Unlocking the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends
Related Articles: Unlocking the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends

Maps, in their diverse forms, are powerful tools for navigating the physical and conceptual landscapes that surround us. They provide a visual representation of space, guiding us through unfamiliar territories and revealing hidden patterns within complex systems. Yet, to fully grasp the information encoded within a map, a crucial element must be understood: the legend.
Often referred to as a map key, this seemingly simple component plays a vital role in deciphering the symbols, colors, and patterns employed on a map. The legend acts as a translator, bridging the gap between the abstract visual language of the map and our understanding of the real world.
The Essence of the Map Legend:
The legend, in its essence, is a table or key that defines the meaning of the symbols, colors, and patterns used on a map. It provides a clear and concise explanation of what each visual element represents, allowing the viewer to interpret the map accurately.
Types of Map Legends:
Legends can be categorized based on the type of information they convey and the map’s purpose. Common types include:
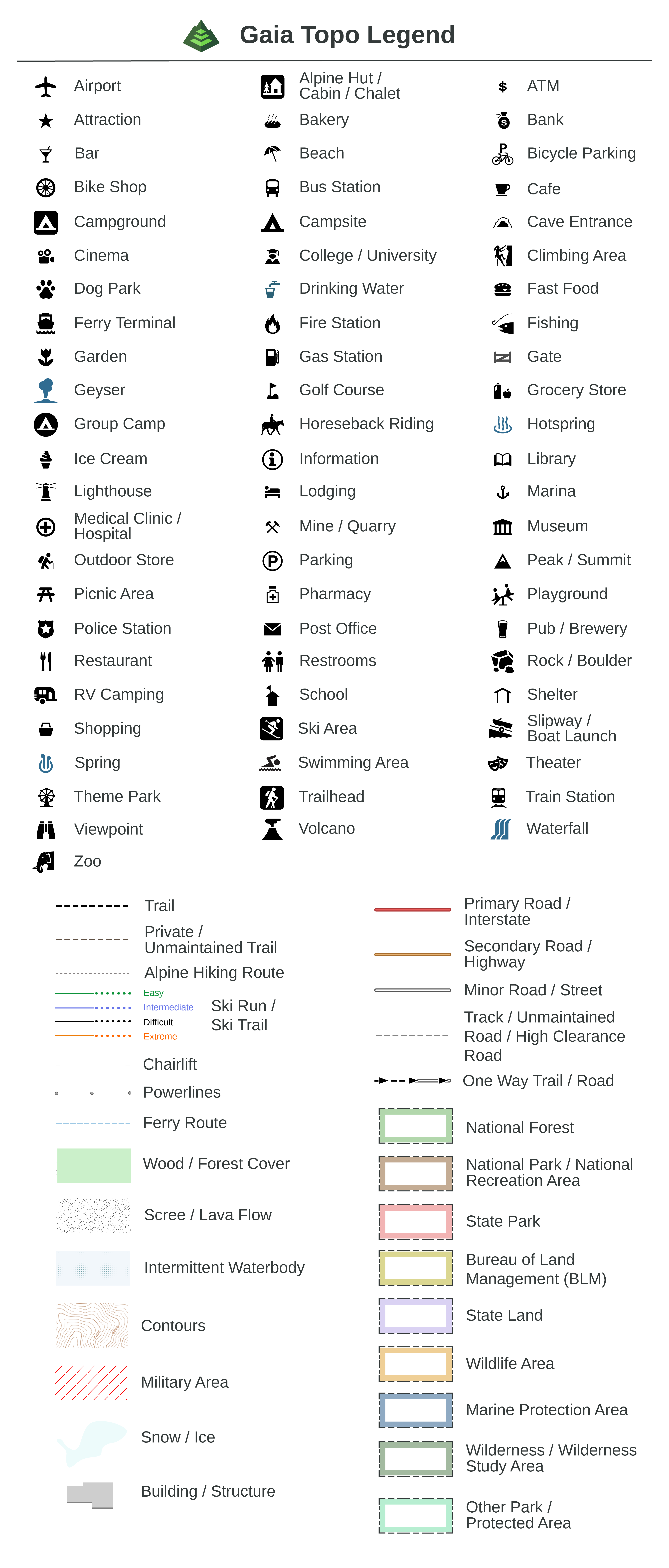
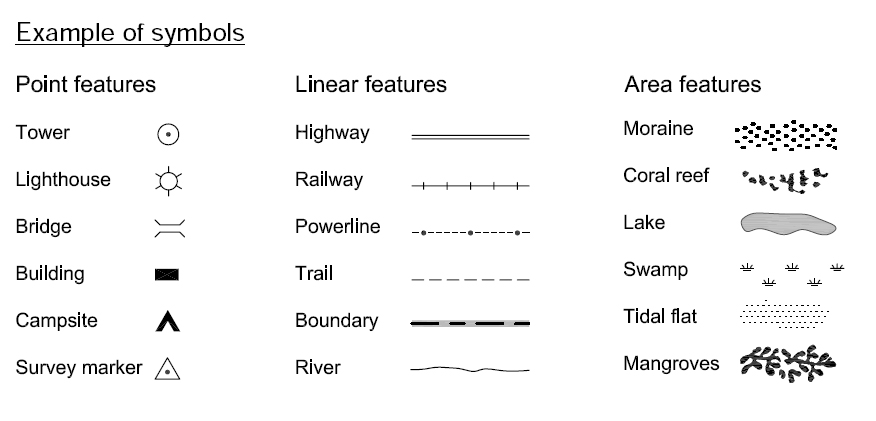
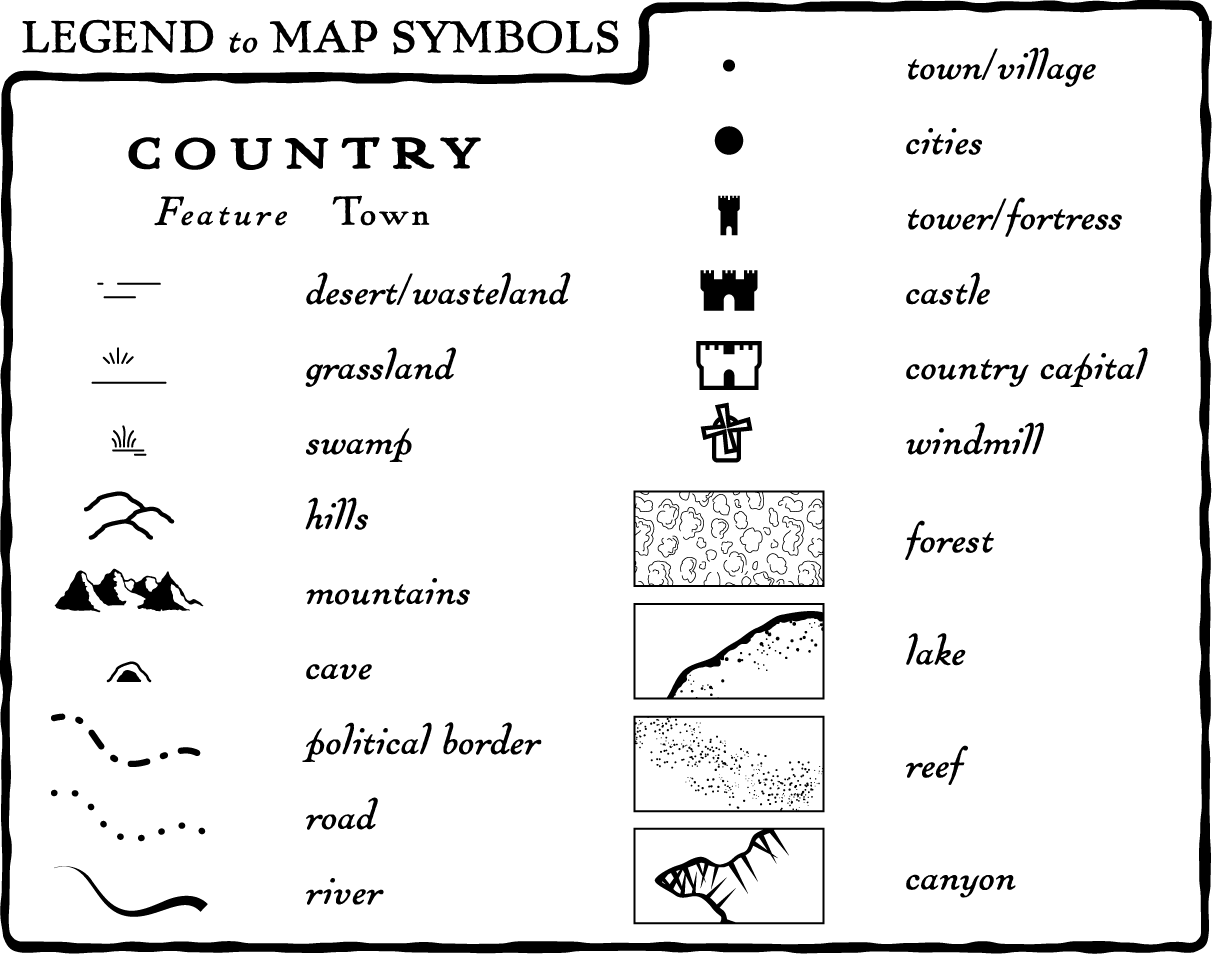
- Symbol Legends: These legends explain the meaning of various symbols used on the map. For example, a symbol legend might define a star as representing a capital city, a triangle as a mountain peak, or a dotted line as a trail.
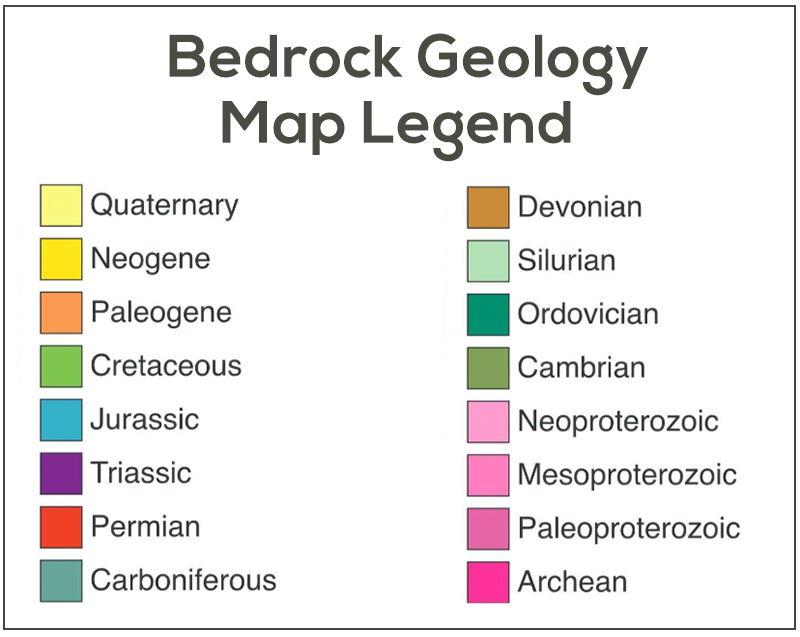
- Color Legends: Color legends are crucial for maps that use color to represent different categories or values. For instance, a thematic map might use different shades of blue to depict varying population densities, or a geological map might employ different colors to represent distinct rock formations.
- Pattern Legends: Some maps utilize patterns, such as hatching or cross-hatching, to represent different features. A legend would explain the specific pattern used for each feature, such as dense forests or areas of agricultural land.
- Scale Legends: Scale legends are essential for understanding the relationship between the map’s representation and the real world. They indicate the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This allows users to accurately measure distances and calculate areas.
Benefits of Understanding the Map Legend:
A comprehensive understanding of the map legend offers numerous benefits, enhancing the user’s ability to:
- Interpret the Map Correctly: The legend ensures that the user understands the meaning of all symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map, preventing misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions.
- Extract Relevant Information: By comprehending the legend, users can effectively identify specific features, locate points of interest, and extract relevant data from the map.
- Compare Different Maps: Legends enable users to compare information from different maps, as they provide a consistent framework for interpreting data presented in diverse visual forms.
- Make Informed Decisions: A clear understanding of the legend empowers users to make informed decisions based on the information presented on the map, whether it be choosing a route, planning a trip, or analyzing geographical data.
Importance of Clear and Concise Legends:
The effectiveness of a map legend hinges on its clarity and conciseness. A well-designed legend should be:
- Organized and Easy to Navigate: The legend should be structured logically, with clear headings and subheadings, enabling users to quickly locate the information they need.
- Visually Appealing and Readable: The legend should use clear fonts, appropriate colors, and sufficient spacing to ensure readability and visual appeal.
- Comprehensive and Accurate: The legend should include all necessary information to interpret the map accurately, avoiding ambiguity and inconsistencies.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Map Legends
Q: What if a map doesn’t have a legend?
A: The absence of a legend significantly hampers the map’s utility. Without a legend, interpreting the map becomes a guessing game, leading to potential misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions. If a map lacks a legend, it is crucial to seek additional information or documentation that clarifies the symbols and patterns used.
Q: What are some common symbols used on maps?
A: Common symbols used on maps include:
- Points of Interest: Stars, circles, squares, and other geometric shapes represent landmarks, cities, or other points of interest.
- Roads and Highways: Different line widths and colors are used to differentiate between major highways, secondary roads, and smaller streets.
- Water Bodies: Blue lines and shades of blue represent rivers, lakes, and oceans.
- Elevation: Contour lines, often depicted as brown lines, indicate changes in elevation.
- Vegetation: Different shades of green represent different types of vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, or wetlands.
Q: How can I create my own map legend?
A: Creating your own map legend requires a clear understanding of the information you want to convey. Start by identifying the symbols, colors, and patterns you will use on your map. Then, create a table or key that clearly defines the meaning of each visual element. Ensure that the legend is organized, visually appealing, and comprehensive.
Tips for Effective Map Legend Interpretation:
- Read the Legend Carefully: Before interpreting the map, take the time to read the legend thoroughly and familiarize yourself with the symbols, colors, and patterns used.
- Pay Attention to Details: Small details in the legend, such as line widths or color variations, can provide crucial information about the map’s content.
- Use the Legend as a Reference: When interpreting the map, refer back to the legend frequently to ensure you are understanding the information correctly.
- Consider the Map’s Purpose: The legend should be designed to support the map’s purpose, providing the necessary information for the intended audience.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Mapmaking
The map legend, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in unlocking the information encoded within maps. It acts as a bridge between the abstract visual language of the map and our understanding of the real world. By providing a clear and concise explanation of the symbols, colors, and patterns used, the legend empowers users to interpret maps accurately, extract relevant information, and make informed decisions. Recognizing and understanding the significance of the map legend is essential for anyone who seeks to navigate the world, both physically and conceptually, through the power of maps.

![[Region map] the verdant lands, a region my dnd players will get to explore soon : r/FantasyMaps](https://4.bp.blogspot.com/-L64YckoDDF8/U6V-0kYEn-I/AAAAAAAAGTM/XYRJ9G6QTts/s1600/0620blog+key.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!