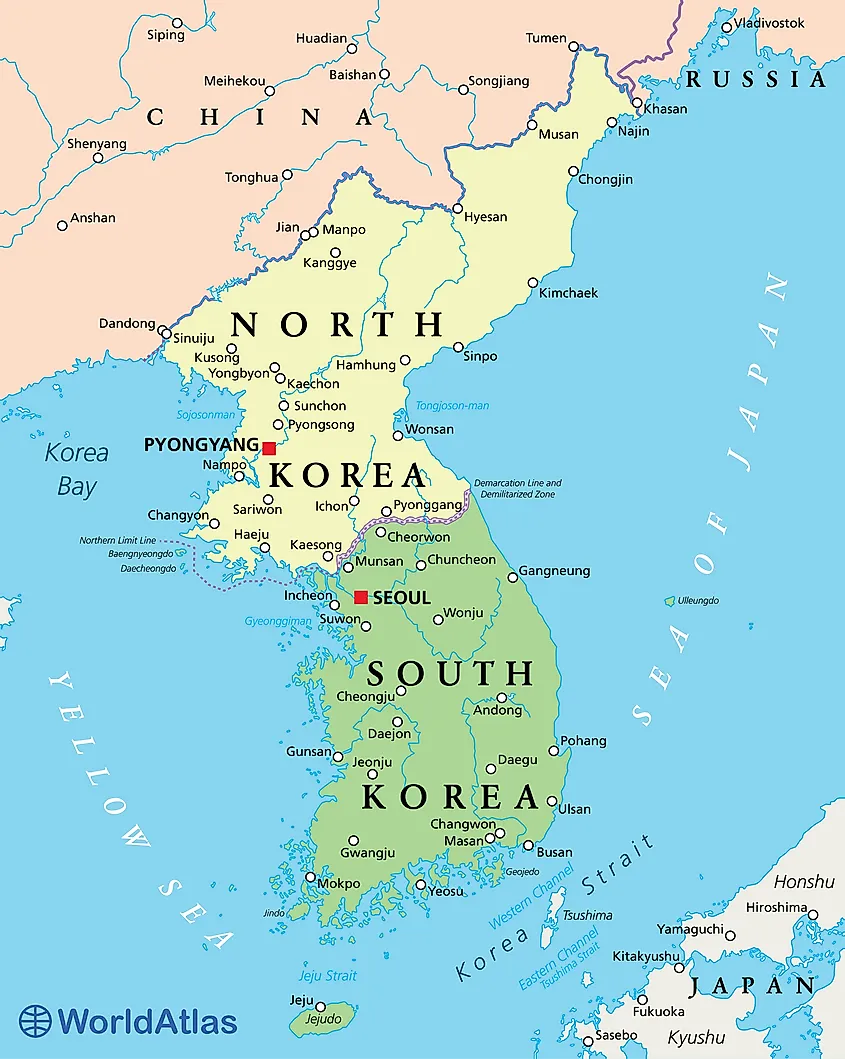
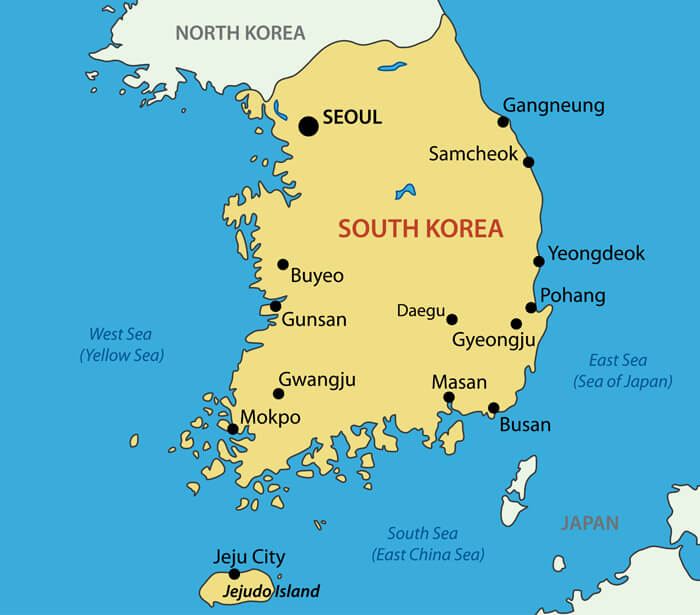
The Korean Peninsula, a landmass jutting out from the eastern edge of the Asian continent, is a region steeped in history, culture, and geopolitical significance. Its unique geography, shaped by mountains, rivers, and a long coastline, has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and continues to influence its present and future. This article explores the geographical features of the Korean Peninsula, examining its physical characteristics, political divisions, and the multifaceted implications of its location.
A Land of Mountains and Rivers
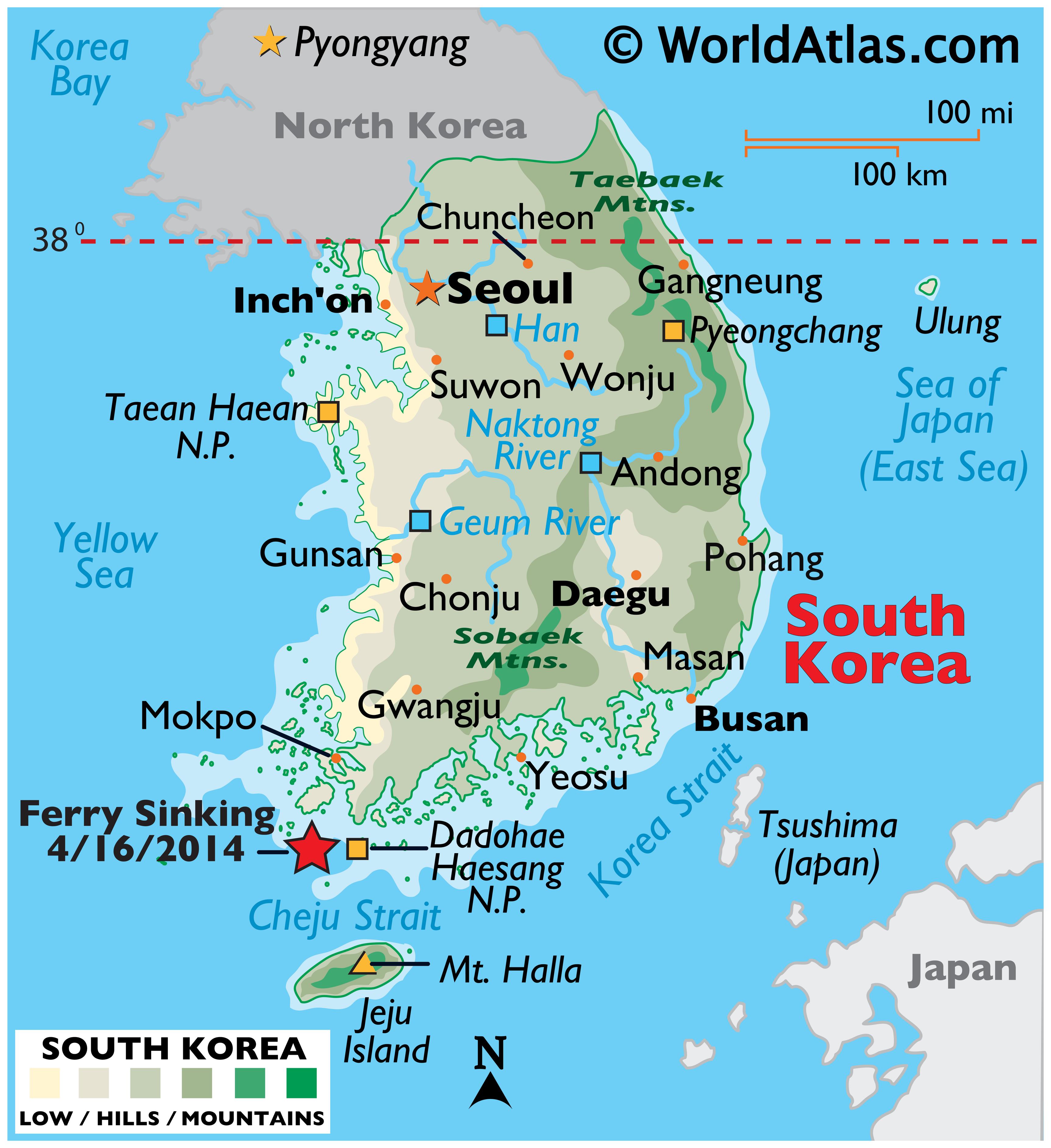
The Korean Peninsula is dominated by a rugged, mountainous terrain. The Taebaek Mountains, running along the eastern coast, form the peninsula’s backbone, reaching heights of over 2,700 meters. These mountains create a natural barrier between the east and west coasts, influencing the distribution of population and economic activity. The Sobaek Mountains, extending southwestward from the Taebaek range, further divide the peninsula, creating distinct geographical regions.
The peninsula’s numerous rivers, including the Han River, the Yalu River, and the Tumen River, flow from the mountains towards the surrounding seas, providing vital sources of water for agriculture and transportation. The Han River, flowing through the capital city of Seoul, is particularly significant, serving as a major waterway and a source of drinking water for millions of people.
A Divided Peninsula: North and South Korea
The Korean Peninsula is divided into two distinct entities: North Korea and South Korea. This division, a consequence of the Korean War (1950-1953), has resulted in a stark contrast in political systems, economic development, and societal structures.
North Korea, officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), occupies the northern portion of the peninsula. It is characterized by a communist regime, a centrally planned economy, and a highly militarized society.
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), occupies the southern portion of the peninsula. It is a democratic republic with a market-oriented economy and a technologically advanced society.
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), a 4-kilometer-wide buffer zone separating North and South Korea, serves as a tangible reminder of the division and the ongoing tension between the two states.
A Strategic Location
The Korean Peninsula occupies a strategically important location in Northeast Asia. Its proximity to China, Japan, and Russia makes it a crucial player in regional dynamics. The peninsula’s strategic importance is further amplified by its control over key waterways, including the Sea of Japan, the Yellow Sea, and the East China Sea.
The peninsula’s strategic significance has been a source of both opportunity and conflict. The Korean War, fueled by Cold War tensions, demonstrates the potential for conflict in the region. However, the peninsula’s strategic location also offers opportunities for economic cooperation and regional integration.
The Impact of Geography on History and Culture
The Korean Peninsula’s unique geography has played a crucial role in shaping its history and culture. The mountainous terrain, for instance, has traditionally hindered communication and transportation, contributing to the development of distinct regional cultures. The peninsula’s long coastline, however, has facilitated trade and cultural exchange with neighboring countries.
The peninsula’s geography has also influenced the development of Korean agriculture. The fertile plains along the rivers have supported a rich agricultural tradition, while the mountainous regions have provided opportunities for forestry and mining.
The Importance of Understanding the Map
Understanding the map of the Korean Peninsula is essential for comprehending its complex history, its current political situation, and its future prospects. The map provides a visual representation of the peninsula’s geographical features, its political divisions, and its strategic location. By studying the map, we can gain insights into the factors that have shaped the peninsula’s past and continue to influence its present and future.
FAQs about the Map of Korea
Q1: What are the main geographical features of the Korean Peninsula?
A: The Korean Peninsula is characterized by a mountainous terrain, with the Taebaek and Sobaek mountain ranges dominating its landscape. The peninsula is also home to numerous rivers, including the Han River, the Yalu River, and the Tumen River.
Q2: What is the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)?
A: The DMZ is a 4-kilometer-wide buffer zone separating North and South Korea. It was established as part of the Korean War armistice agreement in 1953 and remains a highly militarized zone.
Q3: What are the major cities in North and South Korea?
A: Major cities in North Korea include Pyongyang (the capital), Hamhung, and Chongjin. Major cities in South Korea include Seoul (the capital), Busan, Daegu, and Incheon.
Q4: What is the significance of the Korean Peninsula’s location?
A: The Korean Peninsula occupies a strategically important location in Northeast Asia, bordering China, Japan, and Russia. Its control over key waterways makes it a crucial player in regional dynamics.
Q5: How has the Korean Peninsula’s geography influenced its history and culture?
A: The peninsula’s mountainous terrain has traditionally hindered communication and transportation, contributing to the development of distinct regional cultures. The peninsula’s long coastline, however, has facilitated trade and cultural exchange with neighboring countries.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Korea
- Study the major geographical features: Familiarize yourself with the Taebaek and Sobaek mountain ranges, the Han River, and the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ).
- Locate the major cities: Identify the capital cities of North and South Korea (Pyongyang and Seoul) and other major urban centers.
- Understand the political divisions: Recognize the boundary between North and South Korea and the location of the DMZ.
- Consider the peninsula’s strategic location: Analyze the peninsula’s proximity to China, Japan, and Russia and its control over key waterways.
- Explore the historical and cultural influences: Understand how the peninsula’s geography has shaped its history, culture, and society.
Conclusion
The map of the Korean Peninsula is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s complex history, its present political situation, and its future prospects. By studying the map, we can gain insights into the peninsula’s unique geographical features, its political divisions, and its strategic location. This knowledge is crucial for comprehending the challenges and opportunities facing the Korean Peninsula and for fostering a deeper understanding of the region’s role in global affairs.
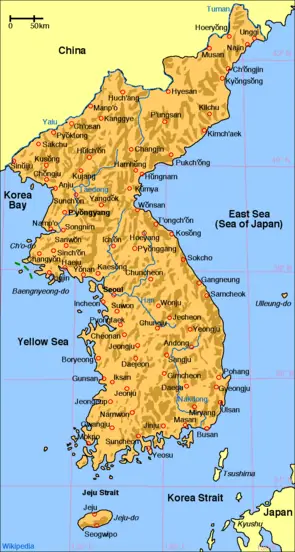


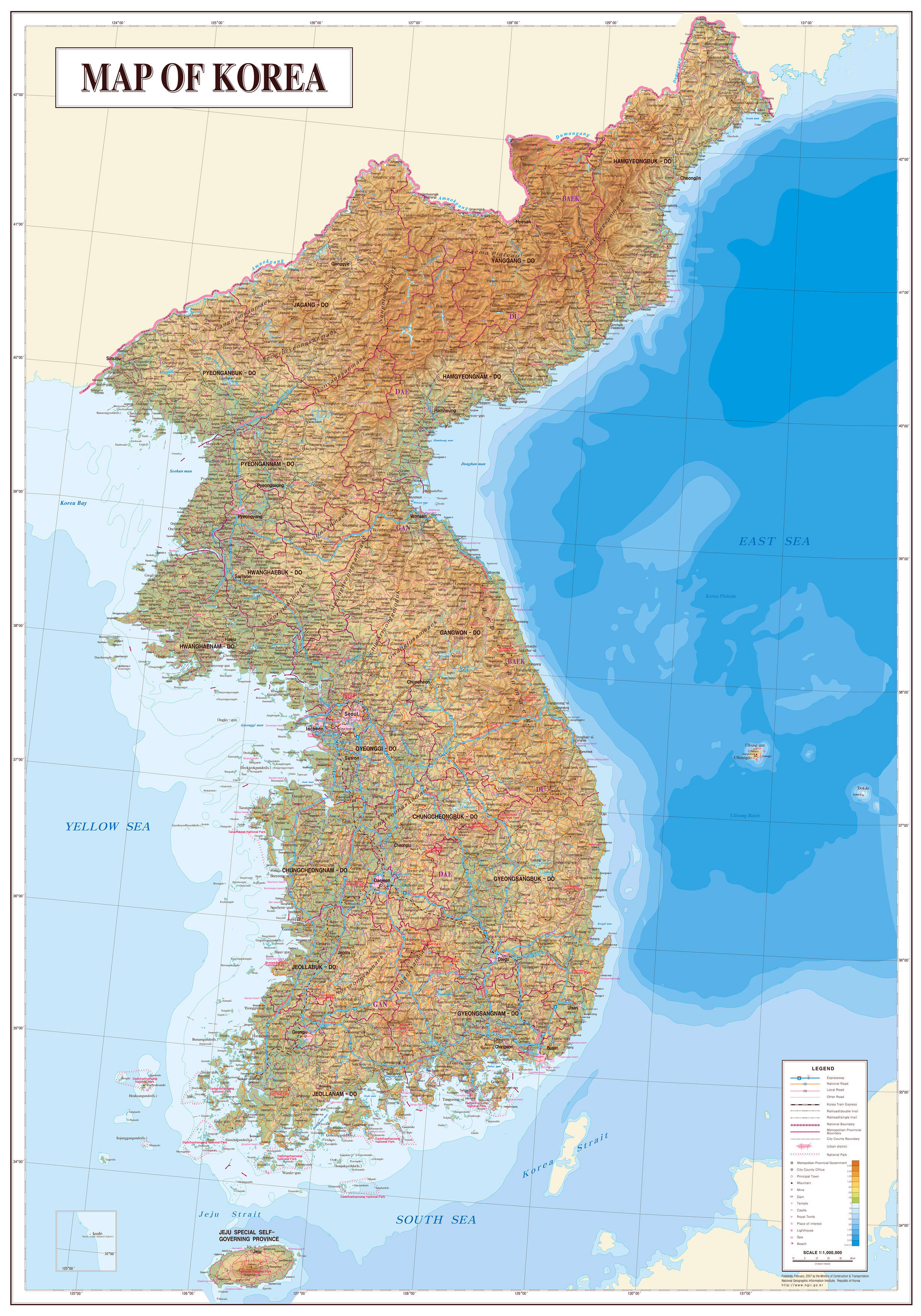
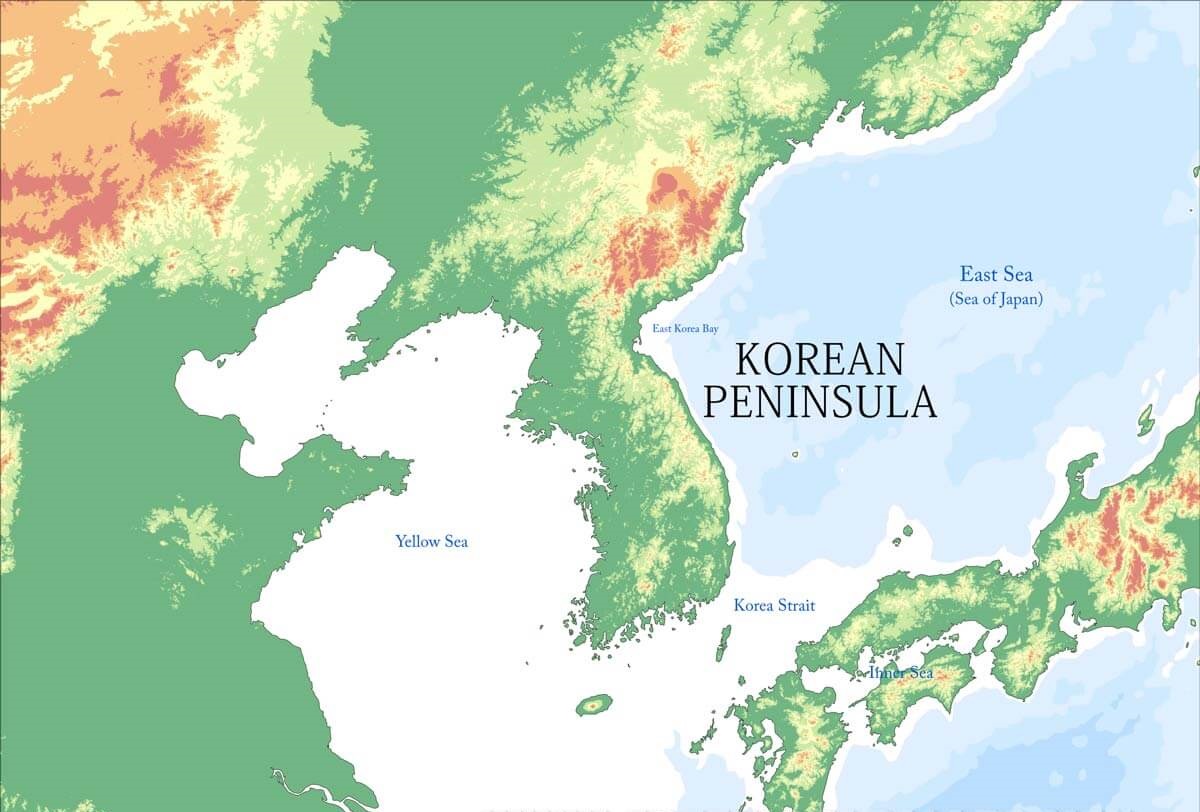

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Korean Peninsula: A Geographic Overview and Its Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!