The Significance of Missing Data in Mapping: Understanding and Addressing Null Values
Related Articles: The Significance of Missing Data in Mapping: Understanding and Addressing Null Values
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Missing Data in Mapping: Understanding and Addressing Null Values. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of Missing Data in Mapping: Understanding and Addressing Null Values

Maps are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding spatial information. They allow us to see patterns, relationships, and trends across geographical areas. However, the accuracy and usefulness of maps rely heavily on the quality of the underlying data. A crucial aspect of data quality is the presence or absence of information, often represented as "null" values.
Null values, indicating missing data points, can be a significant challenge in mapping. While they may seem like mere gaps in information, their presence can distort analyses, lead to inaccurate interpretations, and hinder the effectiveness of maps.
This article aims to explore the concept of null values in mapping, delving into their causes, implications, and potential solutions. We will discuss strategies for addressing missing data, highlighting their importance in creating accurate and reliable maps.
Understanding the Nature of Null Values
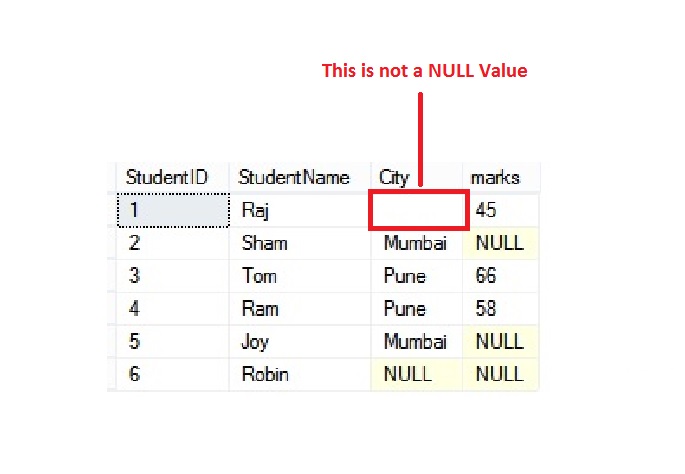
Null values, often represented as "NA" or "NULL" in data sets, signify the absence of a value for a specific attribute or variable. This absence can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Data Collection Errors: Errors during data collection, such as incomplete surveys or faulty sensors, can lead to missing data points.
- Data Entry Errors: Human error during data entry can result in missing or incorrect data values.
- Data Processing Issues: Issues during data processing, such as data transformation or cleaning, can lead to the removal or replacement of values, resulting in nulls.
- Data Availability Limitations: Data may not be available for certain areas or time periods, leading to null values.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Sensitive data may be masked or redacted, resulting in null values to protect privacy.
The Impact of Null Values on Mapping
The presence of null values can significantly impact the accuracy and interpretability of maps. Here are some key consequences:
- Distorted Visualizations: Missing data can create gaps or distortions in maps, potentially misrepresenting the true distribution of phenomena.
- Inaccurate Statistical Analysis: Null values can skew statistical calculations, leading to inaccurate results and misleading conclusions.
- Limited Spatial Analysis Capabilities: Missing data can hinder the ability to perform spatial analyses, such as interpolation, spatial autocorrelation, or cluster analysis.
- Misinterpretation and Decision-Making: Maps with missing data can lead to incorrect interpretations, potentially resulting in flawed decisions.
Addressing Null Values in Mapping
While null values can be problematic, they are not insurmountable. Several strategies can be employed to address missing data and improve the accuracy and reliability of maps:
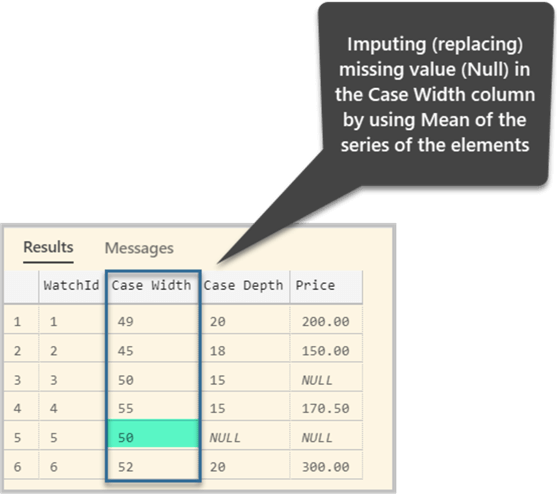
1. Data Imputation: This involves estimating missing values based on existing data. Techniques include:
- Mean/Median Imputation: Replacing null values with the mean or median of the available data.
- Regression Imputation: Using regression models to predict missing values based on relationships with other variables.
- Hot Deck Imputation: Assigning null values with values from similar cases with complete data.
2. Data Deletion: In certain situations, deleting records with null values may be an appropriate approach, particularly when:
- Missing data is insignificant: If the number of missing values is small and does not significantly impact the overall analysis.
- Data is unreliable: If missing data is due to errors or inconsistencies, deletion might be preferable.
3. Data Aggregation: Combining data points to create larger units can reduce the impact of null values. This approach is particularly useful for:
- Large-scale mapping: Aggregating data to create regional or national-level maps.
- Analyzing trends over time: Aggregating data over specific time periods to identify trends.
4. Visualization Techniques: Employing visualization techniques to highlight the presence of null values can help users interpret maps more accurately:
- Null value symbols: Using distinct symbols or colors to represent null values on the map.
- Transparency: Using transparency to indicate areas with missing data, allowing users to see underlying data patterns.
- Legend entries: Clearly labeling null values in the map legend to ensure user understanding.
5. Data Quality Control: Implementing robust data quality control measures during data collection and processing can minimize the occurrence of null values. This includes:
- Data validation: Verifying data accuracy and completeness before entering it into the system.
- Data cleaning: Identifying and correcting errors or inconsistencies in the data.
- Data documentation: Maintaining clear and comprehensive documentation of data sources, collection methods, and processing steps.
FAQs about Null Values in Mapping
1. What are the common causes of null values in mapping data?
Common causes include data collection errors, data entry errors, data processing issues, data availability limitations, and data privacy concerns.
2. How can null values impact the accuracy of maps?
Null values can distort visualizations, skew statistical analyses, limit spatial analysis capabilities, and lead to misinterpretations and flawed decision-making.
3. What are some effective strategies for addressing null values?
Strategies include data imputation, data deletion, data aggregation, visualization techniques, and data quality control.
4. What are the limitations of data imputation techniques?
Data imputation can introduce bias if the imputation method is not appropriate for the data. It is important to carefully consider the choice of imputation method and its potential impact on the results.
5. When is it appropriate to delete data points with null values?
Data deletion is appropriate when missing data is insignificant, data is unreliable, or when the number of null values is substantial and significantly impacts the analysis.
Tips for Working with Null Values in Mapping
- Document the reasons for null values: Clearly document the reasons for missing data to understand its potential impact.
- Consider the context of null values: The significance of null values can vary depending on the specific mapping application and data context.
- Use appropriate visualization techniques: Employ visualization methods that effectively highlight the presence of null values and ensure user understanding.
- Validate and clean data: Implement robust data quality control measures to minimize the occurrence of null values.
- Seek expert advice: Consult with experts in data management and spatial analysis for guidance on addressing null values in specific mapping projects.
Conclusion
Null values are an inevitable aspect of real-world data, including data used for mapping. While they can pose challenges, understanding their causes, implications, and potential solutions is crucial for creating accurate and reliable maps. By employing appropriate strategies to address missing data, we can enhance the effectiveness of maps and ensure they provide a clear and reliable representation of spatial information.
![missingno - Visualize Missing Values (NaNs / Null Values) Distribution in Datasets [Python]](https://storage.googleapis.com/coderzcolumn/static/tutorials/data_science/article_image/missingno%20-%20Visualize%20Missing%20Data%20in%20Python.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Missing Data in Mapping: Understanding and Addressing Null Values. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!