The Power of Interactive Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Pinpoint Locations
Related Articles: The Power of Interactive Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Pinpoint Locations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Interactive Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Pinpoint Locations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Interactive Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Pinpoint Locations

Interactive maps, often referred to as "pinpoint maps," have revolutionized how we visualize, analyze, and share spatial information. These powerful tools allow users to place markers, known as pins, on a map, annotating specific locations with data, images, or other relevant information. This ability to overlay data onto a visual representation of the world has transformed various fields, from urban planning and environmental monitoring to personal travel and social media engagement.
Understanding the Essence of Interactive Maps
At its core, interactive mapping is about creating a dynamic and user-friendly interface for exploring geographic data. These maps go beyond static representations, offering a platform for:
- Data Visualization: Interactive maps facilitate the visualization of diverse datasets, ranging from population density and crime rates to business locations and natural resource distribution. By overlaying data points on a map, users can instantly grasp spatial patterns and trends that might be obscured in tabular data.
- Location-Based Insights: Interactive maps provide a powerful tool for deriving location-based insights. By analyzing the distribution of pins, users can identify clusters, outliers, and areas of interest. This can be invaluable for understanding geographic phenomena, optimizing resource allocation, or identifying potential opportunities.
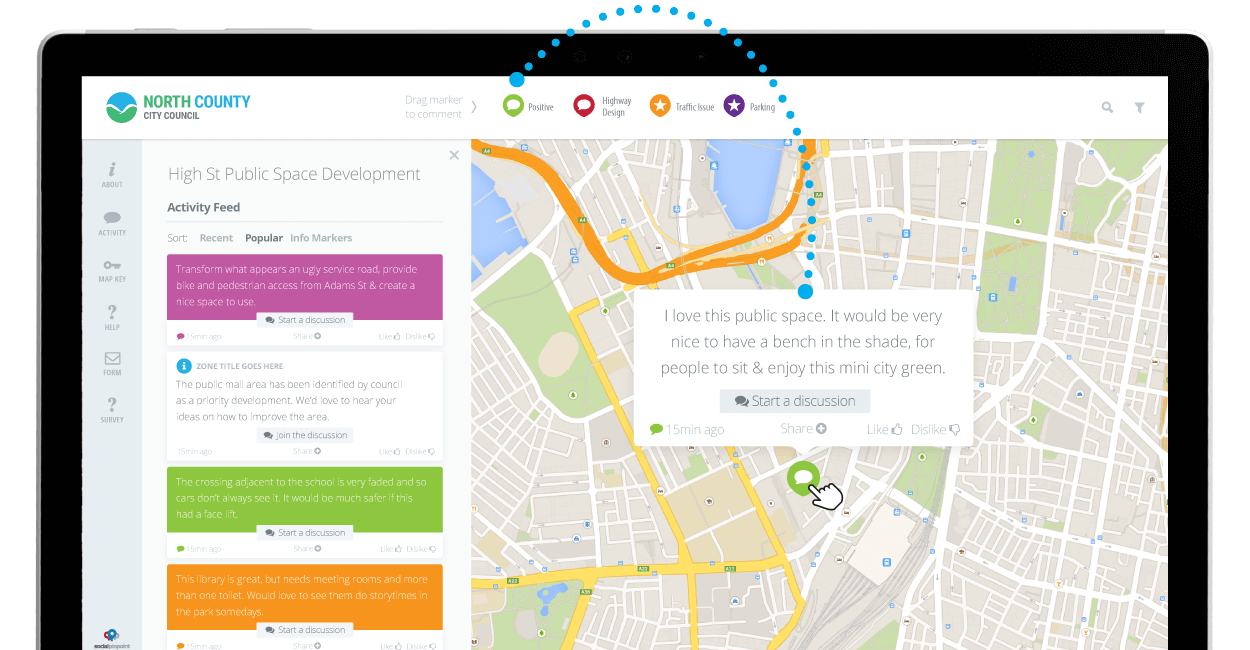
- Collaboration and Communication: Interactive maps foster collaboration and communication by allowing users to share their insights and findings with others. Through annotations, comments, and shared layers, users can work together on projects, exchange ideas, and build a collective understanding of the data.
The Anatomy of an Interactive Map
Interactive maps are typically built on a foundation of geographic information systems (GIS) technology. This underlying framework enables the integration of diverse data sources, including:
- Base Maps: The foundation of an interactive map is the base map, which provides the geographical context. This could be a standard map of the world, a specific region, or even a custom-designed map.
- Data Layers: Data layers represent different datasets that are overlaid on the base map. These layers can include points, lines, polygons, or raster data, each representing a specific type of information.
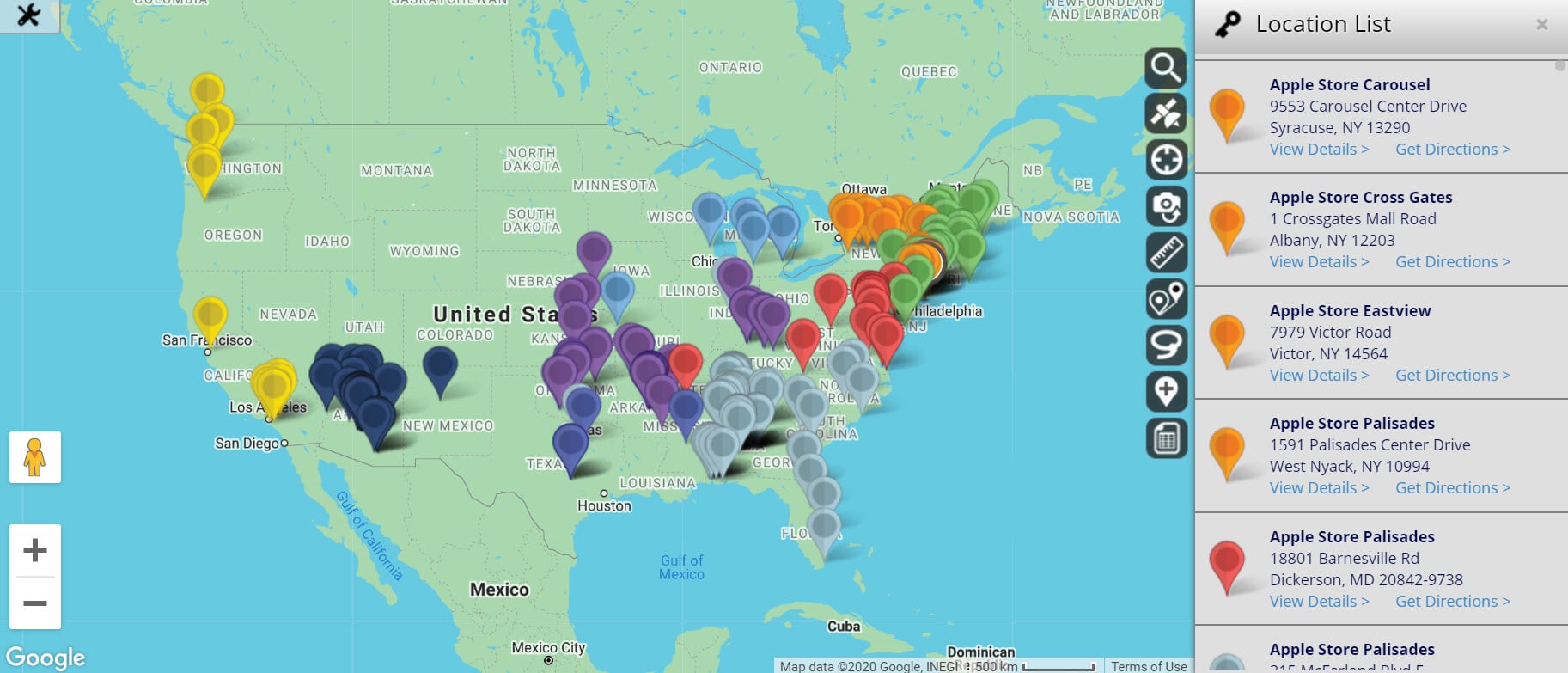
- Pins (Markers): Pins are the visual markers placed on the map to represent specific locations. They can be customized with different colors, sizes, and icons to differentiate between data points.
- Annotations: Annotations allow users to add text, images, or other information to pins, providing context and additional details about the location.
- Interactive Elements: Interactive elements, such as zoom controls, pan functionality, and search bars, allow users to explore the map freely and navigate to specific locations.
Exploring the Spectrum of Interactive Maps
The world of interactive mapping encompasses a diverse range of applications, catering to specific needs and purposes. Some prominent examples include:
- Google Maps: A ubiquitous platform for navigation, location discovery, and mapping, Google Maps integrates street view, traffic updates, and business listings, making it a valuable tool for individuals and businesses alike.
- ArcGIS Online: A professional-grade platform for creating, sharing, and analyzing geographic data, ArcGIS Online offers a robust suite of tools for spatial analysis, data visualization, and collaboration.
- Leaflet and OpenLayers: Open-source mapping libraries, Leaflet and OpenLayers, empower developers to create custom interactive maps, integrating various data sources and functionalities.
- Social Media Platforms: Platforms like Facebook and Instagram utilize interactive maps to visualize user-generated content, such as check-ins, photos, and events, offering a unique perspective on social activity and trends.
The Importance of Interactive Maps in Diverse Fields
The versatility of interactive mapping has led to its widespread adoption across diverse fields, revolutionizing how we approach various challenges and opportunities:
- Urban Planning: Interactive maps enable planners to visualize city layouts, identify areas of congestion, and optimize infrastructure development. By overlaying data on population density, transportation networks, and land use, planners can make informed decisions about urban growth and development.
- Environmental Monitoring: Interactive maps play a crucial role in environmental monitoring, allowing researchers to track deforestation, analyze air pollution patterns, and monitor natural disasters. By visualizing data on environmental variables, researchers gain a deeper understanding of environmental changes and their impact.
- Business and Marketing: Interactive maps empower businesses to visualize customer locations, analyze market trends, and target their marketing efforts effectively. By mapping customer demographics, competitor locations, and potential growth areas, businesses can make data-driven decisions to optimize their operations.
- Public Health: Interactive maps are instrumental in public health initiatives, allowing epidemiologists to track disease outbreaks, identify high-risk areas, and monitor the effectiveness of public health interventions. By visualizing data on disease prevalence, vaccination rates, and healthcare access, public health officials can develop targeted strategies to improve health outcomes.
- Education and Research: Interactive maps provide engaging tools for education and research, allowing students and researchers to explore geographic concepts, analyze data, and visualize complex relationships. By creating interactive maps, educators can bring geographic concepts to life and facilitate deeper learning.
FAQs on Interactive Maps
Q: What are the benefits of using interactive maps?
A: Interactive maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Visualization: Interactive maps provide a clear and intuitive way to visualize geographic data, making it easier to understand spatial patterns and trends.
- Data-Driven Insights: By analyzing the distribution of data points on interactive maps, users can derive valuable insights about geographic phenomena and relationships.
- Collaboration and Communication: Interactive maps facilitate collaboration and communication by allowing users to share their insights, findings, and annotations with others.
- Improved Decision-Making: Interactive maps provide a powerful tool for making informed decisions based on geographic data, optimizing resource allocation and planning strategies.
Q: What are some limitations of interactive maps?
A: While interactive maps offer numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of potential limitations:
- Data Accuracy and Availability: The accuracy and availability of data can significantly impact the effectiveness of interactive maps. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading conclusions.
- Technical Expertise: Creating and customizing interactive maps often requires technical expertise in GIS software and data manipulation.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Using interactive maps with sensitive data raises concerns about data privacy and security. It’s essential to implement appropriate measures to protect user information.
Q: How can I create my own interactive map?
A: There are various tools and platforms available for creating interactive maps, ranging from user-friendly online platforms to more advanced GIS software:
- Online Platforms: Platforms like Google My Maps, Leaflet.js, and Mapbox provide intuitive interfaces for creating and sharing interactive maps.
- GIS Software: ArcGIS Online, QGIS, and other GIS software offer a comprehensive suite of tools for creating and analyzing interactive maps, requiring more technical expertise.
Tips for Effective Use of Interactive Maps
- Choose the Right Tool: Select the appropriate mapping tool based on your specific needs and technical expertise.
- Understand Your Data: Ensure you have accurate and reliable data to use in your interactive maps.
- Design for Clarity: Create a visually appealing and easy-to-understand map, using clear labels, distinct colors, and intuitive icons.
- Engage Users: Include interactive elements, such as zoom controls, search bars, and annotations, to encourage user engagement.
- Promote Collaboration: Enable users to share their insights, annotations, and findings to foster collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Conclusion
Interactive maps have become indispensable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and sharing geographic data. By offering a dynamic and user-friendly interface for exploring spatial information, these maps empower individuals and organizations to gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and foster collaboration. From urban planning and environmental monitoring to business analysis and public health initiatives, interactive maps have revolutionized how we interact with and understand the world around us. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more powerful and innovative applications of interactive mapping, further enhancing our ability to visualize, analyze, and communicate spatial information.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Interactive Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Pinpoint Locations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!