Unraveling the Geography of Kazakhstan: A Comprehensive Guide to its Outline Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Geography of Kazakhstan: A Comprehensive Guide to its Outline Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Geography of Kazakhstan: A Comprehensive Guide to its Outline Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Geography of Kazakhstan: A Comprehensive Guide to its Outline Map

Kazakhstan, the world’s largest landlocked country, sprawls across a vast expanse of Central Asia, encompassing diverse landscapes and a rich history. Understanding its geography is crucial for comprehending its cultural, economic, and political dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of Kazakhstan’s outline map, providing a comprehensive analysis of its geographical features, historical significance, and contemporary relevance.
A Land of Extremes: The Physical Geography of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan’s outline map reveals a country of striking contrasts, shaped by its vast size and diverse geological formations. The map highlights the following key features:
- Vast Steppes: The northern and western regions of Kazakhstan are dominated by the Eurasian Steppe, a vast, treeless plain characterized by fertile soil and rolling grasslands. This region, historically a hub for nomadic cultures, continues to play a significant role in agriculture and livestock production.
- The Tian Shan Mountains: Rising in the southeast, the Tian Shan mountain range forms a natural barrier, shaping the climate and influencing the distribution of flora and fauna. The mountains are home to glaciers, snow-capped peaks, and lush valleys, providing a stark contrast to the steppe landscape.
- Caspian Sea Coastline: Kazakhstan shares a significant coastline with the Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland body of water. This coastline is home to vital ports and serves as a gateway to international trade and transportation.
- The Aral Sea Basin: In the southwestern region, the outline map reveals the shrinking Aral Sea, a victim of water diversion projects. This environmental disaster highlights the challenges of water management and the consequences of unsustainable practices.
- The Ural Mountains: The western boundary of Kazakhstan is marked by the Ural Mountains, which serve as a natural border between Europe and Asia. The mountains are rich in mineral resources and have played a significant role in Kazakhstan’s industrial development.
Historical Significance: A Crossroads of Cultures
The outline map of Kazakhstan reflects a rich tapestry of historical influences. Situated at the crossroads of ancient trade routes, the country witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the exchange of ideas, and the blending of cultures. Key historical highlights include:
- The Silk Road: Kazakhstan’s strategic location along the Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting the East and West, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people for centuries. This historical legacy is reflected in the country’s diverse cultural heritage.
- The Mongol Empire: The Mongol conquests in the 13th century left a lasting impact on Kazakhstan, shaping its political and social landscape. The country served as a vital part of the Mongol Empire, connecting its vast territories.
- The Russian Empire: Following the Mongol period, Kazakhstan came under Russian influence, becoming part of the Russian Empire in the 19th century. This period witnessed significant political and economic changes, including the establishment of Russian settlements and the introduction of new agricultural practices.
- The Soviet Era: After the Russian Revolution, Kazakhstan became a republic within the Soviet Union. This era saw the development of heavy industries, the forced collectivization of agriculture, and the displacement of indigenous populations.
Contemporary Relevance: A Nation in Transition
The outline map of Kazakhstan reflects a nation in transition, grappling with the challenges and opportunities of independence. Since gaining independence in 1991, Kazakhstan has embarked on a path of economic diversification, political reform, and social development. The outline map underscores the following key aspects of contemporary Kazakhstan:
- Energy Resources: Kazakhstan is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and have attracted significant foreign investment. However, the reliance on energy exports also poses challenges in terms of economic diversification and environmental sustainability.
- Infrastructure Development: Kazakhstan has invested heavily in infrastructure development, including roads, railways, and airports, aiming to improve connectivity and facilitate trade. This focus on infrastructure is crucial for the country’s economic growth and integration into global markets.
- Regional Cooperation: Kazakhstan plays a vital role in regional cooperation initiatives, including the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and the Eurasian Economic Union. These partnerships aim to foster economic integration, promote security, and address common challenges in Central Asia.
- Environmental Concerns: The outline map highlights the environmental challenges facing Kazakhstan, including water scarcity, desertification, and pollution. The country is working to address these issues through sustainable development practices and environmental protection policies.
FAQs about Kazakhstan’s Outline Map
1. What is the geographical significance of Kazakhstan’s location?
Kazakhstan’s location at the heart of Central Asia makes it a crucial crossroads for trade and transportation. Its strategic position connects Russia, China, and the Middle East, making it a vital link in regional and global networks.
2. What are the major environmental challenges facing Kazakhstan?
Kazakhstan faces significant environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and pollution. The shrinking Aral Sea serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of unsustainable water management.
3. How has Kazakhstan’s history shaped its contemporary landscape?
Kazakhstan’s history is marked by empires, trade routes, and cultural exchanges. This rich heritage has shaped its diverse population, languages, and traditions. The country’s transition to independence has further influenced its political and economic landscape.
4. What are the key economic sectors in Kazakhstan?
Kazakhstan’s economy is heavily reliant on natural resources, particularly oil and gas. However, the country is diversifying its economy through investments in manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism.
5. How does Kazakhstan’s outline map reflect its cultural diversity?
Kazakhstan’s outline map encompasses diverse landscapes and cultures, reflecting the country’s historical role as a crossroads of civilizations. This cultural diversity is evident in its languages, religions, and traditions.
Tips for Using Kazakhstan’s Outline Map
- Utilize the map to understand geographical features: Identify key geographical features such as mountains, rivers, and lakes. This will help you visualize the country’s landscape and its influence on various aspects of life.
- Relate the map to historical events: Explore the historical significance of key locations on the map. This will provide context for understanding the country’s development and its cultural heritage.
- Analyze the map for economic activities: Identify major cities, industrial centers, and resource-rich areas. This will help you understand the distribution of economic activities and the country’s economic potential.
- Consider environmental issues: Analyze the map to identify areas prone to environmental challenges such as water scarcity or desertification. This will help you understand the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Explore cultural diversity: Use the map to identify regions with distinct cultural identities. This will provide insights into the country’s rich cultural heritage and its diverse population.
Conclusion
Kazakhstan’s outline map serves as a powerful visual representation of a country brimming with geographical, historical, and cultural richness. It reveals a land of extremes, a crossroads of civilizations, and a nation in transition. Understanding the intricacies of Kazakhstan’s outline map provides invaluable insights into its geographical diversity, its historical significance, and its contemporary relevance. By analyzing the map’s features, exploring its historical context, and appreciating its cultural diversity, we gain a deeper understanding of this vast and dynamic nation in Central Asia.

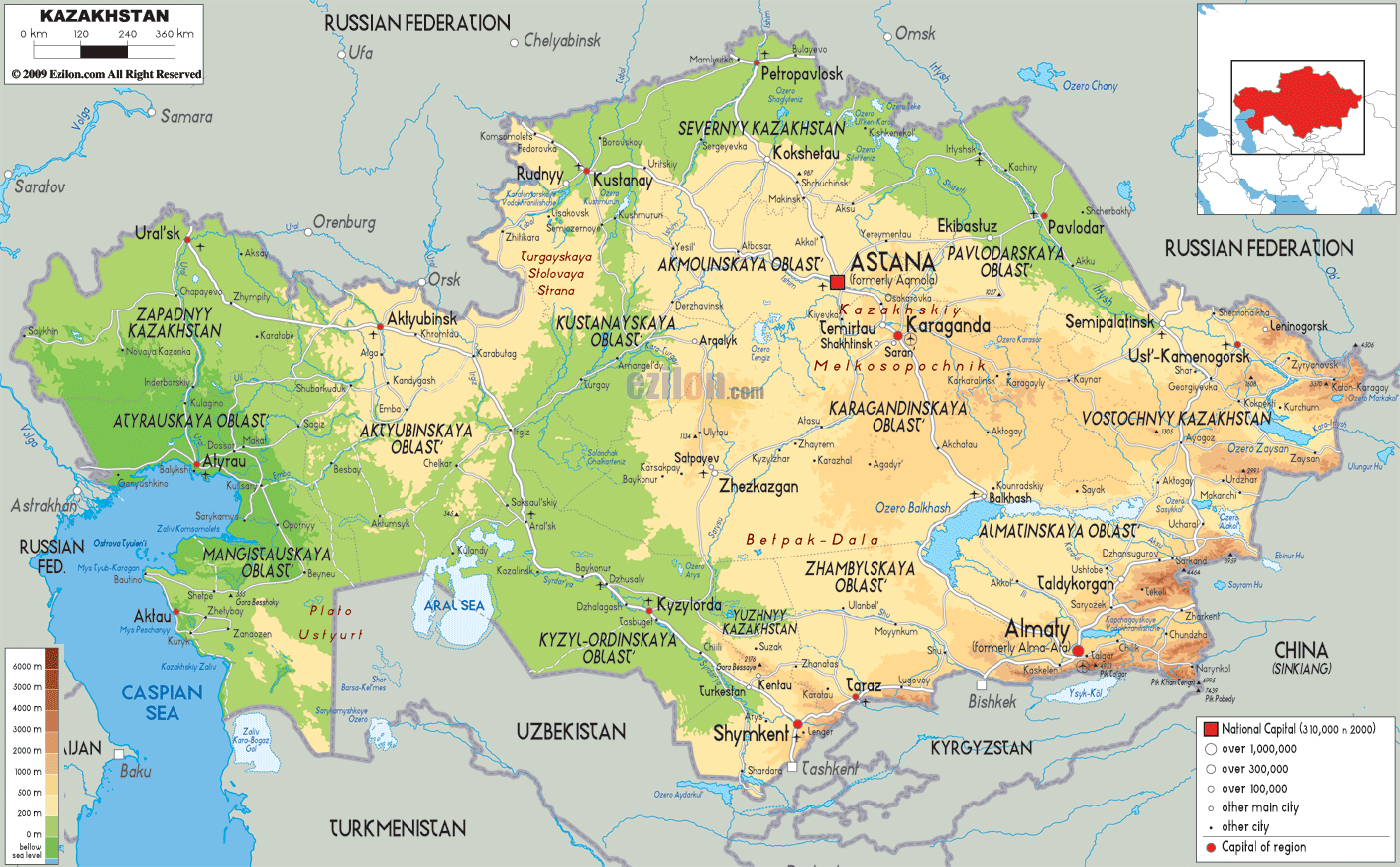



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Geography of Kazakhstan: A Comprehensive Guide to its Outline Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!