Understanding the Kentucky Flood Map: A Guide to Navigating Flood Risk
Related Articles: Understanding the Kentucky Flood Map: A Guide to Navigating Flood Risk
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Kentucky Flood Map: A Guide to Navigating Flood Risk. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Kentucky Flood Map: A Guide to Navigating Flood Risk
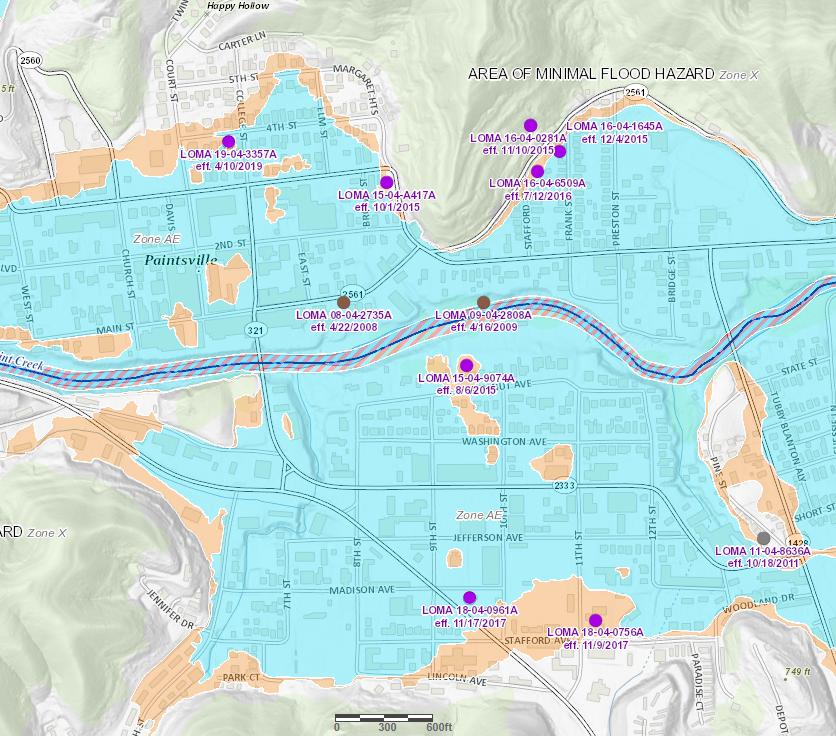
The state of Kentucky, known for its rolling hills and scenic landscapes, also faces a significant risk of flooding. Understanding flood risk is crucial for residents, businesses, and policymakers alike. The Kentucky Flood Map, a vital tool produced by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), provides a comprehensive overview of flood-prone areas within the state. This map serves as a foundational resource for informed decision-making, guiding development, infrastructure planning, and disaster preparedness efforts.
Delving into the Kentucky Flood Map
The Kentucky Flood Map, officially known as the Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM), is a detailed representation of flood risk zones across the state. It is a product of extensive data analysis, incorporating historical flood records, topographic information, and hydrological modeling. The map is organized into distinct flood zones, each representing a specific level of flood risk:
- Zone A: Areas with a 1% chance of flooding in any given year. These zones are typically located in floodplains and are considered high-risk areas.
- Zone B: Areas with a less than 1% chance of flooding in any given year. These zones are generally considered lower-risk areas, but still susceptible to flooding.
- Zone C: Areas that are not specifically designated as high-risk but may still experience flooding. These zones often lack sufficient data for definitive flood risk assessment.
- Zone X: Areas considered to be outside of the 100-year floodplain. While these areas are generally considered low-risk, it is important to note that flooding can occur outside of designated flood zones due to factors such as heavy rainfall or dam failures.
The Importance of the Kentucky Flood Map
The Kentucky Flood Map plays a critical role in numerous aspects of community planning and development:
- Flood Insurance: The FIRM serves as the foundation for the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), a federal program that provides flood insurance to property owners. The map identifies areas eligible for NFIP coverage, and the assigned flood zone determines the insurance premium.
- Development Regulations: Local governments use the FIRM to establish development regulations and zoning ordinances. These regulations aim to minimize the risk of development in high-risk flood zones, protecting lives and property.
- Infrastructure Planning: The map helps guide the planning and construction of infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and utilities. This ensures that critical infrastructure is located in areas less susceptible to flooding.
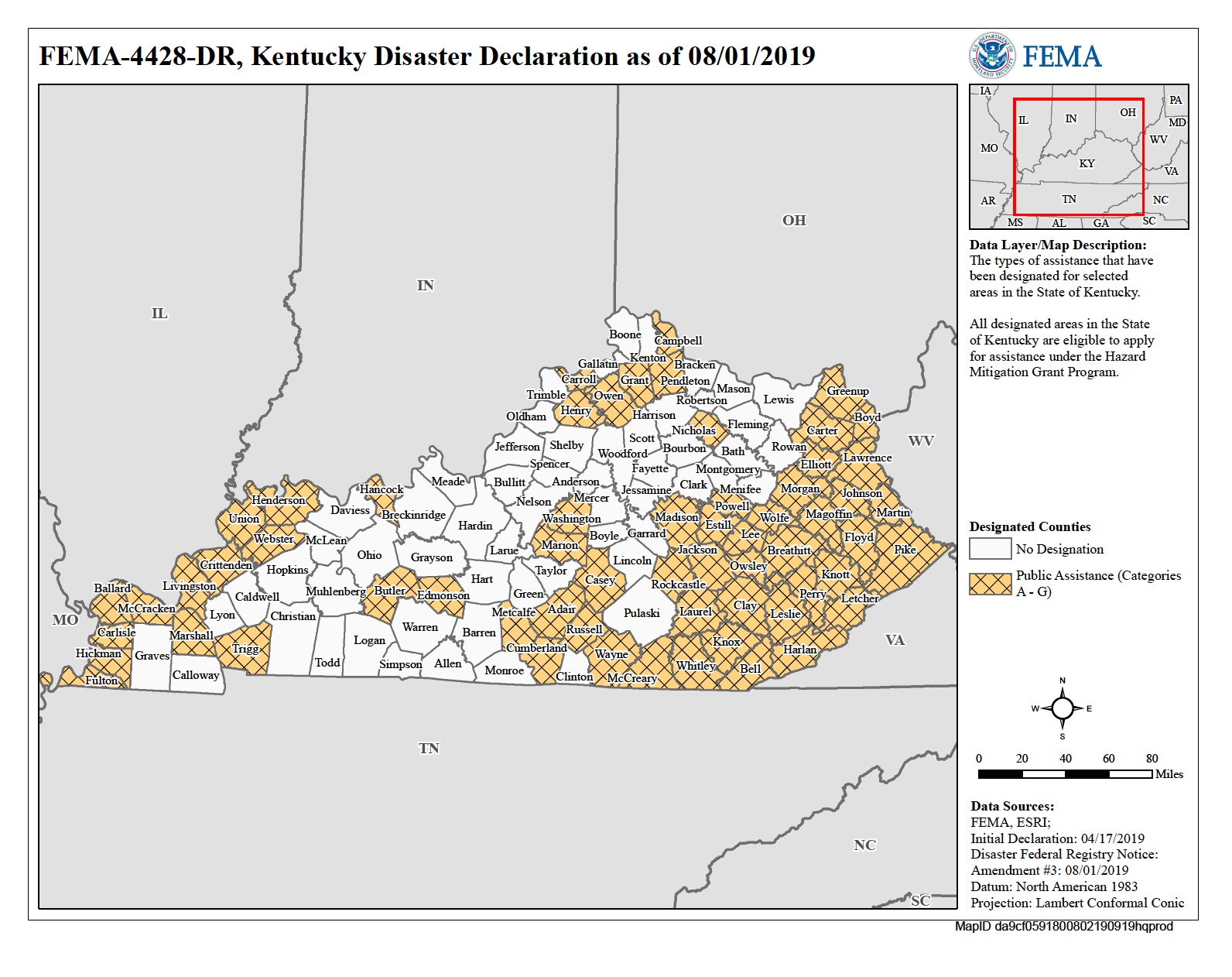
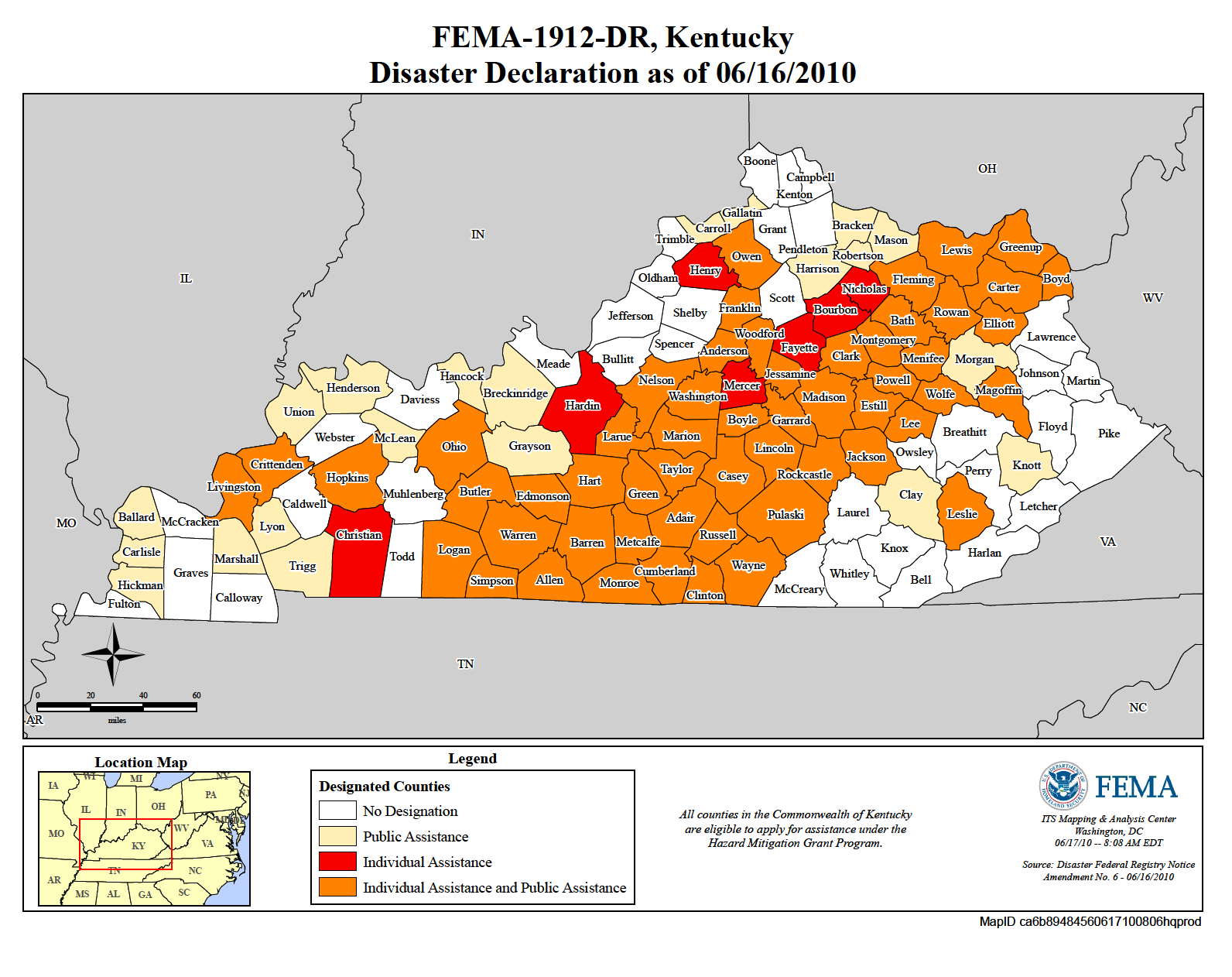
- Disaster Preparedness: The Kentucky Flood Map is an invaluable tool for emergency preparedness and response efforts. It allows communities to identify areas at risk and develop effective evacuation plans, emergency shelter strategies, and resource allocation plans.
- Public Awareness: The map promotes public awareness of flood risk, encouraging residents to understand the potential dangers and take necessary precautions.
Navigating the Kentucky Flood Map
The Kentucky Flood Map is available online through FEMA’s website and can be accessed through various digital platforms. Users can search for specific addresses or areas of interest and view the designated flood zone. The map provides detailed information, including:
- Flood zone designation: The specific flood zone category for the area.
- Base flood elevation: The elevation of the 100-year flood.
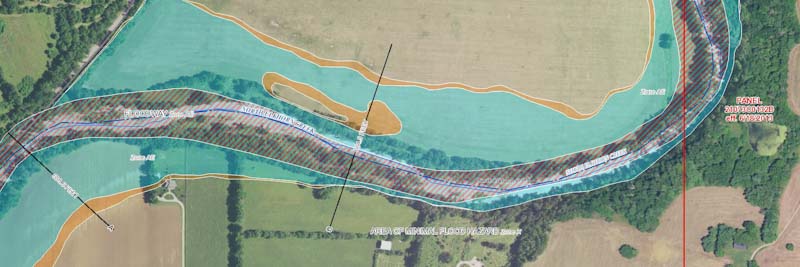
- Floodway: The portion of the floodplain that must be kept open to allow floodwaters to flow freely.
- Flood hazard area: Areas that are subject to flooding but not necessarily within the 100-year floodplain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Kentucky Flood Map
1. How is the Kentucky Flood Map updated?
The Kentucky Flood Map is regularly updated by FEMA based on new data, flood events, and changes in development patterns. These updates may result in changes to flood zone designations and associated insurance premiums.
2. What happens if my property is located in a flood zone?
If your property is located in a flood zone, you may be required to purchase flood insurance as a condition of obtaining a mortgage or refinancing. Flood insurance premiums vary based on the flood zone designation and the value of your property.
3. Can I appeal a flood zone designation?
Yes, property owners can appeal a flood zone designation if they believe it is inaccurate. The appeal process involves submitting evidence to FEMA demonstrating that the designated flood zone is incorrect.
4. What are some tips for mitigating flood risk?
- Elevate your home: Elevating your home above the base flood elevation can significantly reduce flood damage.
- Install flood vents: Flood vents allow water to enter and exit a building safely, preventing pressure buildup that can cause structural damage.
- Use waterproof materials: Use waterproof materials for flooring, walls, and other interior features to minimize water damage.
- Install a sump pump: A sump pump can help remove water from your basement during heavy rainfall.
- Maintain your drainage system: Ensure your gutters, downspouts, and other drainage systems are clear and functioning properly to prevent water from accumulating around your home.
Conclusion
The Kentucky Flood Map is a critical tool for understanding and managing flood risk within the state. By providing a comprehensive overview of flood-prone areas, the map empowers residents, businesses, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding development, infrastructure planning, and disaster preparedness. Utilizing the map’s information and implementing appropriate mitigation measures can significantly reduce the impact of flooding, safeguarding lives and property. As the state of Kentucky continues to face the challenges of climate change and increasingly frequent extreme weather events, the Kentucky Flood Map will remain an indispensable resource for promoting resilience and ensuring the safety of communities across the commonwealth.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Kentucky Flood Map: A Guide to Navigating Flood Risk. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!