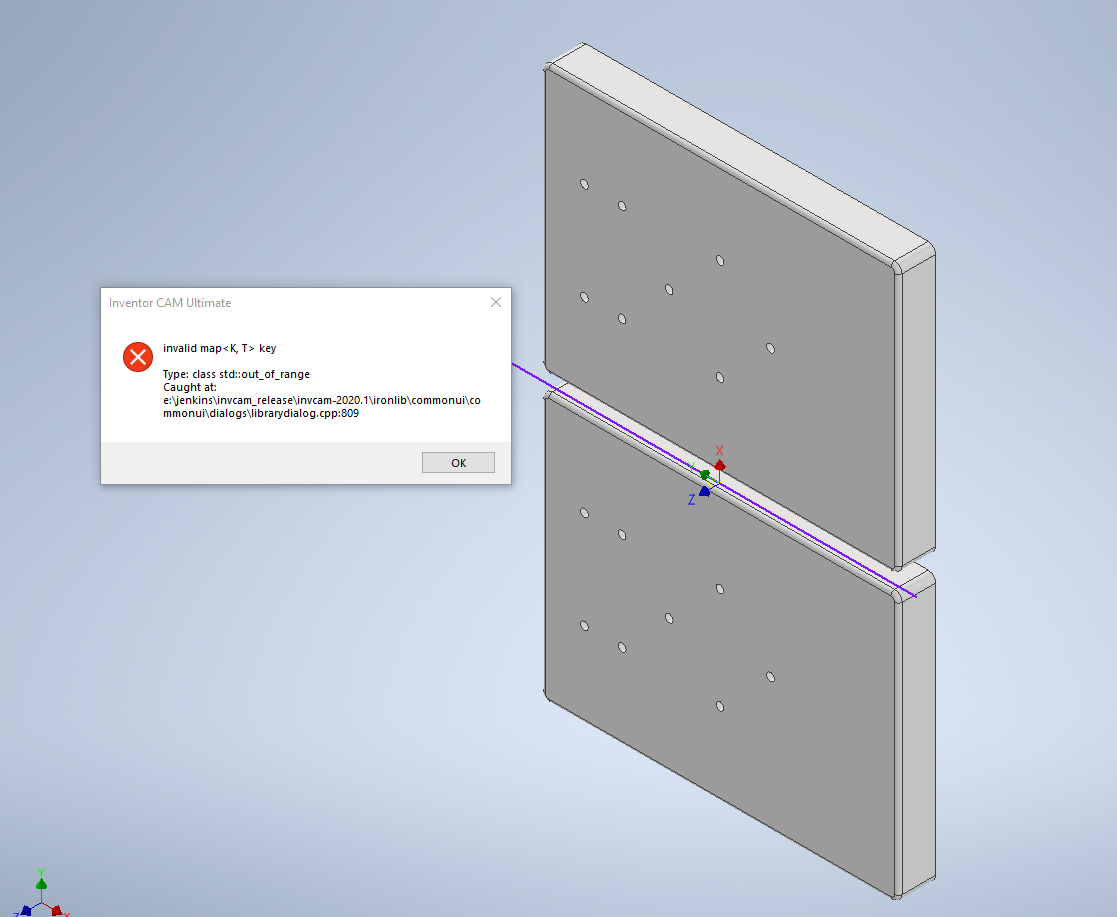
Understanding the Significance of Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau in Data Analysis
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau in Data Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau in Data Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau in Data Analysis
In the realm of data analysis, the concept of "invalid map K-T key tableau" may seem obscure, but it holds significant importance in ensuring data integrity and accuracy. This article delves into the intricacies of this concept, providing a comprehensive understanding of its implications and benefits within data analysis.
Delving into the Concept: A Clear Definition
"Invalid map K-T key tableau" refers to a specific scenario encountered in data analysis where a key, designed to uniquely identify records within a data set, fails to fulfill its purpose. This failure arises when the key, known as the "K-T key," encounters inconsistencies or overlaps, leading to ambiguity in identifying individual records.
Illustrative Example: Unveiling the Problem
Imagine a database containing customer information, with each customer assigned a unique ID number. This ID number acts as the K-T key, facilitating the retrieval and manipulation of individual customer records. However, if multiple customers share the same ID number, the K-T key becomes invalid. This invalidity creates a chaotic situation, making it impossible to accurately distinguish between customers with identical ID numbers.
The Impact of Invalid K-T Keys: A Cascade of Errors
Invalid K-T keys can have far-reaching consequences, leading to a cascade of errors and inaccuracies in data analysis. These consequences include:
- Data Duplication: The presence of duplicate records with identical K-T keys creates a distorted view of the data, leading to inflated counts and skewed statistical analysis.
- Incorrect Data Aggregation: When K-T keys are invalid, data aggregation processes become unreliable, producing inaccurate summaries and misleading insights.
- Erroneous Data Retrieval: Attempts to retrieve specific records using invalid K-T keys will yield incorrect results, hindering the ability to extract meaningful information.
- Compromised Data Integrity: The fundamental principle of data integrity relies on the uniqueness and validity of keys. Invalid K-T keys undermine this principle, compromising the reliability and trustworthiness of the data.
Addressing the Issue: Strategies for Validation and Correction
Identifying and rectifying invalid K-T keys is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring accurate analysis. Several strategies can be employed to achieve this:
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Implementing data cleansing techniques, such as removing duplicate records and standardizing data formats, can help identify and eliminate invalid K-T keys.
- Data Validation Techniques: Implementing data validation rules, such as unique key constraints and data type checks, can prevent the creation of invalid K-T keys during data entry or data processing.
- Data Auditing and Verification: Regularly auditing data for consistency and accuracy, including verifying the uniqueness of K-T keys, can help detect and correct invalid keys.
- Data Transformation and Aggregation: Techniques such as data transformation and aggregation can be used to create new, valid keys based on existing data, addressing the issue of invalid K-T keys.
The Importance of Data Integrity: A Foundation for Accurate Analysis
The concept of invalid map K-T key tableau underscores the fundamental importance of data integrity in data analysis. Accurate data forms the bedrock of reliable insights and informed decision-making. By ensuring the validity of K-T keys, data analysts can build confidence in their findings and make meaningful contributions to their respective fields.
FAQs Regarding Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau:
Q1: What are some common causes of invalid K-T keys?
A: Common causes of invalid K-T keys include:
- Data entry errors: Mistakes during data entry, such as typos or incorrect data values, can lead to duplicate records and invalid keys.
- Data integration issues: Combining data from different sources can introduce inconsistencies and duplicate records, resulting in invalid K-T keys.
- Data transformation errors: Incorrect data transformation operations can create duplicate records or modify existing keys, rendering them invalid.
- Lack of data validation: Insufficient data validation procedures can allow invalid K-T keys to slip through the cracks.
Q2: How can I identify invalid K-T keys in my data?
A: Several methods can be employed to identify invalid K-T keys:
- Data profiling: Analyze data for patterns and inconsistencies, including identifying duplicate records and potential invalid keys.
- Data validation rules: Implement rules that check for the uniqueness of K-T keys and flag any violations.
- Data visualization: Visualize data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate invalid K-T keys.
- Database queries: Use SQL queries to identify duplicate records and potential invalid keys.
Q3: What are the consequences of ignoring invalid K-T keys?
A: Ignoring invalid K-T keys can lead to:
- Biased and unreliable data analysis: Inaccurate data will lead to skewed results and misleading conclusions.
- Incorrect decision-making: Decisions based on invalid data can be detrimental to business operations and strategic planning.
- Reputational damage: Data errors can erode trust in the organization and its findings.
- Legal and regulatory issues: In certain industries, data integrity is crucial for compliance with regulations.
Q4: How can I prevent invalid K-T keys from occurring in the future?
A: To prevent future instances of invalid K-T keys:
- Implement robust data validation procedures: Ensure that data is thoroughly validated before it is entered into the system.
- Standardize data entry processes: Establish clear guidelines for data entry to minimize errors and inconsistencies.
- Regularly audit data quality: Conduct periodic audits to identify and address any data quality issues, including invalid K-T keys.
- Train data entry personnel: Provide training to data entry personnel on data integrity and the importance of accurate data entry.
Tips for Managing Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau:
- Prioritize data quality: Treat data quality as a top priority, recognizing its impact on data analysis and decision-making.
- Invest in data management tools: Utilize data management tools that support data validation, cleansing, and transformation, ensuring data integrity.
- Promote a culture of data accuracy: Foster a culture within the organization that values data accuracy and encourages responsible data handling practices.
- Continuously monitor data quality: Regularly monitor data quality metrics to identify and address any issues promptly.
Conclusion: Embracing Data Integrity for Reliable Insights
The concept of invalid map K-T key tableau highlights the critical role of data integrity in data analysis. By addressing the issue of invalid keys and ensuring data accuracy, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data, deriving reliable insights and making informed decisions. The pursuit of data integrity is not merely a technical exercise but a fundamental principle that underpins the value and trustworthiness of data.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of Invalid Map K-T Key Tableau in Data Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!