The Shifting Landscape of Europe: A Geographic Analysis of the Impact of World War I
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Europe: A Geographic Analysis of the Impact of World War I
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Europe: A Geographic Analysis of the Impact of World War I. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape of Europe: A Geographic Analysis of the Impact of World War I
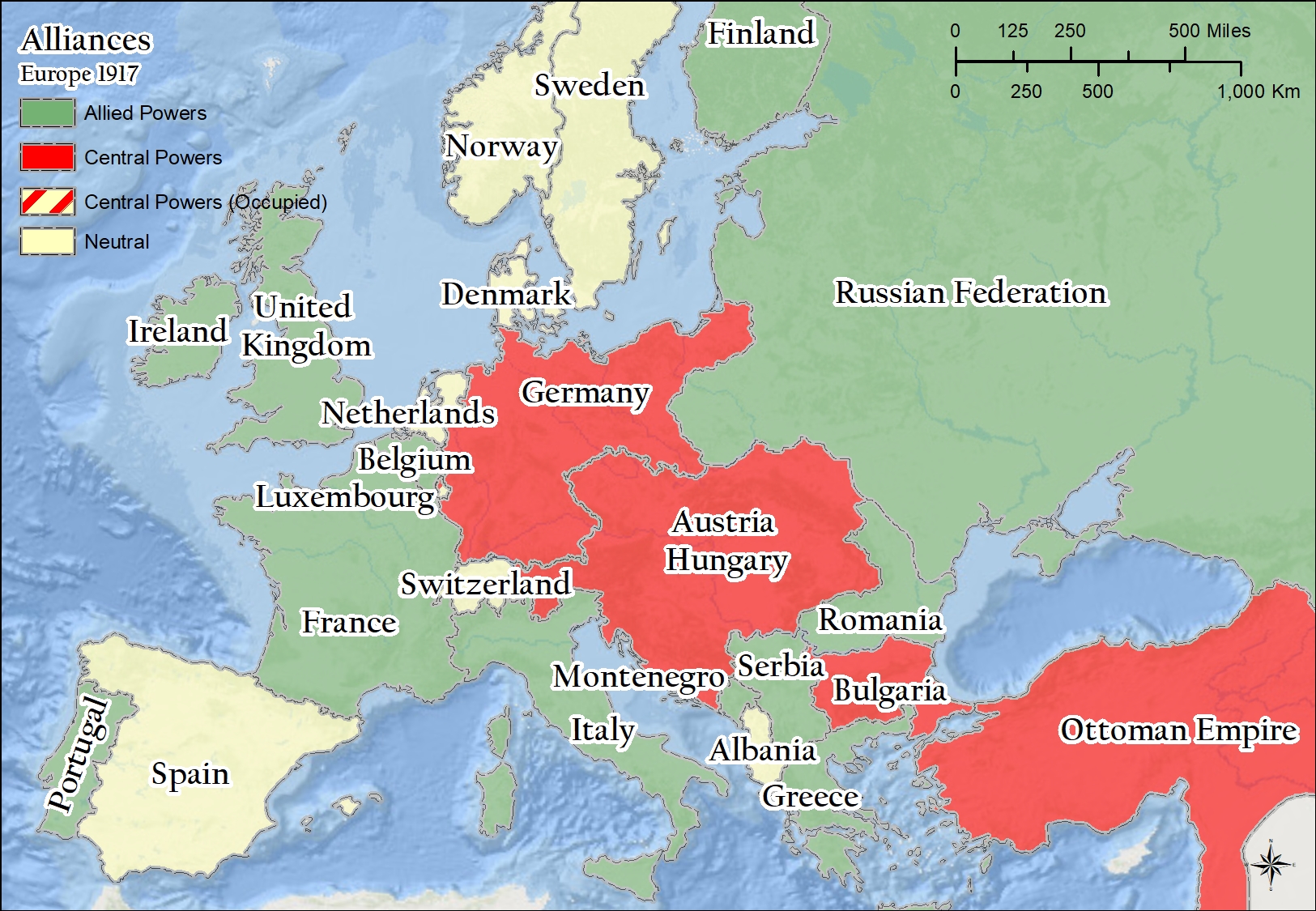
World War I, a cataclysmic event that reshaped the global order, also profoundly altered the political and geographical landscape of Europe. A comparative analysis of maps from the pre-war era and the immediate post-war period reveals the dramatic transformations that occurred, leaving an indelible mark on the continent’s political, social, and economic fabric.
Europe Before the Great War: A Patchwork of Empires and Kingdoms
Pre-World War I Europe was a complex mosaic of empires, kingdoms, and smaller states, each with its unique history, culture, and political system.
- The Austro-Hungarian Empire: This vast, multi-ethnic empire, encompassing present-day Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and parts of Romania, Ukraine, and Italy, was a major power in Central Europe. Its diverse population, coupled with internal tensions, laid the groundwork for its eventual disintegration.
- The Russian Empire: Stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Pacific Ocean, the Russian Empire was a vast landmass encompassing a multitude of ethnic groups. Its autocratic rule and internal economic disparities contributed to its vulnerability and ultimate collapse.
- The German Empire: Unified in 1871, the German Empire was a relatively new power, but its rapid industrialization and military strength made it a formidable force in Europe. Its ambitions for expansion and dominance fueled tensions with other European powers.
- The Ottoman Empire: Once a vast empire spanning much of the Middle East, North Africa, and the Balkans, the Ottoman Empire was in decline by the early 20th century. Its weakening hold on its diverse territories contributed to instability in the region.
- The British Empire: The British Empire, at its peak, encompassed a vast network of colonies and dominions across the globe. Its naval dominance and economic power made it a major player in European politics.
- France: A major power in Europe, France had been weakened by the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71 but remained a significant player in international affairs.
- Italy: Unified in 1861, Italy was still a relatively new nation-state, seeking to expand its territory and influence.
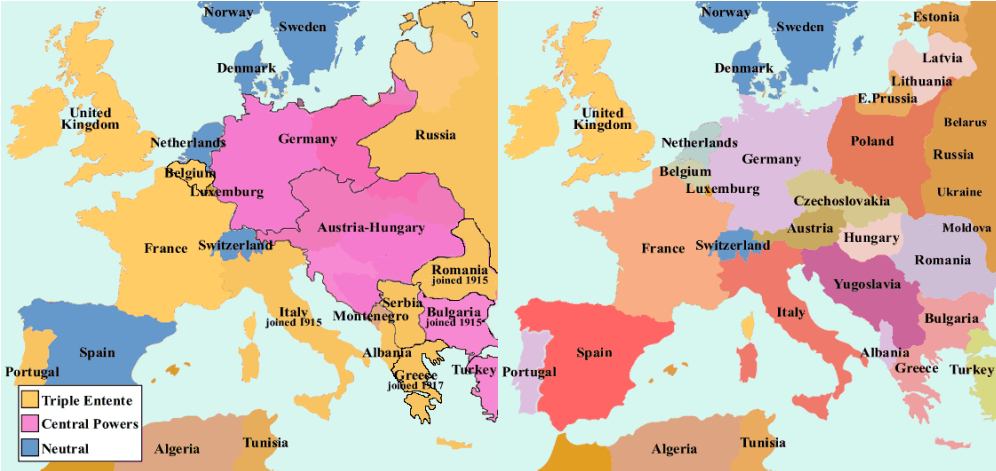
The Impact of World War I: A Remapping of Europe
The First World War brought about a profound reshaping of Europe’s political map, leading to:
- The Collapse of Empires: The war witnessed the disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian, Russian, and Ottoman Empires. The Austro-Hungarian Empire was dissolved, giving rise to new nations like Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, and Poland. The Russian Empire collapsed, leading to the formation of the Soviet Union and the emergence of independent Baltic states. The Ottoman Empire was significantly reduced in size, with territories in the Middle East, North Africa, and the Balkans being carved up into new states.
- The Rise of New Nations: The collapse of empires paved the way for the creation of new nation-states, including Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Finland, and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (later Yugoslavia). These new nations were often formed based on ethnic and linguistic principles, contributing to a more fragmented map of Europe.
- The Creation of New Boundaries: The redrawing of boundaries following the war led to significant changes in the political geography of Europe. Some boundaries were drawn along ethnic lines, while others were determined by strategic considerations or the interests of victorious powers. This process often resulted in the displacement of populations and the creation of new minority groups within newly formed states.
- The Rise of Germany and the Treaty of Versailles: Germany, despite its defeat in the war, emerged as a significant power in Europe. The Treaty of Versailles, while imposing harsh penalties on Germany, ultimately contributed to the rise of nationalist sentiment and contributed to the instability that would lead to the outbreak of World War II.
- The League of Nations: The establishment of the League of Nations, an international organization aimed at preventing future wars, was a significant development in the post-war period. However, its lack of enforcement power and the absence of major powers like the United States limited its effectiveness.
The Legacy of the First World War: A New Order and Enduring Tensions
The First World War left a lasting impact on Europe’s political and geographical landscape, shaping the continent’s future in significant ways.
- The Rise of Nationalism and Ethnic Conflicts: The creation of new nation-states based on ethnic principles often led to the emergence of new nationalisms and ethnic conflicts. These tensions continued to simmer in the interwar period, contributing to the rise of extremism and instability.
- The Rise of Totalitarian Regimes: The economic and social upheaval caused by the war contributed to the rise of totalitarian regimes in Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union. These regimes promised a return to order and stability, but ultimately led to further instability and conflict.
- The Seeds of World War II: The unresolved issues from the First World War, including the Treaty of Versailles, the rise of nationalism, and the emergence of totalitarian regimes, laid the groundwork for the outbreak of World War II.
FAQs: Exploring the Impact of World War I on Europe’s Map
1. What were the main reasons for the redrawing of boundaries after World War I?
The redrawing of boundaries after World War I was driven by several factors:
- Ethnic Considerations: The creation of new nation-states based on ethnic principles was a major driving force behind the redrawing of boundaries.
- Strategic Considerations: The victorious powers sought to create boundaries that would weaken potential adversaries and ensure their own security.
- Economic Interests: The redrawing of boundaries also reflected economic interests, with the victorious powers seeking to control key resources and trade routes.
2. How did the Treaty of Versailles impact the political map of Europe?
The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including the loss of territory, military restrictions, and heavy financial reparations. These punitive measures contributed to the rise of nationalist sentiment in Germany and sowed the seeds of future conflict.
3. What were the main challenges faced by the new nation-states created after World War I?
The new nation-states created after World War I faced numerous challenges, including:
- Ethnic Tensions: Many of these states were comprised of diverse ethnic groups, leading to internal tensions and conflicts.
- Economic Instability: The war had devastated economies across Europe, and the new states struggled to rebuild their infrastructure and economies.
- Political Instability: The newly formed governments often lacked experience and faced challenges in establishing stable political systems.
4. How did World War I contribute to the rise of totalitarian regimes in Europe?
The economic and social upheaval caused by the war, coupled with the disillusionment with traditional political systems, created fertile ground for the rise of totalitarian regimes. These regimes promised a return to order and stability, but ultimately led to further instability and conflict.
5. How did the First World War change the balance of power in Europe?
The First World War significantly altered the balance of power in Europe. The collapse of the Austro-Hungarian, Russian, and Ottoman Empires led to the emergence of new nation-states and the rise of new powers, such as Germany and the Soviet Union. The war also weakened traditional powers like France and Britain, contributing to a more multipolar world order.
Tips for Analyzing Maps of Europe Before and After World War I
- Pay attention to the scale and date of the maps: The scale of the maps will determine the level of detail you can see, while the date will indicate the specific period being represented.
- Compare and contrast the maps: By comparing maps from the pre-war and post-war periods, you can identify the changes that occurred in the political geography of Europe.
- Focus on specific regions: Analyzing maps of specific regions, such as the Balkans or Central Europe, can help you understand the local impacts of the war.
- Consider the political, economic, and social context: The political, economic, and social context of the time period will help you understand the forces that shaped the changes in the map.
- Use historical sources: Consult historical sources, such as treaties, documents, and eyewitness accounts, to gain a deeper understanding of the events that led to the changes in the map.
Conclusion: A Reshaped Continent and a Legacy of Conflict
The First World War had a profound impact on the political and geographical landscape of Europe. The collapse of empires, the creation of new nation-states, and the redrawing of boundaries transformed the continent, leaving a legacy of conflict and instability. By examining maps from before and after the war, we can gain valuable insights into the dramatic transformations that occurred and the enduring consequences of this pivotal event in European history. The study of these maps serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of geography, politics, and history, and the profound impact that conflict can have on the world around us.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Europe: A Geographic Analysis of the Impact of World War I. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!